Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 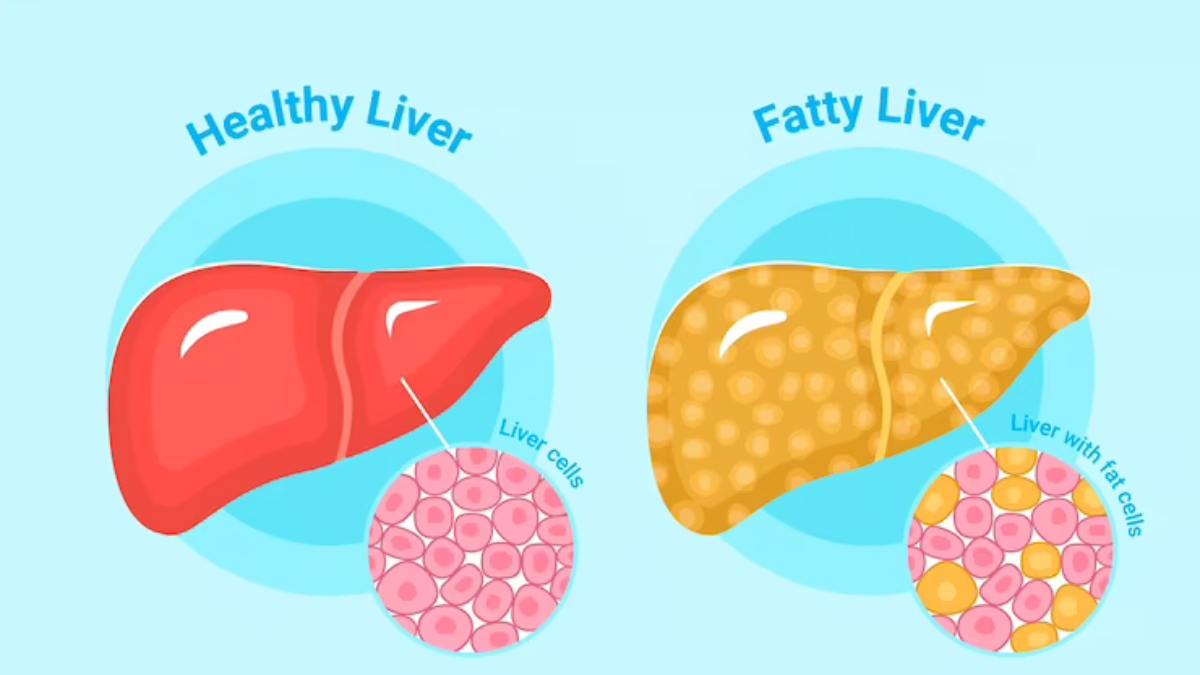 |
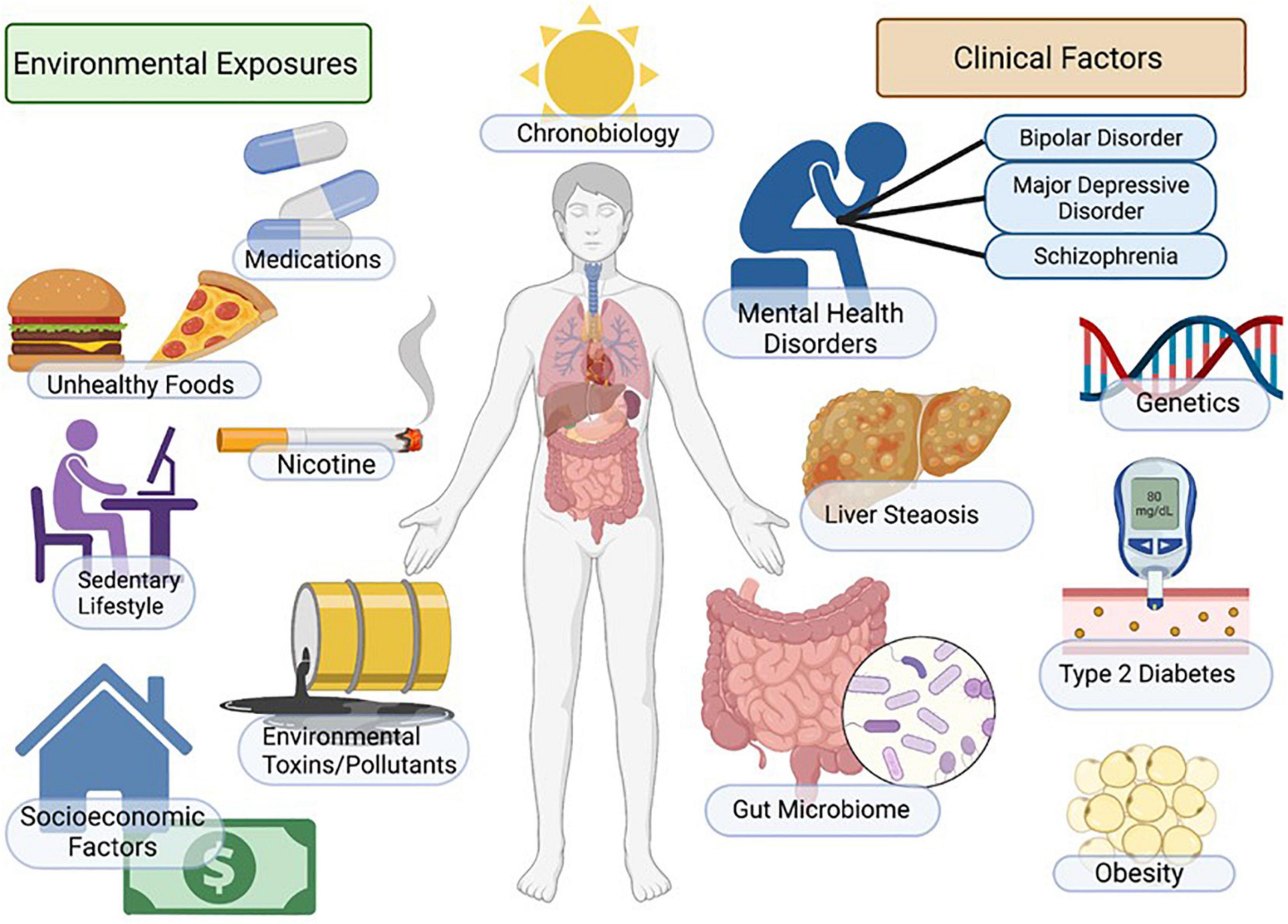
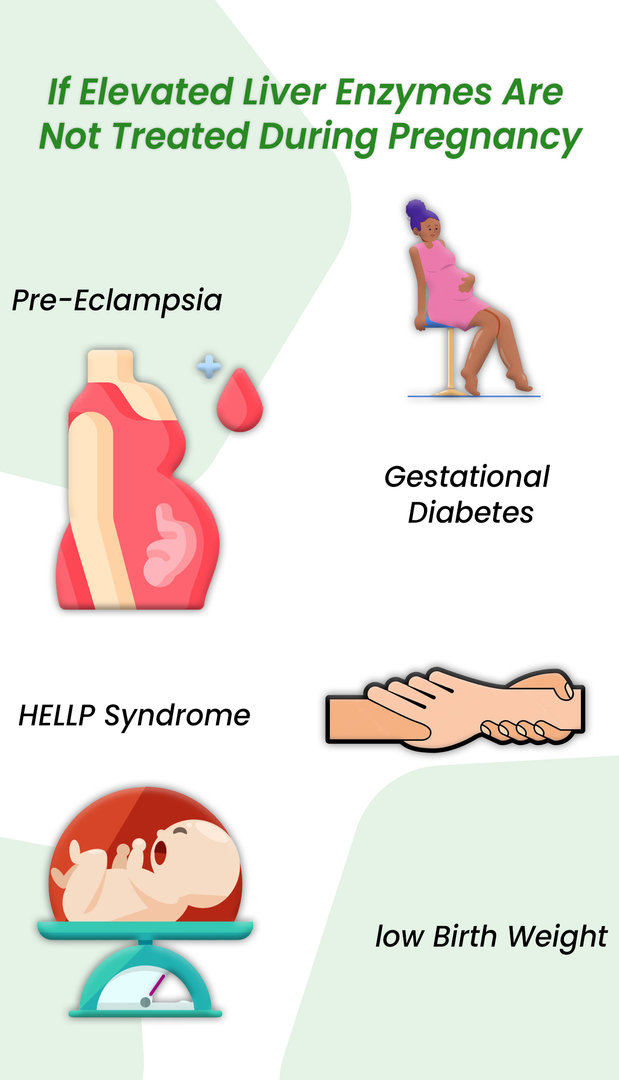
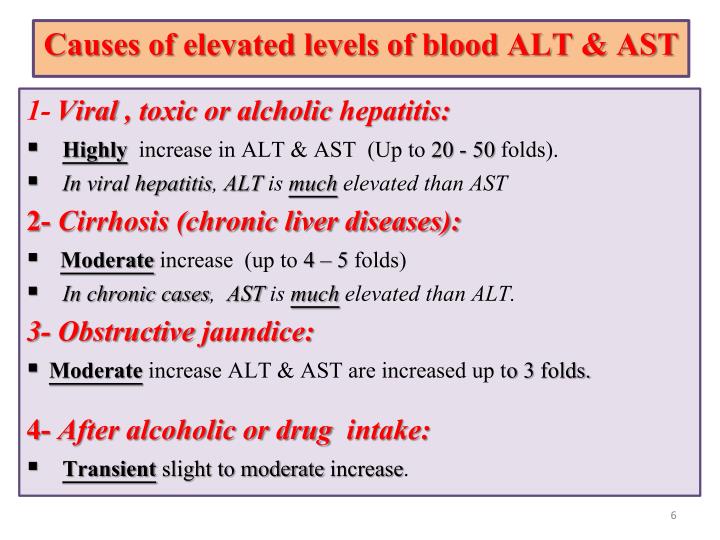
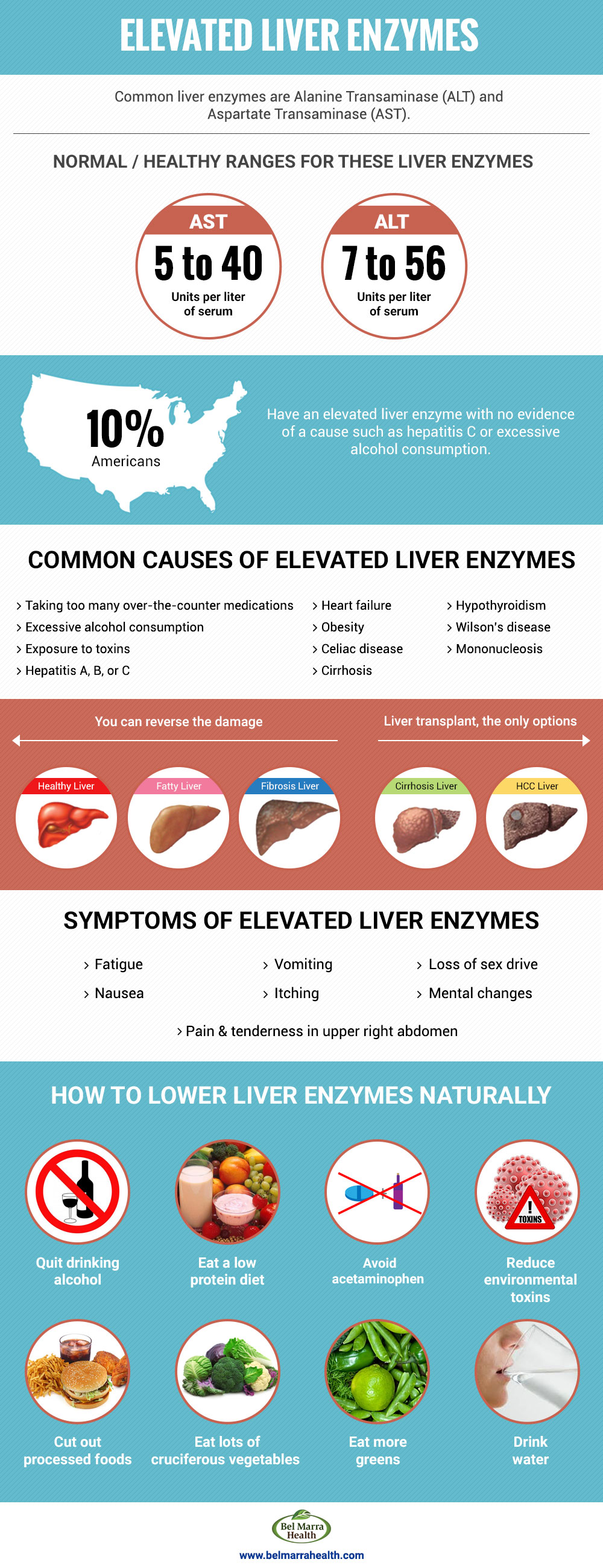
Most research indicates that Gabapentin does not adversely affect liver enzymes or overall liver health in most patients. In fact, studies have shown that even patients with preexisting liver conditions can often tolerate Gabapentin without significant issues. Gabapentin is an uncommon cause of DILI reported to cause a hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed picture of liver injury. Given the limitations of prior cases, we feel our report most closely ties gabapentin use to the resultant transaminase elevation. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. Gapentin has no appreciable liver metabolism, but suspected cases of gabapentin-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported. Even high doses of gabapentin (400mg/kg) for 30 days do not produce deleterious adverse effects on the liver or haematological parameters. Can gabapentin cause liver enzymes to be elevated? Gabapentin is a unique anticonvulsant used as an adjunctive therapy in managing epilepsy and neuropathic pain syndromes. It is a structural analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and has been approved for use in the United States in 1993. Can administration of gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia dramatically increase liver function tests? We study 323,232 people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin) or have Elevated liver enzymes. No report of Elevated liver enzymes is found in people who take Gabapentin. The phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports from the FDA, and is updated regularly. Gabapentin-Induced Liver Toxicity. Chahal, Japjot MD 1; You can read the full text of this article if you: Elevated Prothrombin Time and International The activity of liver enzymes, with 20 mg/kg of GPN were not significantly different from the control group but, the serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, direct bilirubin and total bilirubin were enhanced significantly with 100 mg/kg of GPN. Most often, you won’t have any signs of elevated liver enzymes unless these elevations become severe, and you develop liver damage. Symptoms can also vary depending what underlying liver disease is causing your particular liver enzyme abnormality. TPM can infrequently lead to elevated liver enzymes. We came across two possible cases of TPM-induced hepatotoxicity 61, 62 in the literature, and one case report suggesting reversible hepatic failure after adding TPM to VPA. 63 These are isolated case reports requiring further corroborating evidence. 2. Can gabapentin cause elevated liver enzymes in dogs? While gabapentin itself is not usually associated with elevated liver enzymes, some rare cases of clinically apparent liver injury have been reported. This warrants caution and proper monitoring. 3. How long can a dog safely take gabapentin? There is no maximum time limit for gabapentin Elevated levels of liver enzymes can indicate liver dysfunction and may require further investigation. Potential Effects of Gabapentin. Research suggests that gabapentin may have minimal impact on liver enzymes in most individuals. However, there have been rare cases where gabapentin use has been associated with elevated liver enzyme levels. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. Keywords: drug-induced liver injury; gabapentin; hepatotoxicity. Gabapentin caused elevated liver function enzymes AST, ALT, and ALP beside bilirubin. Gabapentin effects on lipid profile, Blood electrolytes, and functions of kidney and liver of laboratory Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography showed no biliary abnormalities. After gabapentin was discontinued, liver enzymes began to downtrend with discharge values of AST 16, ALT 35, ALP 413, Tbili 9.3 and INR 1.1 (Figure). Discussion: Gabapentin induced liver injury is rare with few reported cases, many of which did not exclude other Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. There are several liver enzymes, but the ones that show liver damage from medications are aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT). Medications may cause liver enzymes to be elevated without serious liver damage until they reach 3 to 5 times the normal levels.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |