Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
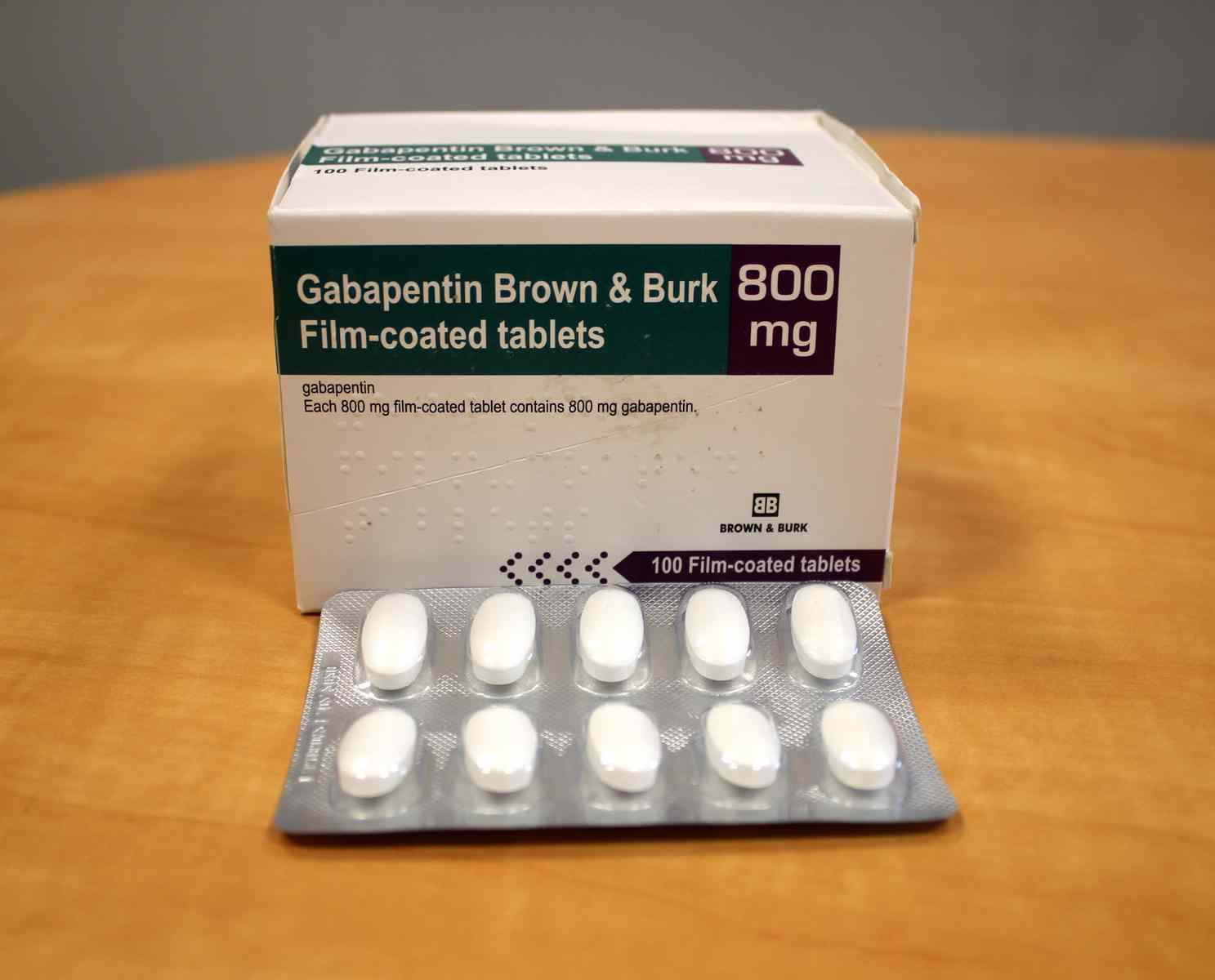
The optimal use of gabapentin for sleep involves careful consideration of timing, dosage, and integration with good sleep hygiene practices. Typically, taking gabapentin 1-2 hours before bedtime allows for its sleep-promoting effects to align with the desired sleep onset. Several studies have been conducted on the safety and effectiveness of taking gabapentin for sleep issues. The results of these studies are listed below: According to a 2010 study, gabapentin can improve sleep quality and slow-wave sleep (deep sleep), lower your risk of spontaneous nighttime wake-ups, and prevent premature morning awakenings Gabapentin enhances slow-wave sleep in patients with primary insomnia. It also improves sleep quality by elevating sleep efficiency and decreasing spontaneous arousal. The results suggest that gabapentin may be beneficial in the treatment of primary insomnia. 15 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gabapentin and Sleep Aids 1. Can I take gabapentin every night for sleep? While gabapentin can improve sleep, it’s not usually the first-line treatment for insomnia due to potential risks like dizziness, falls, and dependence. Use should be supervised by a doctor. 2. Gabapentin has a slower onset of action, usually taking effect within 1-2 hours, but its effects can last longer, potentially providing more consistent sleep throughout the night. Side effect profiles are an important consideration when choosing between these medications. Because Gabapentin improves your ability to stay asleep, you should only take it when you have 7-8 hours to sleep. Only take your prescription before bed. Never use this medication if you won’t be able to go to bed right away and stay asleep for at least 7 hours. Research suggests that gabapentin may influence sleep architecture, potentially increasing slow-wave sleep and reducing sleep latency. However, the impact on sleep can vary significantly from person to person, and the optimal dosage for sleep-related issues may differ from its use in pain management or epilepsy treatment. Preliminary evidence indicates that gabapentin can attenuate insomnia, bolster sleep quality, and increase total sleep duration. Moreover, gabapentin has been shown to increase slow-wave sleep (SWS), promote sleep maintenance, and decrease unwanted awakenings throughout the night. Yes! researchers say that taking the right gabapentin dosage for sleep and anxiety can improve slow-wave sleep. They suggest that this medication can help you achieve a deeper sleep during the night, thereby increasing your sleep time. Some studies have found that gabapentin may increase slow-wave sleep, also known as deep sleep, which is crucial for physical restoration and cognitive function. Additionally, it may reduce sleep fragmentation, leading to fewer nighttime awakenings and improved sleep continuity. Most studies show that gabapentin improves slow wave sleep (“deep sleep”) and total sleep time. Two small studies showed that gabapentin may help people with primary insomnia and occasional sleep disturbance improve total sleep time and wakefulness in the morning. For individuals struggling with conditions like insomnia, restless sleep, or frequent awakenings, Gabapentin can support more tranquil and restorative rest. Gabapentin improves sleep by calming the brain, reducing nerve overactivity, and inducing drowsiness. I'm a lifetime insomniac who's taken and withdrawn from many sleep meds. I've been taking between 100-300mg gabapentin as needed for sleep for about 4 months now. Take gabapentin one to two hours before bedtime. This timing allows for proper absorption, improving sleep quality. Studies show 250 mg or 400 mg doses taken 30 minutes to two hours before bed can extend sleep duration effectively. Gabapentin works by affecting neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to calm neural activity. 9. Does gabapentin put you in a deep sleep? Gabapentin can enhance slow-wave sleep, which is a deep and restorative phase of sleep, potentially improving sleep quality and decreasing nighttime arousals. 10. How long does it take for gabapentin to kick in after taking it for sleep? Immediate-release gabapentin starts working in two to three hours. When used for insomnia, most doctors will write a prescription for 100-400 mg of Gabapentin. This should be taken once a day right before you’re ready to go to bed. In some cases, your doctor may start you off with a lower dose and adjust as needed. Always be sure to take your prescription as written. It’s best to avoid taking gabapentin with other medications that cause drowsiness, like opioids and benzodiazepines. You toss, you turn. It’s nearly time to wake up, and you feel like you’ve barely slept. But you’re not alone. In fact, 1 in 7 adults regularly struggle to fall asleep. This is very relevant for individuals recovering from alcoholism. Post-acute withdrawal symptoms (PAWS) create disruptive and ongoing insomnia. A study tested gabapentin and trazodone (separately) to assess how well they induced sleep. The sleep quality of both improved greatly over time. But the gabapentin group had stronger improvements faster. While melatonin can help signal to the body that it’s time to sleep, gabapentin’s calming effects on the nervous system may help quiet racing thoughts and reduce anxiety that often delays sleep onset. This dual action can be particularly beneficial for those who struggle with falling asleep due to both physiological and psychological factors.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |