Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1369889825-309a0c942f2c4ad0a5595047104135fb.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
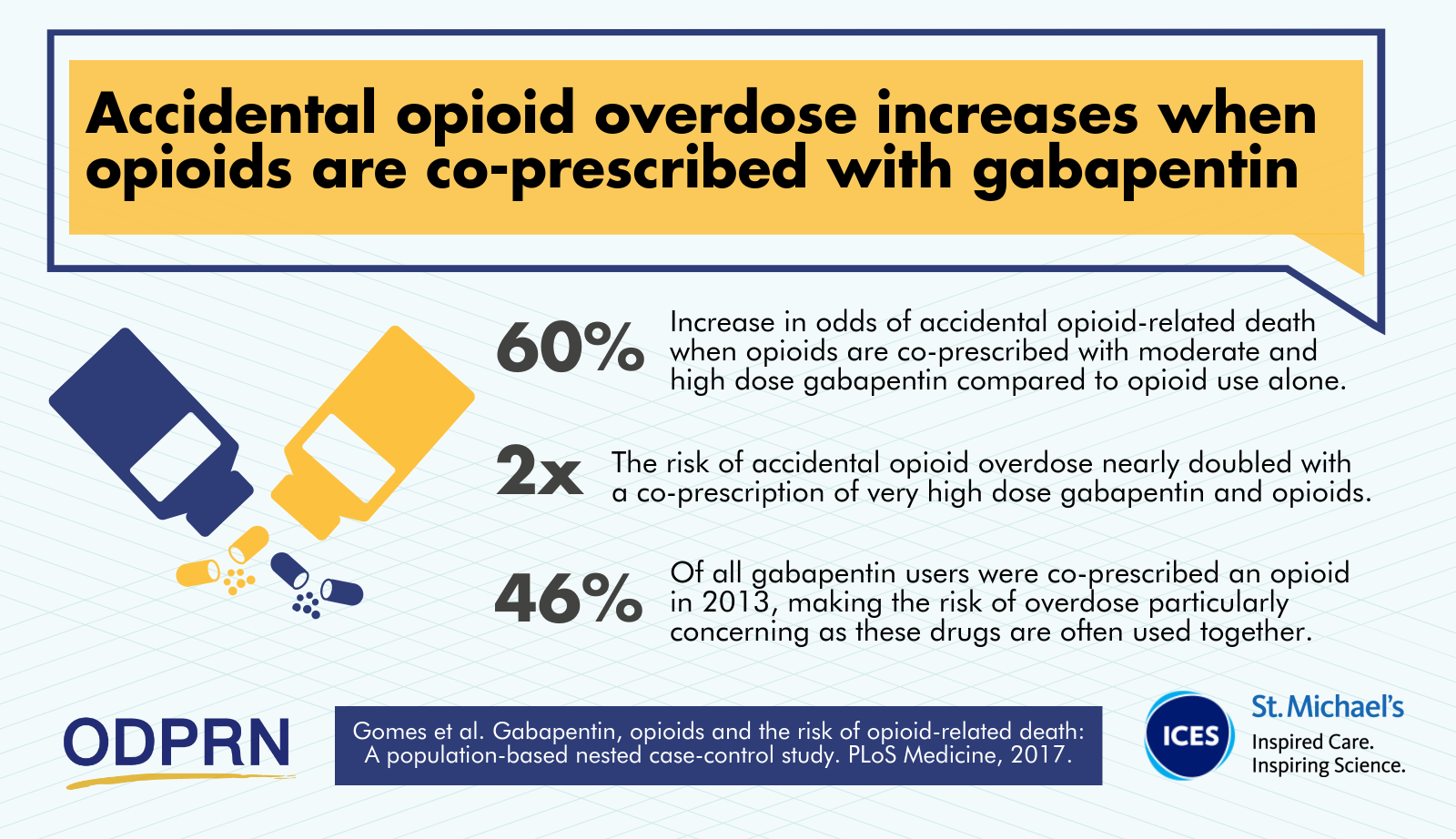 | 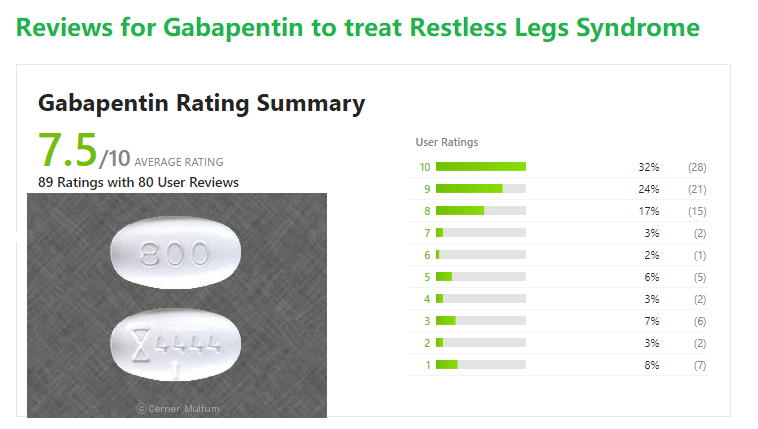 |
Therapy is widely delivered to treat anxiety and depression for those prescribed gabapentin, and it’s highly effective. Although there are many types of depression and anxiety therapy, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective. Gabapentin is also used off-label to treat conditions such as anxiety and nerve pain from diabetes. It may also be used to treat alcohol use disorder. Though gabapentin has many potential uses, it can cause side effects too. Knowing about gabapentin side effects in advance can help you manage them if they happen to you. Link between gabapentin and depression. Does gabapentin affect your mood and can it cause depressive symptoms? Gabapentin can affect mood and may cause depressive symptoms, though this is considered a rare side effect. While it is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain, some individuals have reported experiencing feelings of sadness or Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Gabapentin FAQs, answered: Knowing how long gabapentin takes to work, and what to expect while taking it, can help you get a better understanding of your treatment. Gabapentin for anxiety dosage In studies, gabapentin doses for anxiety range from 300 mg to 3,600 mg daily. Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly In conclusion, gabapentin is a medication that can be used as a treatment for depression, particularly for individuals who have not responded well to other medications. By understanding how gabapentin works in the brain and its potential effectiveness for depression, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options in There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. Limitations of available data include variation in dosing between studies, gabapentin as monotherapy or adjunctive treatment, and differing primary outcomes between trials. Drugs such as gabapentin have been linked in rare cases to an increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors. If you take gabapentin, you or your family should tell the doctor about any unusual changes in your mood, such as agitation, violence, aggression, depression, or talking about wanting to hurt yourself. While gabapentin isn’t typically used as a standalone treatment for depression, some studies suggest it may have a role as an adjunct therapy, particularly in bipolar disorder. It’s like adding a secret ingredient to a recipe – it might not be the main component, but it can enhance the overall effect. Overall, while Gabapentin can be highly beneficial in treating various conditions, it must be used responsibly and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize potential risks and adverse effects. In the context of the question, "can Gabapentin cause depression?", there is no direct evidence linking Gabapentin to depression. This use of gabapentin for the treatment of anxiety is referred to as an off-label use, meaning there is limited data on its effectiveness to treat anxiety. Other off-label uses include treating alcohol withdrawal for alcohol use disorder and hot flashes associated with menopause. Neurontin - also known as Gabapentin - is a drug that is sometimes prescribed to those who experience anxiety especially in situations where the anxiety is co-occurring with bipolar disorder. This article explores the usage of Neurontin, as well as the benefits, weaknesses, and side effects for those looking to learn more about this medication Research indicates that gabapentin has no substantial evidence supporting its effectiveness in treating major depressive disorder. Some studies even suggest that while it may relieve certain anxiety symptoms, it may inadvertently contribute to depressive symptoms in other users. Gabapentin is an oral medicine that we may prescribe to treat certain anxiety or depression disorders. We may also use this medication to treat nerve pain. Gabapentin is a synthetic version of the neurotransmitter GABA, which means it mimics the role GABA has in the body. Our team takes an individualized and comprehensive approach to treatment by seeking the underlying cause of the addiction first. Our prescription drug treatment programs provide outpatient addiction options that are tailored to your specific needs. What We Provide. Caring medical personnel; Individualized prescription drug addiction treatment Gabapentin isn’t the main treatment option for anxiety, but it can be an effective alternative when other medications haven’t worked. Despite the absence of direct evidence linking Gabapentin to depression, the medication can influence mental health through its side effects. Individuals taking Gabapentin should be vigilant and report any mood or behavioral changes to their healthcare provider promptly.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1369889825-309a0c942f2c4ad0a5595047104135fb.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |