Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
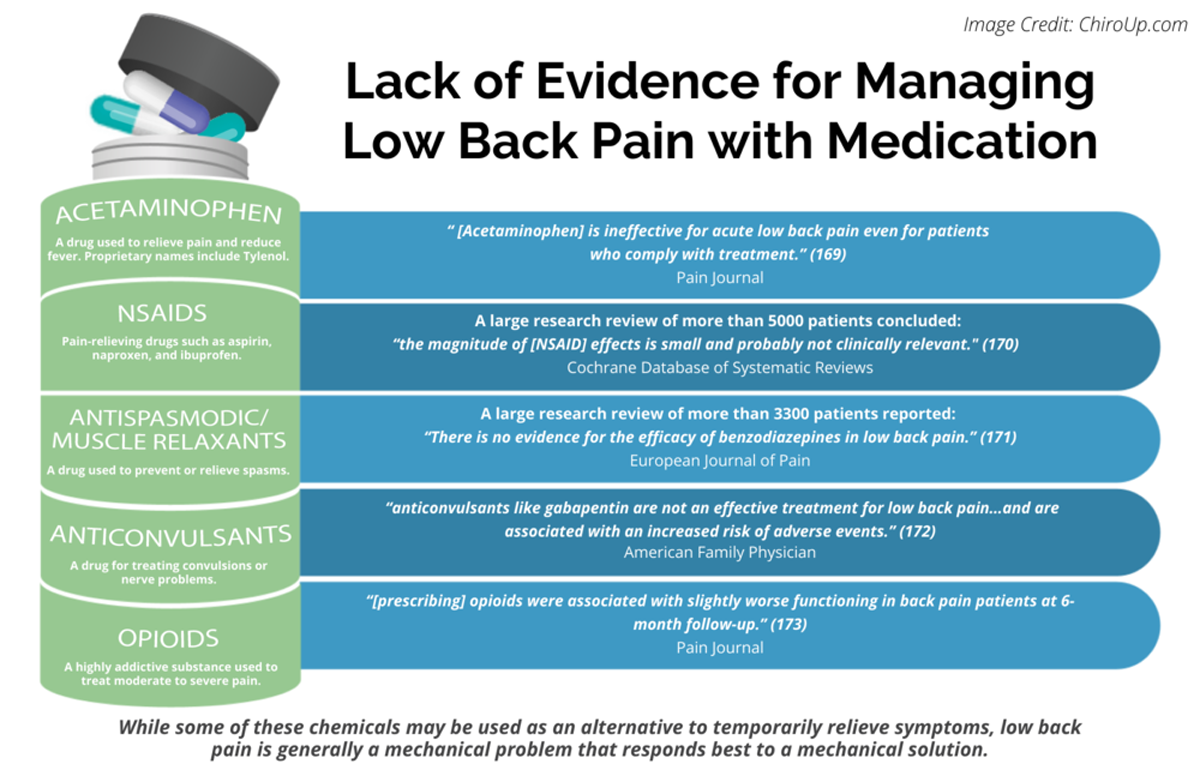
a specific patient. It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider’s examination and assessment of a patient’s specific and unique circumstances. Patients must speak with a health care Evaluate the patient’s understanding of gabapentin, including its purpose, dosage regimen, potential side effects, and the importance of medication adherence. Assessing the patient’s compliance and educational needs allows for appropriate support and reinforcement of medication instructions. Why have I been prescribed Gabapentin? Gabapentin is used to treat some types of persistent pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as sharp, shooting, burning and stabbing types of pain. Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants which are also used to treat epilepsy. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. Generic name: Gabapentin. Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant, Gabarone. Pharmacologic class: Anticonvulsant, Antiepileptic. Therapeutic class: Anticonvulsant, Analgesic for neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is used to control the symptoms of seizures and works by reducing the abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Exactly how it does this is not fully understood. Gabapentin is also prescribed to treat certain types of long-lasting pain caused by damage to nerves. Some people may become dependent on Neurontin (a need to keep taking the medicine). They may have withdrawal effects when they stop using Neurontin (see section 3, “How to take Neurontin” and “If you stop taking Neurontin”). If you have concerns that you may become dependent on Neurontin, it is important that you consult your doctor. Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin — Gabapentin is an anti-seizure medication. It is usually taken by mouth three times daily. Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Brand Names: US Gabarone; Gralise; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada Gabapentin tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat: • • Who should not take gabapentin tablets? Do not take gabapentin tablets if you are allergic to gabapentin or any of the other ingredients in gabapentin tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in gabapentin tablets. Patients taking Neurontin for seizures may have through assessment, patient education, and monitoring for therapeutic and adverse effects of gabapentin. Why have I been prescribed Gabapentin? • Gabapentin is used to treat some types of persistent pain. • It is especially good for nerve pain, such as burning, shooting or stabbing pain. • Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants which are also used to treat epilepsy. Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking to a healthcare provider. • Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus). • Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines Patient Teaching Associated with Gabapentin. Advise the patient that gabapentin can be taken with or without food. Instruct to swallow extended-release tablets without breaking, crushing, dissolving, or chewing. Inform to take gabapentin at bedtime to minimize adverse effects. Do not suddenly stop gabapentin due to the increased risk of seizure. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Gabapentin This information from Lexicomp explains what you need to know about this medication, including what it’s used for, how to take it, its side effects, and when to call your healthcare provider. Brand Names: US Gabarone; Gralise; Neurontin Brand Names: Canada Gabapentin extended-release tablets (Horizant) are used to treat restless legs syndrome (RLS; a condition that causes discomfort in the legs and a strong urge to move the legs, especially at night and when sitting or lying down). Gabapentin is in a class of medications called anticonvulsants. Changing how the world understands and treats cancer. Our scientists pursue every aspect of cancer research—from exploring the biology of genes and cells, to developing immune-based treatments, uncovering the causes of metastasis, and more. Instruct patient to read the Medication Guide before starting and with each Rx refill, as changes may occur. Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. SN to educate patient concerning the use of gabapentin is to increased pain relief affects by using the CNS to decrease symptoms of pain and assist Tramadol or other prescribed pain medications, even Tylenol ER in ultimate pain relief.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |