Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
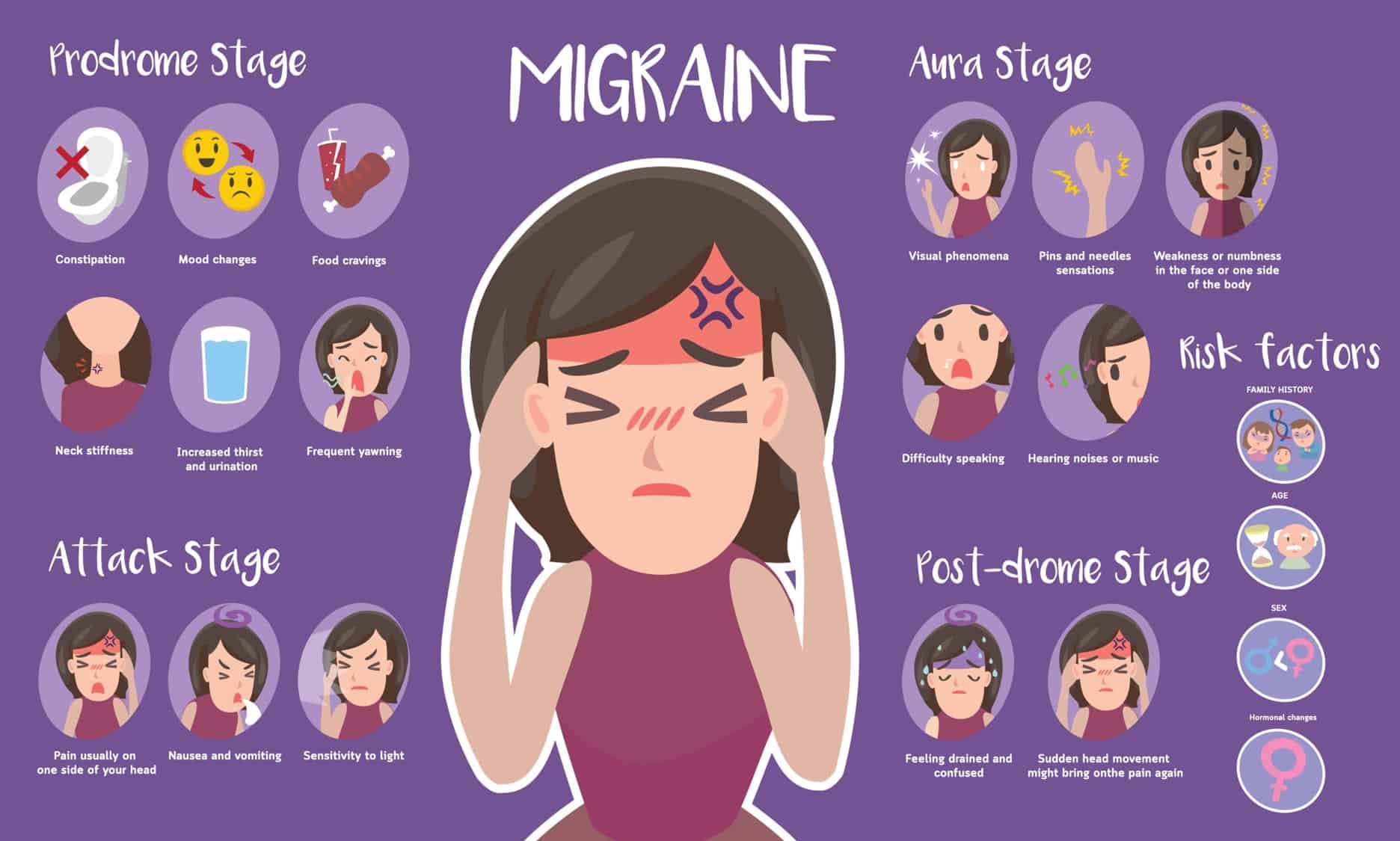
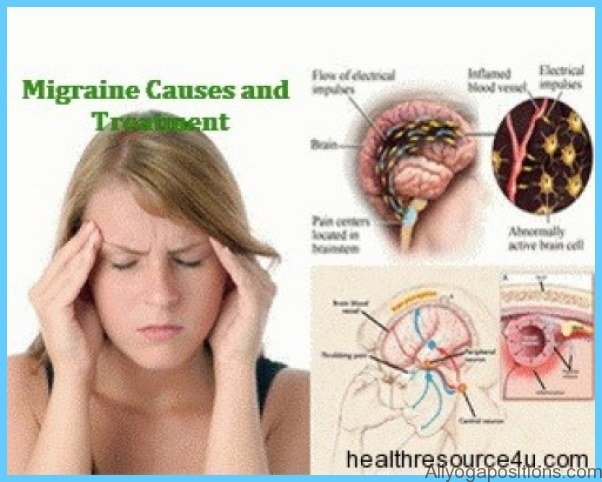
Gabapentin also dramatically worsened my migraines. Nothing worked to treat or prevent them while I was on it. Stopped gabapentin, and my Botox treatments started working again. Gabapentin’s role in migraine prevention isn’t well known. It’s believed that it may influence electrical activity in the brain through neurotransmitters and block calcium channels. Just started gabapentin and have taken it the past two nights. To start, I am taking 100mg at night, then in two weeks can up it to 200mg a night. The past two nights it has caused me to not sleep well (waking up every hour or two), and I've woken up with blurry vision, dizziness and a migraine that is worse than usual. Gabapentin is used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type nerve pain that can occur due to an outbreak of shingles, and restless legs syndrome (RLS), an uncomfortable urge to move your legs around, often at night. Official answer: Gabapentin may make you feel a little drowsy, dizzy, or clumsy when you first start taking it. Gabapentin can make you hungrier, so it can be hard to stop yourself putting on weight. Try to eat a healthy, balanced diet without increasing your portion sizes. Do not snack on foods that contain a lot of calories, such as crisps, cakes, biscuits and sweets. If you feel hungry between meals, eat fruit and vegetables and low-calorie foods. Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. Because gabapentin can enhance the psychological effect of opioids, it has the potential to be abused and has contributed to drug overdose deaths. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Reviews and ratings for Gabapentin when used in the treatment of migraine. 121 reviews submitted with a 7.9 average score. Taking gabapentin with opioids (e.g., morphine, hydrocodone) can cause respiratory depression and sedation, and lead to fatal outcomes. Tell your healthcare provider if you are also taking opioids. Do not stop taking gabapentin without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping suddenly can cause serious problems. Some side effects of gabapentin may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects. Long-term history of headaches. A long-term history of headaches, especially migraines, raises the risk. Medication overuse headache often occurs when a headache condition such as migraine is not well controlled and may make the underlying headache condition difficult to treat. Regular use of headache medicines. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems, like withdrawal symptoms or the return of seizures. Your doctor will help you stop taking the drug safely. Drug interactions admittedly, the distinction between chronic/episodic can be a little murky, but basically, it sounds like the odds that gabapentin will help you are better if you have chronic migraine (which is defined as 15 or more headache days per month.) hopefully that's something your doctor took into account, although in my experience, not all doctors Key Takeaways: Gabapentin and Migraines Individual Reactions Vary: Gabapentin affects everyone differently. Not a Direct Cause: Gabapentin is not typically linked to migraines. Anecdotal Evidence Exists: User experiences with gabapentin vary widely. Monitor Interactions: Other medications can impact headache frequency. Overuse of certain headache medications, including opioids, triptans, and combination analgesics, can lead to medication overuse headaches (MOH) and exacerbate migraine symptoms. “The very Gabapentin is the only thing that has brought the pain down without making things worse on whole. No medication overuse headaches, no gastritis. The dosage can be adjusted a lot, so when everything flared up due to extreme stress, I was able to increase my dosage. Along with causing dizziness, gabapentin can worsen your coordination. This can increase your risk of falls, which is especially dangerous for older adults. If you’re just starting to take gabapentin or your dose has increased, avoid driving or doing any activity that requires alertness. Gabapentin can decrease neuronal excitability in spinal trigeminal nuclei and inhibit the forma-tion of central sensitization during migraine by reducing excitatory amino acid content in the brospinal fluid and by inhibiting protein kinase C activation. Just don't stop cold-turkey—you'll likely have to taper off of the medicine, since suddenly stopping gabapentin can make you feel worse, says Patel. You're kind of wobbly too. Headaches: Headaches are another common side effect of gabapentin, which can be attributed to other symptoms, including mood changes, dizziness, and thinking issues. These are just a few of the most common gabapentin side effects; it is not an exhaustive list. Some medications you’re taking may provoke, prolong, or make your migraines worse. Rebound medications. When you take pain medications frequently, your pain can return faster and be more debilitating after each dose. These “rebound headaches” can result when you take: Aspirin; Ibuprofen; Acetaminophen; Naproxen; Sleeping pills; Codeine
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |