Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
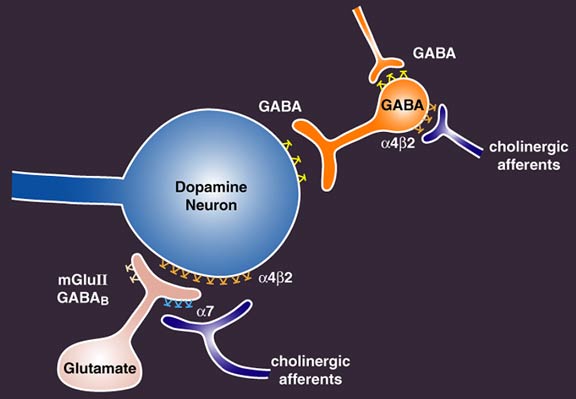
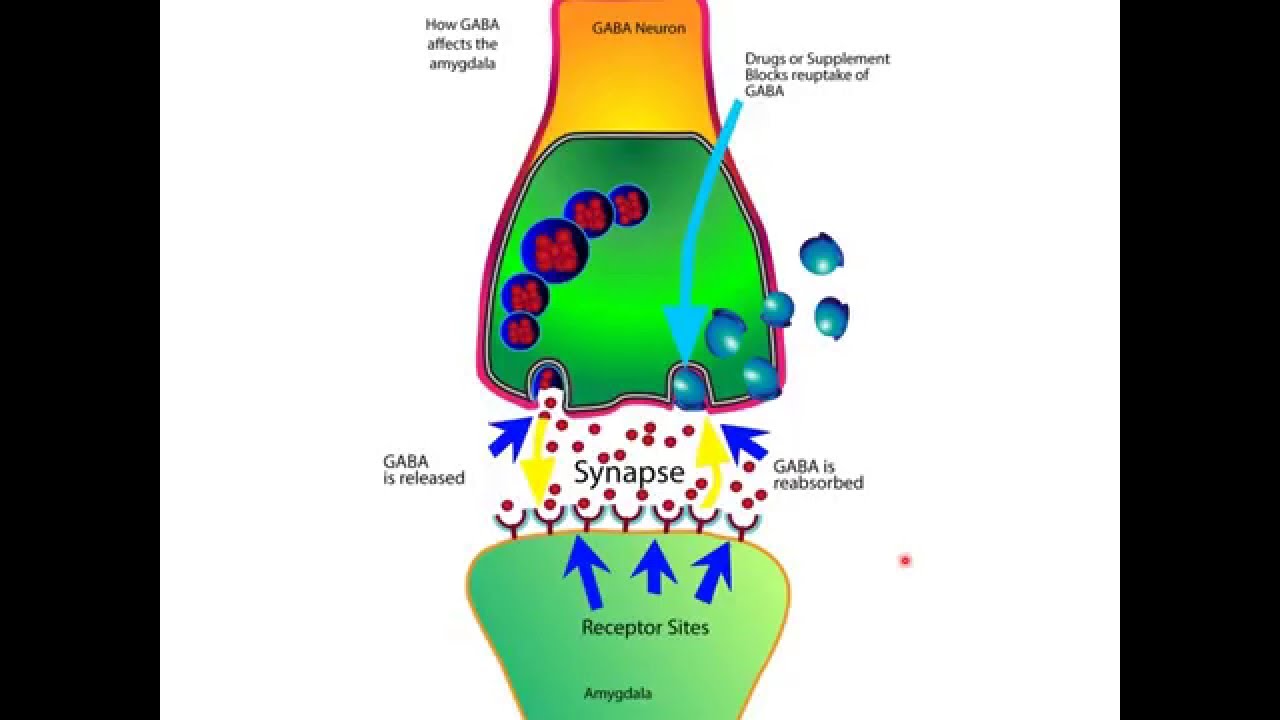
Gabapentin is usually taken with a meal or snack to protect against possible gastrointestinal disturbances (such as nausea) when taken on an empty stomach. How does gabapentin work in the brain? Gabapentin is believed to work by altering the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, although the exact mechanism is not fully understood. Gabapentin prevents neuronal death in several models including those designed to mimic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This may occur by inhibition of glutamate synthesis by branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase (BCAA-t). How Does Gabapentin Work for Anxiety in Dogs? Gabapentin works by influencing neurotransmitters in the brain, primarily by mimicking GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). GABA is a natural neurotransmitter known for its calming effects on the brain. It acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means it reduces nerve Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium Abstract Background. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. A2δ is expressed in Purkinje cells, which use gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) as a neurotransmitter. The author states that gabapentinoids inhibit the α2δ subunit and reduce neurotransmitter release, resulting in the induction of cerebellar ataxia. 1,2 Gabapentin works by showing a high affinity for binding sites throughout the brain corresponding to the presence of the voltage-gated calcium channels, especially α-2-δ-1, which seems to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters in the presynaptic area that participate in epileptogenesis. In vitro, gabapentin reduces the release of several mono-amine neurotransmitters. Gabapentin prevents pain responses in several animal models of hyperalgesia and prevents neuronal death in vitro and in vivo with models of the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are key front‐line therapies for various neuropathies of peripheral and central origin. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α 2 δ‐1 and α 2 δ‐2 auxiliary subunits How Does Gabapentin Work? Gabapentin reduces the number of neurons that are firing in your brain. By doing so, this medication can help improve mood and cognition while also reducing anxiety or depression-related symptoms. The neurotransmitter GABA is responsible for slowing down neuronal activity when it binds to its receptors found on nerve Gabapentin appears to work by altering electrical activity in the brain and influencing the activity of chemicals called neurotransmitters, which send messages between nerve cells. Brand names for gabapentin include Horizant, Gralise, and Neurontin. By binding to the alpha-2-delta subunit, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P. This reduction in neurotransmitter release helps to dampen neuronal excitability and, consequently, alleviate neuropathic pain. How does gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) work? GABA is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in your central nervous system. Inhibitory neurotransmitters prevent or block chemical messages and decrease the stimulation of nerve cells in your brain. Neurotransmitters all generally work in the same way. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that exhibits an analgesic effect through binding to presynaptic calcium-channels and modulating the release of glutamate and other excitatory neurotransmitters. It is available in 100-, 300-, 600-, and 900-mg tablets as well as a 50-mg/mL oral solution. For example, by reducing the release of glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, gabapentin may indirectly modulate dopamine release in certain brain regions. Additionally, gabapentin’s effects on calcium channels could potentially influence dopamine neurotransmission, as calcium plays a crucial role in neurotransmitter release. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major neurotransmitter for fast inhibitory synaptic transmission and tonic inhibitory control, is present in 25–50% of all synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000). L -glutamic acid (glutamate) is responsible for fast excitatory neurotransmission and is present at approximately 80% of brain synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000). In conclusion, the multifaceted role of GABA as a neurotransmitter and its therapeutic applications underscore its significance in neurological health. From regulating nerve cell activity to its potential in addressing specific medical conditions, GABA continues to be a subject of interest in both neuroscience and clinical research. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Carisoprodol (Soma) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Lorazepam (Ativan) There are also herbs and amino acids available without a prescription that can be used as GABA surrogates: Valerian root. Ashwagandha. Taurine. Brahmi. Bacopa. Glutamine: GABA’s Precursor
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |