Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
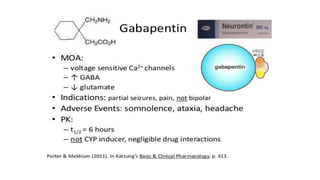
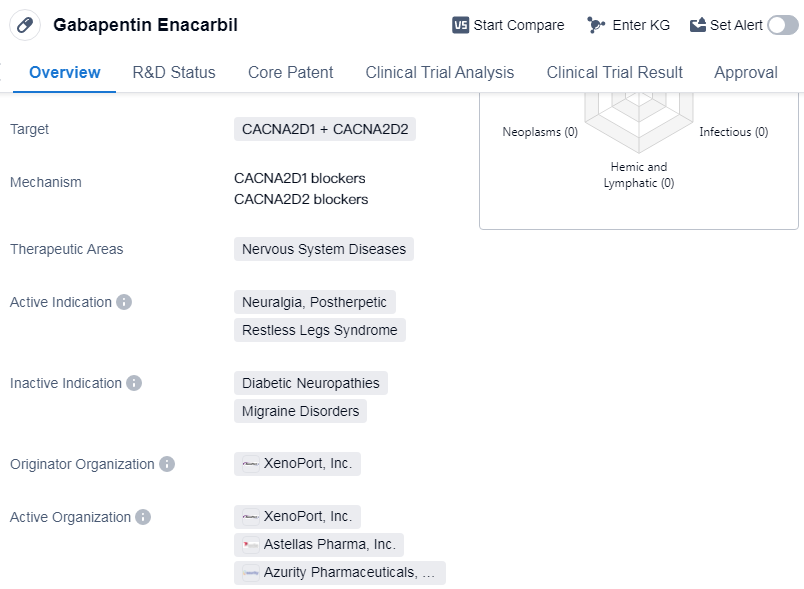
Mechanism of Action Gabapentin is designed as GABA analog (similar to pregabalin ), which means it binds to the α2δ (alpha-2-delta) subunit of presynaptic voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels (VSCCs), and block the release of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate. While gabapentin's mechanism of action is generally understood, it appears to be a pharmacologic option for treating issues involving the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor system. Gabapentin is a relatively safe, readily available, and effective drug for alcohol-use disorder treatment, specifically for the abstinence maintenance phase. The binding to α2δ-1 subunits inhibits nerve injury-induced trafficking of α1 pore forming units of calcium channels (particularly N-type) from cytoplasm to plasma membrane (membrane trafficking) of pre-synaptic terminals of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons and dorsal horn neurons. Mechanisms of action. Gabapentin and pregabalin do not bind to GABA receptors despite their structural similarity but have a high affinity for the α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs). 19 VGCCs are composed of multiple subunits: α 1, β, γ and α 2 δ. Gabapentin has no direct GABAergic action and does not block GABA uptake or metabolism. Gabapentin blocks the tonic phase of nociception induced by formalin and carrageenan, and exerts a potent inhibitory effect in neuropathic pain models of mechanical hyperalgesia and mechanical/thermal allodynia. Mechanism of action By inhibiting the voltage-gated calcium channels in the CNS, gabapentin reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters (mostly noradrenaline, dopamine and serotonin), and therefore decreases epileptogenesis. Gabapentin, like other gabapentinoid drugs, acts by decreasing activity of the α 2 δ-1 protein, coded by the CACNA2D1 gene, first known as an auxiliary subunit of voltage gated calcium channels. [13][14][15] However, see Pharmacodynamics, below. Gabapentin crosses several lipid membrane barriers via system L amino acid transporters. In vitro, gabapentin modulates the action of the GABA synthetic enzyme, glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) and the glutamate synthesizing enzyme, branched-chain amino acid transaminase. Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug but its use has expanded to treat multiple other diseases including post-herpetic neuralgia, neuropathic pain, and spasticity. The mechanism of action is not fully understood but may be related to gabapentin’s action on calcium channels leading to diminution of excitatory neurotransmitters. Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin is structurally related to GABA. However, it does not bind to GABA A or GABA B receptors, and it does not appear to influence synthesis or uptake of GABA. High affinity gabapentin binding sites have been located throughout the brain; these sites correspond to the presence of voltage-gated calcium channels This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, administration, significant adverse effects, contraindications, monitoring, and characteristics of gabapentin toxicity. As with many other agents, GBP was licensed for the treatment of epilepsy with little or no understanding of its mechanism of action. Continued research and the parallel development of PGB have contributed to a contemporary pharmacological view of GBP (and PGB) as drugs with multiple modest cellular effects at therapeutic concentrations, but with a single predominant mechanism of action that Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. Mechanism of action of gabapentinoids Site of action The actions of gabapentinoids are mainly at an intracellular site and require active uptake.21 They were originallydesigned as g aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogues but do not have any effects on GABA receptors. Gabapentin binds to a 2d receptors with greater affinity to the a 2d-1 subtype.22 Mechanism of Action. Gabapentin's exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It is thought to bind to calcium channels, modulating their activity and reducing the release of neurotransmitters involved in seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug with an unknown mechanism of action apparently dissimilar to that of other antiepileptic agents, and possessing some desirable pharmacokinetic traits. The drug is not protein bound, is not metabolised and does not induce liver enzymes, diminishing the likelihood of drug interactions with other antiepileptic Mechanism of action. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is Several mechanisms of gabapentin have been proposed after neuropathy including an inhibition of NMDA receptors, inhibition of sodium currents and reducing β4a subunit mediated VGCC trafficking (Hara and Sata 2007; Mich and Horne 2008; Yang et al. 2009). However, these drugs remain highly misunderstood in terms of mechanism of action, indications and, more recently, abuse liability. Few clinicians understand the complex role of CCα2δ in chronic pain states, and many have most likely over-prescribed the drugs under the impression that they will benefit anyone suffering with pain. Conversely Drug Class: Antiepileptic Mechanism of Action: gabapentin is an amino acid & a structural analog of GABA, but does not bind to GABA receptors.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |