Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
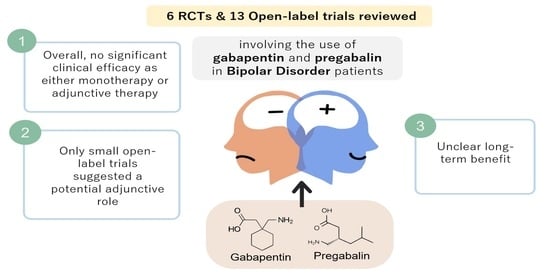 |  |
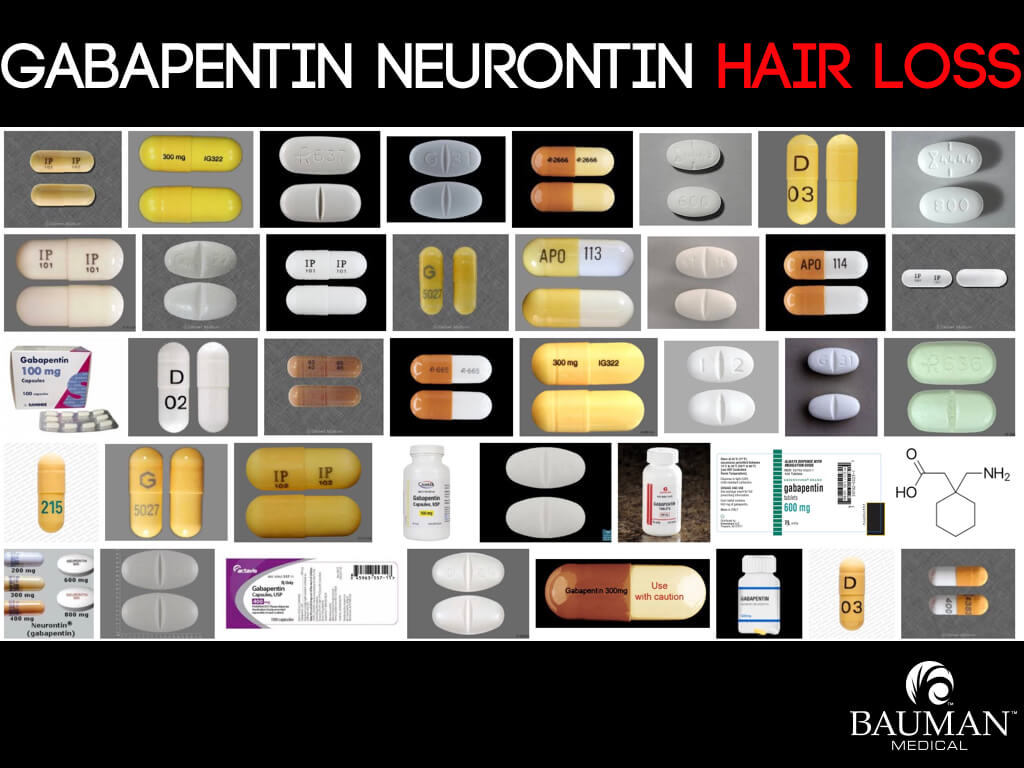
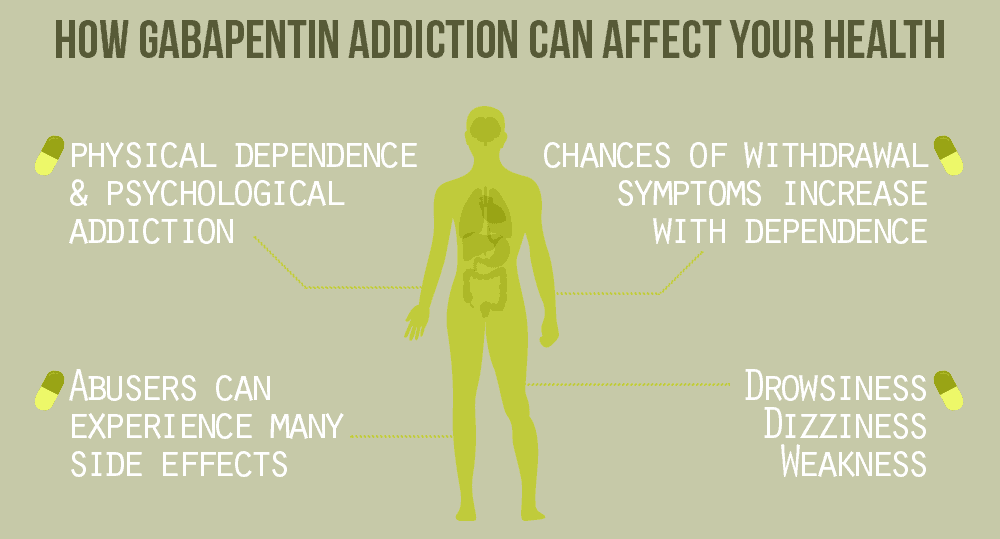
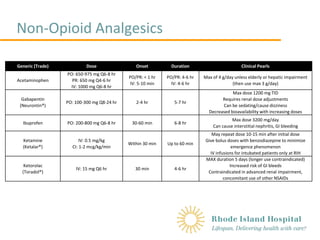
A systematic search strategy employing different combinations of the keywords (bipolar, mania, hypomania, gabapentin, neurontin, gralise, gabarone, fanatrex, pregabalin, lyrica) was developed and performed in five databases namely OVID Medline, PubMed, ProQuest, PsychInfo and ScienceDirect from database inception to 7 June 2021. Gabapentin, a medication commonly used to treat seizures and nerve pain, has also been explored as a potential treatment for bipolar disorder. Research suggests that gabapentin may help alleviate symptoms of bipolar disorder, particularly in patients who have not responded to traditional treatments. What is Bipolar Disorder? A recent survey using the US-based TriNetX electronic health records network showed that gabapentin had been prescribed at least once in 13.6% of patients with bipolar disorder (BD), 11.5% with anxiety disorders, and 12.7% with insomnia disorder; for pregabalin, the figures were 2.9%, 2.6%, 3.0% respectively (PJH, unpublished observations). As with any medication, gabapentin can cause side effects. Some common side effects may include dizziness, drowsiness, and coordination problems. It is important to discuss any potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider before starting gabapentin for managing anxiety or bipolar disorder. Consult with a Healthcare Professional Gabapentin's relatively benign side-effect profile. Gabapentin has been successful in controlling rapid cycling and mixed bipolar states in some people who have not received adequate relief from carbamazepine (Tegretol) and/or valproate (Depakote). Research indicates that Gabapentin is good at lowering the highs, but though it can pull one out of deep depression, it's not as affective at pulling ppl out of low-grade depression on its own. I have been on HIGH doses of Gabapentin for 11 years, and have not once experienced hypomania in that time. However, I live in a constant state of the Gabapentin isn’t usually used to treat anxiety alone. More often, it’s given to ease anxiety symptoms for someone who also has depression or bipolar disorder. (Anxiety is commonly comorbid For bipolar disorder, four double-blind RCTs investigating gabapentin, and no double-blind RCTs investigating pregabalin, were identified. A quantitative synthesis could not be performed due to heterogeneity in the study population, design and outcome measures. Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. There are now five medications with specific, FDA approval for acute bipolar depression. Gabapentin (Neurontin) Topiramate (Topamax) Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) Lamotrigine (Lamictal) Bipolar disorder can cause trouble with sleep, changes in weight, and heart issues. It's important Additionally, gabapentin can cause multiorgan hypersensitivity or DRESS syndrome, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention if symptoms such as rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes, or liver problems occur.Consulting with a healthcare professional and being aware of the potential risks and benefits of gabapentin are important Researchers gathered existing research on gabapentinoid use in bipolar disorder, anxiety and insomnia. They found that the drugs had a moderate effect for some types of anxiety. But studies did not support the use of the drugs in bipolar disorder or insomnia. The team says these drugs should be used with extreme caution. I take a lot of gabapentin. I’ve only had issues when I stop taking it and going through withdrawals. It seems there are people on this thread who have had possibly same experiences as you. Talk to your med provider as soon as you can and stay safe friend Only one of five patients with rapid cycling had a positive response. Gabapentin was well tolerated by all patients, with the most common side-effect being sedation. Conclusions: Gabapentin appears to have acute anti-manic and anti-depressant properties as an adjunctive agent for refractory bipolar illness. Prospective double-blind studies are Researchers found that gabapentin does not help people with bipolar disorder. Learn more about the history of why some doctors prescribe gabapentin for bipolar as an adjunct therapy, even though there’s no evidence that it works for bipolar treatment or maintenance. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Can Gabapentin Cause Depression? The relationship between gabapentin and depression is a complex matter that requires careful examination. While gabapentin is not typically prescribed for the treatment of depression, some studies suggest that it may have the potential to contribute to depressive symptoms or worsen existing depression in certain The subtypes of bipolar disorder include bipolar I and bipolar II. Patients with bipolar I disorder experience manic episodes and nearly always experience hypomanic and major depressive episodes. Bipolar II disorder is marked by at least one hypomanic episode, at least one major depressive episode, and the absence of manic episodes. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |