Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
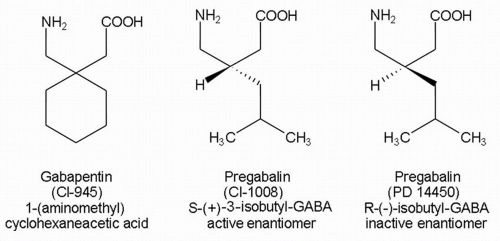 |  |
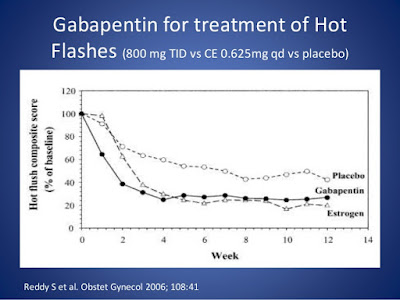
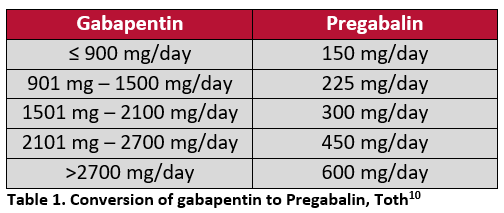
Gabapentin and pregabalin are FDA-approved to treat some of the same conditions, including postherpetic neuralgia in adults. Both drugs are also indicated to treat partial seizures in adults and certain children with epilepsy (a seizure disorder) when taken along with other medication. While limited data demonstrate a beneficial effect of pregabalin for the treatment of hot flashes, no studies have compared its efficacy with other pharmacologic options such as HT or other nonhormonal drugs such as antidepressants, clonidine, Bellergal or gabapentin. Comparisons of gabapentin and placebo revealed reductions of 20–30% in the frequency and severity of hot flashes with gabapentin. Dizziness/unsteadiness and fatigue/somnolence were the most frequently reported adverse events associated with gabapentin and resulted in a higher dropout rate. Gabapentin appears to be effective for reducing hot flashes, although potentially not as effective as estrogen therapy. A 2019 review and meta-analysis in the American Journal of Gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) Multiple randomized controlled trials have shown that when compared with placebo, gabapentin is effective at reducing hot flash frequency by 54% and hot flash composite score (combined hot flash frequency and severity score) by 31% to 51%. 9513 Background: Hot flashes are a major problem in many women for which better treatment options are needed. Given the known efficacy of gabapentin for decreasing hot flashes, it was decided to evaluate pregabalin, with hopes that it would work better Non-hormonal treatments for hot flashes include the use of certain antidepressants (Celexa ®, Lexapro ®, Brisdelle ®, Lyrica ®, and Effexor ®) and medications that act on the central nervous system such as gabapentin (Neurontin ®) and pregabalin (Lyrica ®). Data presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology indicate that pregabalin (Lyrica), an anticonvulsant drug similar to gabapentin, may also be helpful for alleviating hot flashes. This study included 207 women who reported at least 28 hot flashes per week. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin and others) are drugs used to prevent seizures and to treat nerve pain associated with various conditions (shingles, diabetic neuropathy). Lyrica and gabapentin both cause similar side effects, including tremors, blurred or double vision, memory or concentration problems, dizziness, and drowsiness. Overall, gabapentin was found to reduce the frequency of hot flushes at both 4 and 12 weeks (mean difference: -1.62 [95% CI: -1.98 to -1.26], and -2.77 [95% CI: -4.29 to -1.24], respectively). 28 Among the two crossover studies reported in the meta-analysis, there was no statistically significant difference between the use of gabapentin and For women with mild to moderate hot flashes and/or night sweats, trouble sleeping through the night, and physical aches and pains, gabapentin is worth trying. Risks are low and side effects minimal with the low doses used for these symptoms. Treatment begins with a low dose that is increased slowly. Lyrica vs. Gabapentin for Fibromyalgia. Pregabalin is one of the main treatments often used alongside non-drug therapies to treat fibromyalgia. It has been studied at a total daily dose of 450 mg to treat the condition. Although gabapentin has also been studied for fibromyalgia, its use is currently limited to research. Lyrica vs. Gabapentin Compare Gabapentin vs Pregabalin head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. For example, when used for menopause symptoms, health experts only recommend gabapentin as a treatment option for hot flashes or night sweats. This is mostly due to a lack of research on pregabalin for this use. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. Pregabalin decreases hot flashes and is reasonably well tolerated. A target dose of 75 mg twice daily is recommended. Its effects appear to be roughly comparable to what has been reported with gabapentin and with some newer antidepressants. Gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) Multiple randomized controlled trials have shown that when compared with placebo, gabapentin is effective at reducing hot flash frequency by 54% and hot flash composite score (combined hot flash frequency and severity score) by 31% to 51%. 28–30 Gabapentin could reduce hot flash frequency (mean difference, -1.62, 95% confidence interval, -1.98 to -1.26 after 4 weeks; mean difference, -2.77, 95% confidence interval, -4.29 to -1.24 after 12 weeks) and composite score (standardized mean difference, -0.47, 95% confidence interval, -0.71 to -0.23 after 4 weeks; standardized mean difference Pandya KJ, Morrow GR, Roscoe JA, et al. Gabapentin for hot flashes in 420 women with breast cancer: a randomized double blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2005; 366:818–24. DOI 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67215-7 Talk to your healthcare professional about the pros and cons of treatments for hot flashes. If hot flashes don't bother you much, you likely don't need treatment. For most people, hot flashes go away slowly, even without treatment. But it can take several years for them to stop.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |