Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 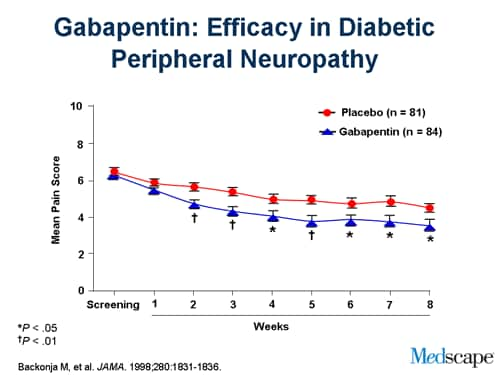 |
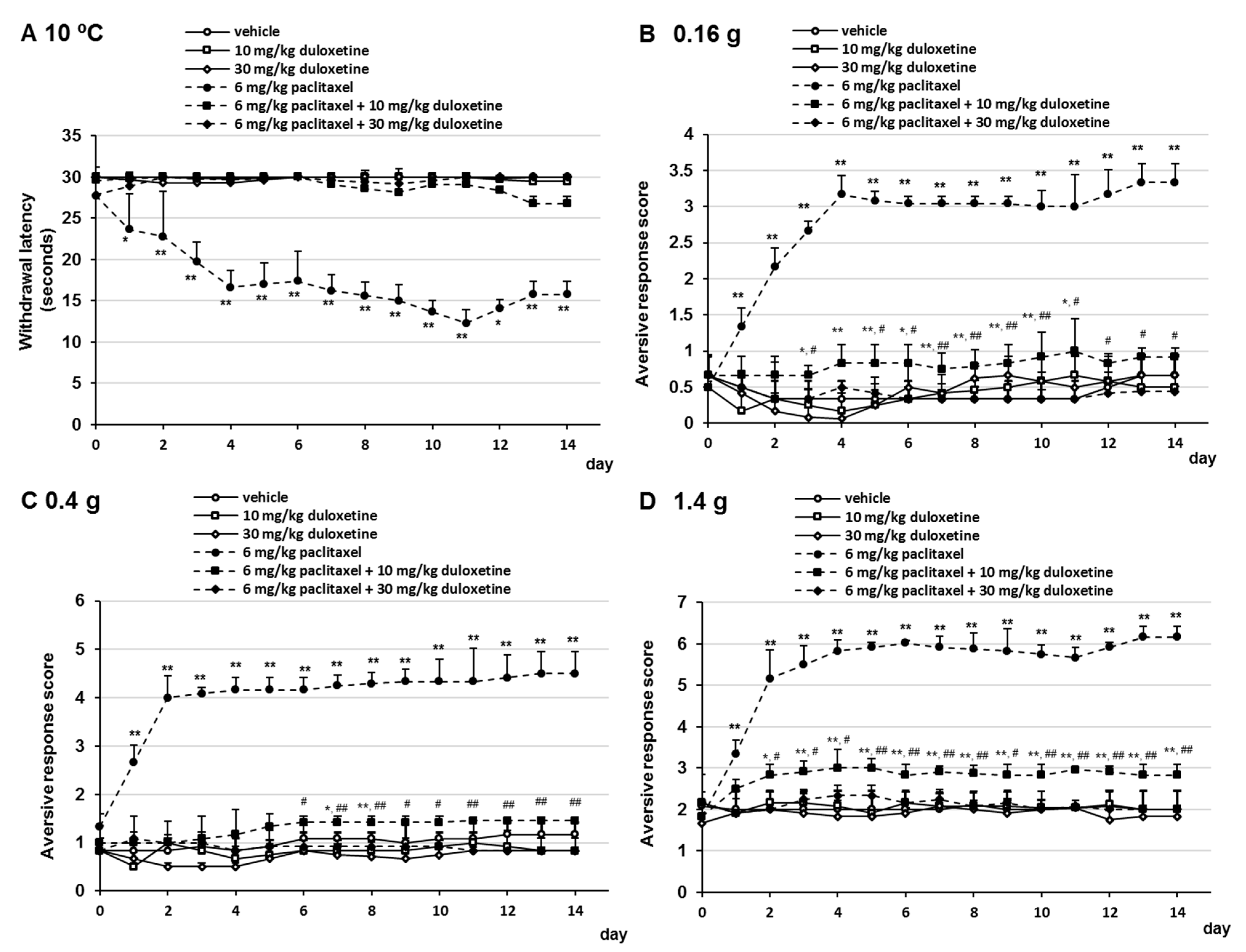
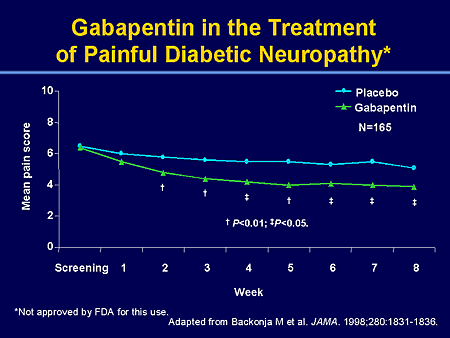
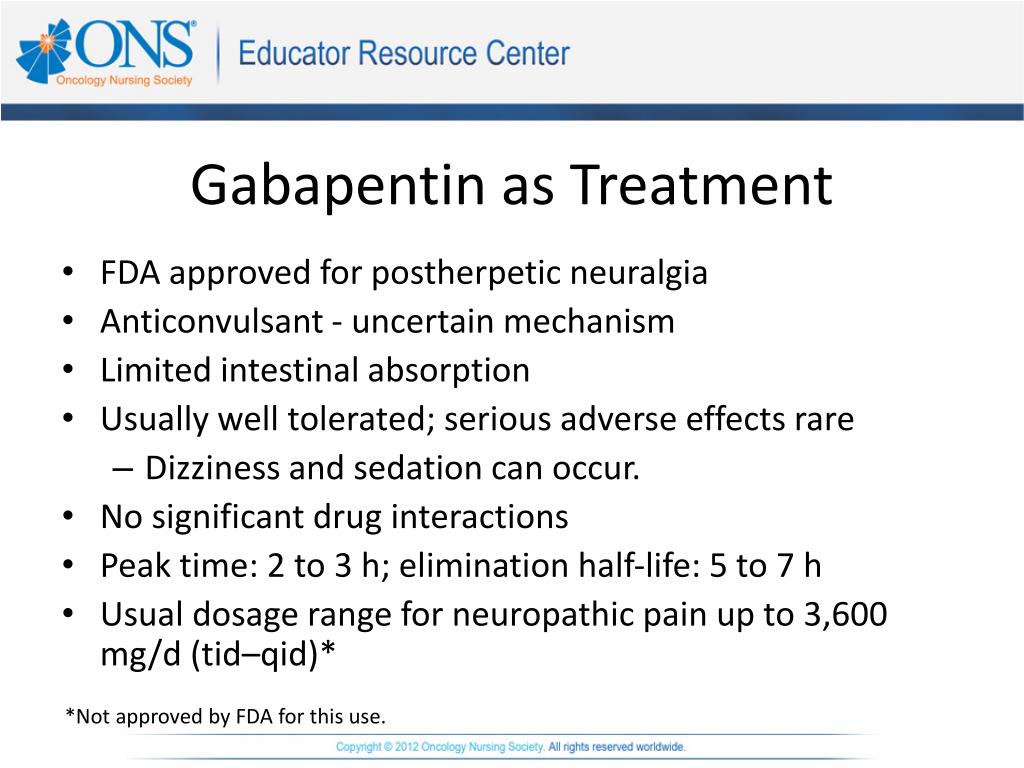
Several studies have evaluated the efficacy of gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of neuropathic pain, yielding contradictory results. On one hand, it has been observed that gabapentin is more effective, especially at higher doses, compared to pregabalin (8, 9). “Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. The treatment you'll need depends on the neuropathy-related complications you have: Urinary tract problems. Some drugs affect bladder function, so your health care provider may recommend stopping or changing medications. (A Comprehensive Look at Peripheral Neuropathy and Nerve Pain Treatment) If you’re someone dealing with nerve pain or peripheral neuropathy, you may have been prescribed gabapentin as part of your treatment plan. Gabapentin is commonly used to manage nerve pain by calming down the overactive nerves that send pain signals to your brain. The Neuropathic Pain Special Interest Group of the International Association for the Study of Pain recently sponsored the development of evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain. Tricyclic antidepressants, dual reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and norepinephrine, calcium channel α2-δ ligands (ie, gabapentin and pregabalin), and topical lidocaine were Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for Medicines such as gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica), developed to treat epilepsy, often improve nerve pain. Side effects can include drowsiness and dizziness. Topical treatments. Lidocaine cream that is available without a prescription can be applied to the skin. Current medication management for neuropathic pain includes select neuromodulating agents such as anticonvulsants, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and certain opioids. 1,2 Gabapentin remains among the most commonly used anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain. Abd-Elsayed et al (2016) presented a series of three cases where treatment with SCS led to marked improvement in otherwise treatment-resistant cases of peripheral neuropathy secondary to HIV, diabetes mellitus, and chemotherapy (see Table I).¹⁹ In one patient with CIPN, SCS leads were placed at T10-T11. On follow-up at 3 months and 2 years Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and other neuropathic pain syndromes. It relieved symptoms of allodynia, burning pain, shooting pain, and hyperesthesia. Adverse effects were typically mild to moderate and usually subsided within approximately 10 days from the initiation of treatment. Ten percent of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy reported feeling “much improved,” and for HIV peripheral neuropathy, the NNT to report being “much improved” was 8.8 (5.3–2.6) . Finnerup and colleagues’ meta-analysis for the treatment of PHN and HIV peripheral neuropathy demonstrated a combined NNT of 10 (7.4–19) . For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). s initial treatment for neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia)”. Pregabalin and duloxetine are recommended as initial treatment options due to their wider licences, however the full guideline for CG173 acknowledges that both these treatments represent poor value. ssessment if inadequate response to treatment or treatments not tole. Pregabalin (Lyrica), gabapentin (Neurontin), amitriptyline (except in older adults), or duloxetine (Cymbalta) should be used as first-line treatment for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A 1 Physicians should address underlying risk factors such as poor glycemic control, vitamin B12 deficiency, elevated blood pressure, and obesity to reduce the likelihood of developing neuropathy. First-line drug therapy for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy includes duloxetine, gabapentin, amitriptyline, and pregabalin; however, these Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral and central neuropathic pain in adults in the UK at doses up to 3.6 grams (3600 mg) daily. It is given orally, usually as tablets or capsules, but sometimes as an oral solution (50 mg/ml). Pregabalin and gabapentin are first-line treatment options for diabetic peripheral neuropathy, with pregabalin being slightly preferred. 33 Higher pregabalin doses are more effective; a 50% Unfortunately, it can take many months or even longer to find a treatment that works. Doctors have little guidance to know which ones to start with. That’s why research comparing treatment options is so important — and yet, precious little comparative research on treatments for idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy has been published. Ten percent of patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy reported feeling “much improved,” and for HIV peripheral neuropathy, the NNT to report being “much improved” was 8.8 (5.3–2.6) . Finnerup and colleagues’ meta-analysis for the treatment of PHN and HIV peripheral neuropathy demonstrated a combined NNT of 10 (7.4–19) . Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |