Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
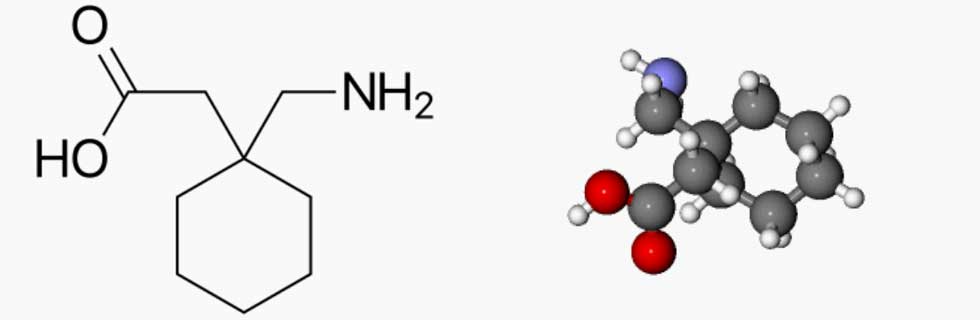
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Even though gabapentin is a structural GABA analogue, and despite its name, it does not bind to the GABA receptors, does not convert into GABA Tooltip γ-aminobutyric acid or another GABA receptor agonist in vivo, and does not modulate GABA transport or metabolism within the range of clinical dosing. [85] Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually The gabapentinoid drugs do not bind significantly to other known drug receptors and so the α 2 δ VGCC subunit has been called the gabapentin receptor. [ 15 ] [ 4 ] Recently, the same α 2 δ-1 protein has been found closely associated not with VGCCs but with other proteins such as presynaptic NMDA-type glutamate receptors , cell adhesion The new work also pinpoints, for the first time, the biochemical mechanism by which the widely prescribed drug gabapentin (also marketed under the trade name Neurontin) works. "We have solved the longstanding mystery of how this blockbuster drug acts," said Ben Barres, MD, PhD, professor and chair of neurobiology. The study shows that Gabapentin has no activity at GABAA or GABAB receptors of GABA uptake carriers of brain. Gabapentin interacts with a high-affinity binding site in brain membranes, which has recently been identified as an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. However, the functional correlate of gabapentin binding is unclear and remains under study. Mechanisms of Gabapentin Antalgic Action: GABA Synthesis and Glutamatergic Inhibition (A) The pathways leading to GABA synthesis and degradation.(B) The analgesic effect of gabapentin depends on the inhibition of excitatory glutamatergic neurons, occurring through mechanisms that do not involve GABA receptors. Although it is rapidly absorbed, readily crosses the blood–brain barrier and is orally active in several animal models of epilepsy, gabapentin neither binds to GABA A or GABA B receptors nor is it metabolized to GABA (Goa and Sorkin, 1993; Kammerer et al, 2011; Taylor et al, 1992). Research regarding gabapentin's effects on GABA and glutamate Gabapentin's binding site is located on the α 2 δ subunit of voltage gated calcium channels. 6 In vitro, gabapentin can inhibit neuronal calcium currents by 35% and decrease neuronal tachykinin-mediated activity. 7,8 It has been suggested that mitigation of hypothalamic tachykinin neurotransmitter activity via a decrease in neuronal calcium Abstract Background. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin was designed as a GABA analog, and some studies have suggested that it modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase, resulting in increased GABA synthesis. 139 Gabapentin increases non-synaptic GABA responses from Gabapentin (GBP) was originally developed as a potential agonist for Gamma-Amino-Butyric-Acid (GABA) receptors, aiming to inhibit the activation of pain-signaling neurons. Contrary to initial expectations, it does not bind to GABA receptors. Instead, it exhibits several distinct pharmacological activities, including: (1) binding to the alpha-2-delta protein subunit of voltage-gated calcium What part of the brain does gabapentin work on? In epilepsy, it is thought that gabapentin may help to reduce the number of seizure-causing electrical impulses in the brain by binding to a specific receptor (known as the alpha2-delta subunit) and inhibiting the release of neurotransmitters. How do gabapentinoids work? Gabapentinoids are known to bind to a specific receptor in the body, the alpha-2-delta calcium channel receptor. When the drug binds to these receptors, it reduces the excitability of the nervous system. Hyperexcitability of the nervous system is thought to contribute to many types of pain. Evidence linking gabapentin to the NMDA receptor follows research demonstrating the reversal of the antihyperalgesic effect of gabapentin by d-serine, an agonist at the NMDA-glycine binding site [33, 34, 36, 37]. However, receptor binding studies have failed to demonstrate a direct binding site for gabapentin at the NMDA receptor . Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ. The α 1 subunit allows entry of calcium and the extracellular α 2 δ is bound to the γ The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are key front‐line therapies for various neuropathies of peripheral and central origin. Originally designed as analogs of GABA, the gabapentinoids bind to the α 2 δ‐1 and α 2 δ‐2 auxiliary subunits [3,4].Gabapentin isa structuralanalog of the inhibitory neurotransmit-ter GABA, yet it has no direct effects on GABA A receptor function, nor does it increase inhibitory synaptic transmission [1,8]. Thus, the molecular basis of gabapentin's GABAergic properties has remained enigmatic. GABA A receptors are pentameric transmitter-gated ion channels Gabapentin, a novel anticonvulsant and analgesic, is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue but was shown initially to have little affinity at GABA(A) or GABA(B) receptors. It was recently reported to be a selective agonist at GABA(B) receptors containing GABA(B1a)-GABA(B2) heterodimers, although
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |