Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
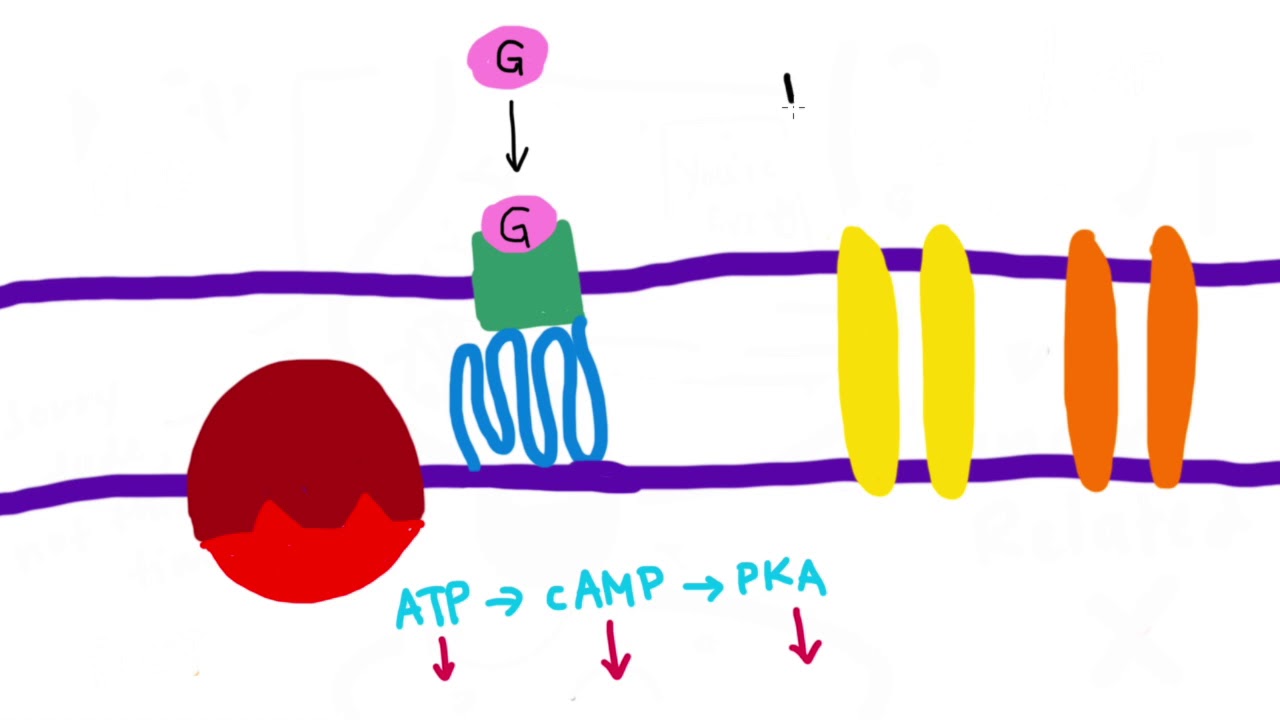
We selected gabapentin (Neurontin), a medication reported to be widely used off label, as a specific example to explore specialist physicians' experiences with off-label prescribing. This paper describes one component of this exploratory study, focusing on the knowledge and experiences of physicians with emphasis on resources and information The authors concluded that gabapentin is associated with reduction in acute pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (the later indication is not approved by the FDA), and that there is limited evidence to support the use of gabapentin for other types of neuropathic pain and pain disorders. 1 This Editorial Gabapentin’s off-label uses—meaning prescribing gabapentin for a problem not on the FDA approval list for this medication—that physicians are finding include: Alcohol withdrawal; Anxiety; Cocaine withdrawal; Fibromyalgia; Headaches; Hiccups; Hot flashes; Hyperhidrosis; Insomnia; Migraines; Mood disorders; Pain syndromes; Peripheral Key takeaways: Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizure disorder and nerve pain from shingles. But it’s also used off-label to treat many other conditions, including anxiety, nerve pain from diabetes, and hot flashes. Off-label uses for gabapentin. Doctors often prescribe gabapentin off-label to treat conditions such as: pain from diabetic neuropathy, which is numbness or uncomfortable tingling caused by nerve damage from diabetes; nerve pain in the neck and back from conditions such as sciatica, a painful compression of the sciatic nerve related to off-label gabapentin use; (3) review medical information pertaining to the off-label use of gabapentin; (4) outline alternatives to off-label use of gabapentin in an evidence-based fashion, where literature exists to support such alternatives; and (5) encourage key clinicians and decision makers in managed Because gabapentin is FDA approved for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults and as an adjunct therapy for the treatment of partial-onset seizures, the use of this medication for anything other than these indications is considered off-label. The rise in gabapentin prescribing is multifactorial but thought to be due in part to efforts by the pharmaceutical industry to promote the use of the medication for off-label uses. (In 2004, the manufacturer of Neurontin, Pfizer, pleaded guilty to multiple counts of illegally promoting the off-label use of gabapentin, resulting in nearly $430 We examined clinical trials of gabapentin (Neurontin, Pfizer) for off-label use for migraine prophylaxis, bipolar disorders, neuropathic pain, or nociceptive pain. Off-label gabapentin (Neurontin) got a bad rep when it missed the mark in bipolar disorder, but there may be something worth salvaging in this drug. Here, we weigh its pros and cons for anxiety, substance use disorders, sleep, pain, and hot flashes, and compare it to its underutilized cousin, pregabalin (Lyrica). Off-label: It is estimated that approximately 9/10 prescriptions for Gabapentin are “off-label” or for conditions that the drug isn’t approved to treat. Off-label prescriptions have a reduce chance of actually working for the treatment of anxiety. for an off-label use. Examples of Off-Label Medication Use for Mental Health Conditions . Amitriptyline • Insomnia • Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) Clonidine • Smoking cessation • Excessive saliva caused by clozapine Gabapentin • Alcohol dependence • Social anxiety Prazosin • Post traumatic stress disorder Gabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for various pain syndromes, including chronic pain and neuropathic pain, despite limited FDA-approved indications. This trend is partly driven by the search for alternatives to opioid medications. This study examined off-label use of gabapentin for psychiatric indications and its concomitant use with CNS-D prescription drugs in a nationally representative sample of ambulatory care office visits. Less than 1% of outpatient gabapentin use was for FDA-approved indications. “Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids For gabapentin, the only pain-related indication approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is postherpetic neuralgia. For pregabalin, FDA-approved indications related to pain are limited to postherpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain associated with diabetic neuropathy or spinal cord injury, and fibromyalgia. While Gabapentin is FDA-approved for partial seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, its off-label uses are more extensive, especially in psychiatry. Gabapentin for anxiety disorders is notable, with doses between 900 and 3,600 milligrams per day showing effectiveness in reducing symptoms. Gabapentin is widely used in the United States for a number of off-label indications, often as an alternative to opioid therapy. Increasing evidence has emerged suggesting that gabapentin may not be as benign as once thought and may be associated with substance abuse in concert with opioids. Off-label prescribing does not necessarily signify that the medication is being used improperly, and in some cases, reliable research might validate its use. Nonetheless, prescribing gabapentin for off-label use might also result in negative consequences, including adverse drug effects, liability concerns, and a lack of reimbursement due to the This Special Communication summarizes the limited published evidence to support off-label gabapentinoid uses, describes clinical cases in which off-label use is problematic, and notes how review articles and guidelines tend to overstate gabapentinoid effectiveness.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |