Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
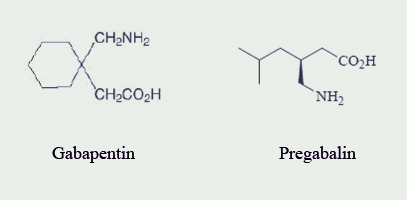
Studies on the effects of gabapentin on blood pressure. Several studies have been conducted to examine the effects of gabapentin on blood pressure. These studies have shown mixed results, with some indicating a potential increase in blood pressure and others finding no significant change. Gabapentin is sold under the brand name Neurontin and is available as a generic product as well. (Generic medications are chemically the same as brand-name drugs but may cost less.) Gabapentin is also available as an extended-release tablet that works for a longer length of time; this is the only formulation that is approved for restless legs Overall, gabapentin does not raise blood pressure; in fact, it tends to lower BP, particularly in hypertensive models and during stress-inducing procedures like surgery. Its hypotensive effects are primarily mediated through the sympathetic nervous system and central mechanisms involving the NTS. Neurontin and generic forms of Neurontin tablets may be broken into two pieces. You can take the second half for your next dose. Don't use the half-tablet beyond 28 days after the whole tablet was cut or broken. Carefully measure the liquid formulation of gabapentin using the measuring device that comes with the drug. Fluid retention causes either an increase in cardiac output or an increase in blood pressure . Velocity of blood flow increases either way, thereby increasing turbulence of blood flow [ 43 ]. Increased turbulence reduces shear stress upon arterial walls, thereby increasing endothelial dysfunction, which is a well-established cardiovascular risk Gabapentin is an analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), however its mechanism is unclear. 1 Gabapentin does not bind to GABA(A) or GABA(B) receptors (or benzodiazepine, opioid, or cannabinoid receptors), but it can increase GABA and decrease glutamate concentrations. 2, 3 Its mechanisms of antiepileptic and analgesic actions are unknown The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Fluid retention causes either an increase in cardiac output or an increase in blood pressure . Velocity of blood flow increases either way, thereby increasing turbulence of blood flow [ 43 ]. Increased turbulence reduces shear stress upon arterial walls, thereby increasing endothelial dysfunction, which is a well-established cardiovascular risk High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of Pain and blood pressure appear to be strictly related. According to available evidence, both pain and analgesic therapies may induce a clinically significant destabilization of blood pressure values. The subsequent implications on hypertension incidence and blood pressure control remain unclear and should be explored in future studies. Funding 3. Does gabapentin raise blood pressure? While studies suggest that gabapentin can lower blood pressure and heart rate acutely, it is also listed as a potential side effect to cause hypertension, or high blood pressure, particularly with long term use. 4. Can gabapentin cause heart palpitations? The question of whether gabapentin is bad for blood pressure is complex, with the answer not being a simple yes or no. While research indicates that gabapentin can actually reduce blood pressure and heart rate in some cases, there are also potential risks related to blood pressure, especially with long-term use and withdrawal. The key lies in The Risks of Taking Gabapentin for High Blood Pressure. Research indicates that gabapentin can cause blood pressure to rise in some cases, which may be due to its effects on the body’s blood vessels. When blood vessels constrict, blood pressure can increase, leading to potential complications. Does Gabapentin Raise Blood Pressure? Understanding the Cardiovascular Effects. The question of whether gabapentin raises blood pressure is complex, and the answer isn’t a straightforward yes or no. While some studies and initial findings suggested that gabapentin might actually Ended up in the ER twice with severe blood pressure spikes. I had blood pressure spikes previously but the Gabapentin added chest pain/heaviness on my chest, short labored breathing, and tingling sensations in head and arms to my previous BP issues. It also delayed response of my BP meds to bring my pressure down. Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. As mentioned above, NSAIDs may increase your blood pressure. Cough and cold medications also frequently contain decongestants . Decongestants can make blood pressure worse in two ways: While Gabapentin itself may not directly increase blood pressure, it is essential to monitor and manage blood pressure levels while on this medication. 1. Regular blood pressure monitoring: It is recommended to regularly monitor your blood pressure while taking Gabapentin. We have explained how gabapentin can cause high blood pressure. However, not every individual taking gabapentin would experience high blood pressure or the same side effects. Other factors can increase one’s risk of high blood pressure besides gabapentin. Let’s discuss factors that can increase an individual’s risk of high blood pressure.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |