Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
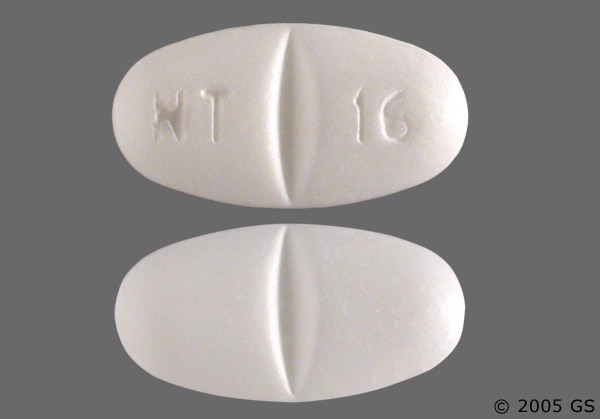
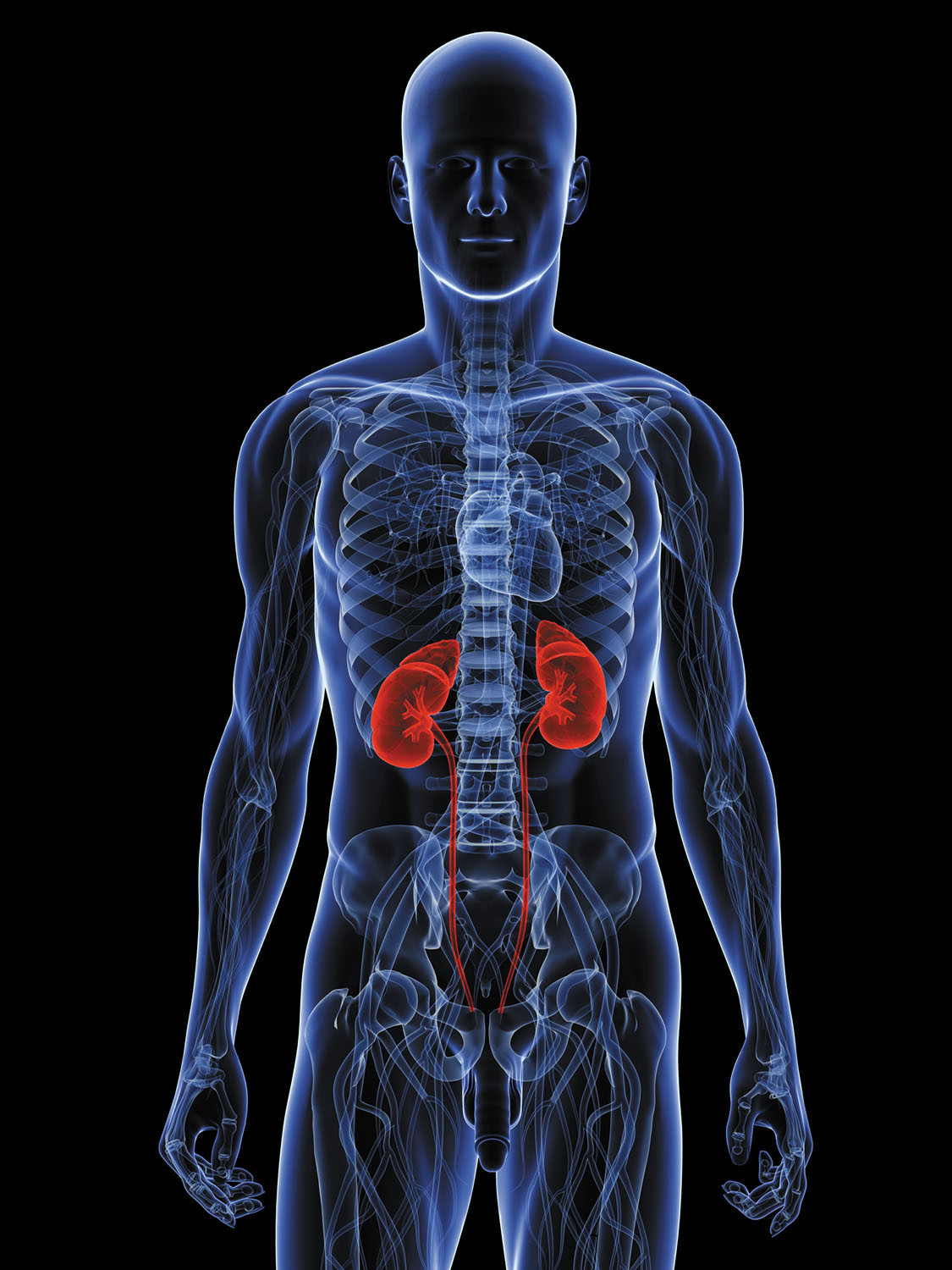
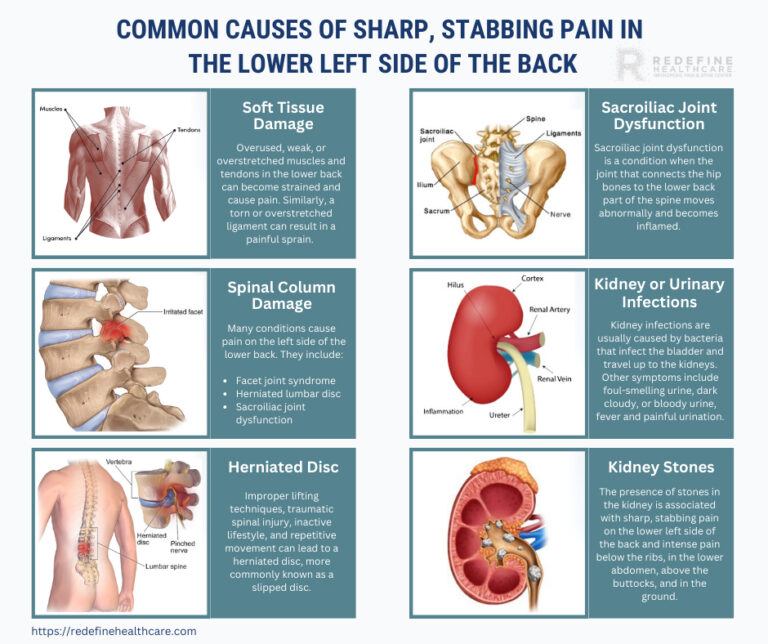
Gabapentin doesn’t usually cause kidney problems. But as discussed above, gabapentin may rarely cause DRESS syndrome. Along with the liver, the kidneys may be damaged as a result of DRESS. However, if you have existing kidney problems, they won’t be able to remove gabapentin as well as they should. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. NSAIDs have the most potential for risk when it comes to your kidneys. The best pain med for you depends on a variety of factors, including kidney health. Let's discuss: In recent years, gabapentin has been increasingly used off-label for expanded indications, including migraine headache, 1 phantom limb pain, 2 cancer-related pain, 3,4 spinal cord injury pain, 5 and a variety of neuropathic pain. 6,7 Off-label prescriptions, by some estimates, account for approximately 90% of gabapentin sales, 8 exceeding 2 Can Gabapentin Affect Your Liver and Kidneys? Written By Daphne Berryhill, RPh Published on Sep 25, 2023 The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. Taper gabapentin and start to return to normal. Then hit with severe body pain back shoulders legs. Start increasing gabapentin. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. Given that gabapentin relies heavily on the kidneys for elimination, careful dose adjustments are crucial for those with pre-existing kidney problems. Healthcare providers typically start individuals with renal impairment on a lower dose and closely monitor their response to the medication. This means that your kidneys degrade and remove medications from the body. When your kidneys aren't working properly, medications can build up and cause you harm. It's important to get your kidneys checked and to work with your doctor to make any adjustments to your medication regimen, such as dosing changes or substitutions. Steven Coca, professor of medicine and a nephrologist at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, says you should know your estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), the primary measurement of kidney function, and your urine albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR), a marker of kidney damage. Learn about the potential effects of Gabapentin on your liver and kidneys. Find out if it is safe to use and how to protect your organs while taking this medication. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication, commonly used to manage neuropathic pain, and it also finds widespread off-label use in treating various pain and sleep disorders. Notably, gabapentin is exclusively excreted through the kidneys, making its dose reduction essential when given to patients with impaired renal function. The patient had visited the Emergency Department two days before due to lumbosacral pain, was diagnosed with mechanical low back pain, and began treatment with 600mg gabapentin every 8 hours. Relevant medical history included smoking 1 packet/day, active use of multiple substances (alcohol, heroin, cocaine, etc.) and a recent hospital admission. Pharmacology. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used first-line agents for diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other common neuropathies. Pharmacologically, both agents inhibit alpha-2-delta (α2δ) subunit of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels, a key receptor involved in regulating the excitability of neurons. 3 Peripheral nerve injury results in the upregulation of α2δ-1 receptors When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Acetaminophen (Tylenol): For mild to moderate pain, acetaminophen remains a generally safe choice, although it should be used judiciously and at recommended doses. Opioids: Certain opioids like oxycodone, hydromorphone, fentanyl, methadone, and buprenorphine are generally considered safer to use in patients with kidney disease when used appropriately and under medical supervision.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |