Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
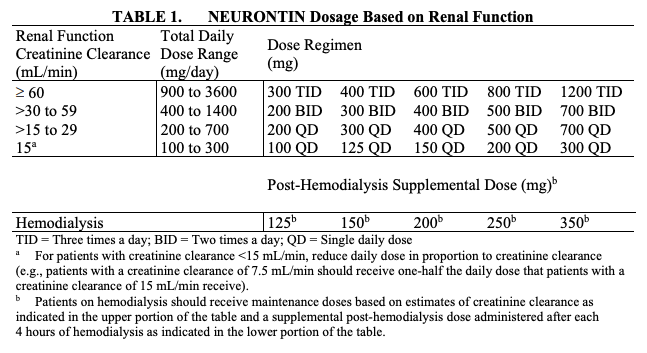
This case report outlines a significant type of morbidity due to continued use of gabapentin during an episode of acute renal failure. Setting. University teaching hospital. Discussion. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. In other words, your actual kidney function (eGFR level) may be higher or lower than what is reported in your lab results, although this is not very common. Some factors that can lead to higher creatinine levels (making your eGFR number appear lower than it might really be) include: Eating large amounts of cooked meats; Taking creatine supplements The standard doses of gabapentin prescribed for people with normal kidney function are not suitable for those with CKD. Typically, healthcare providers will significantly reduce the dose of gabapentin based on a patient’s estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) , a measure of kidney function. I currently take gabapentin for trigeminal neuralgia and have CKD stage 3. Take 900-1200 gabapentin daily over past 20 years. Experiencing severe side effects of gabapentin that Im beginning to think correlate with decreased kidney function. It’s becoming cyclic. Take normal dose of gabapentin until start to become confused and lethargic. How they can affect the kidneys: If you have kidney disease, understand what your kidney function is before you take an antibiotic. That will help you and your doctor determine the dosage. Owen says that some medications used to treat viruses can cause kidney injury. medicine used. The harm to your kidneys can be sudden, and result in acute kidney injury (AKI). In some cases, if you stop the pain medicine you may reverse short-term harm to your kidneys, meaning kidney function may recover. Continued overuse or misuse of certain pain medicines can also lead to a slow loss of kidney function over time, or chronic Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Population-based cohort study. The question of whether gabapentin is hard on the kidneys is a nuanced one. While not directly known as a primary cause of kidney damage, the reality is more complex. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Medications can impact your kidneys, especially with chronic kidney disease. Learn which drugs may need adjustments to protect your kidney health. Medications save and improve lives, but it can be easy to overlook their risks and side effects, especially if you don't think they apply to you. Gabapentin is cleared from the body by the kidneys. With age-related decline in kidney function, the medication can accumulate, increasing the risk of side effects and further stressing the kidneys. This may necessitate a lower dose or even avoidance of gabapentin in elderly individuals. 4. Can gabapentin cause cognitive impairment in older adults? Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. The straightforward answer is yes, you can potentially take gabapentin if you have stage 3 kidney disease, but with significant caveats. It’s crucial to understand that gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys, meaning that impaired kidney function can lead to a buildup of the drug in your system. This accumulation can increase the If you have existing kidney problems, you may need a lower dose of gabapentin. This is because the kidneys help the body get rid of gabapentin. If your kidneys don’t work well, gabapentin may build up in the body and cause side effects. Patients receiving higher gabapentinoid doses with decreased kidney function may be at an increased risk of adverse effects (AEs), but limited evidence exists evaluating gabapentinoid dosing and AEs in this population. Older adults who take gabapentin also are at higher risk of breathing problems. Because gabapentin can enhance the psychological effect of opioids, it has the potential to be abused and has contributed to drug overdose deaths. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive dangerously high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, which can lead to all sorts of problems. An alternative we recommend instead of Gabapentin is Alpha Lipoic Acid. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. However, when kidney function is impaired, gabapentin can accumulate in the body, leading to potential side effects like excessive sedation, dizziness, and confusion. Therefore, cautious dosing, usually significantly lower than what might be given to a cat with healthy kidneys, is essential.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |