Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 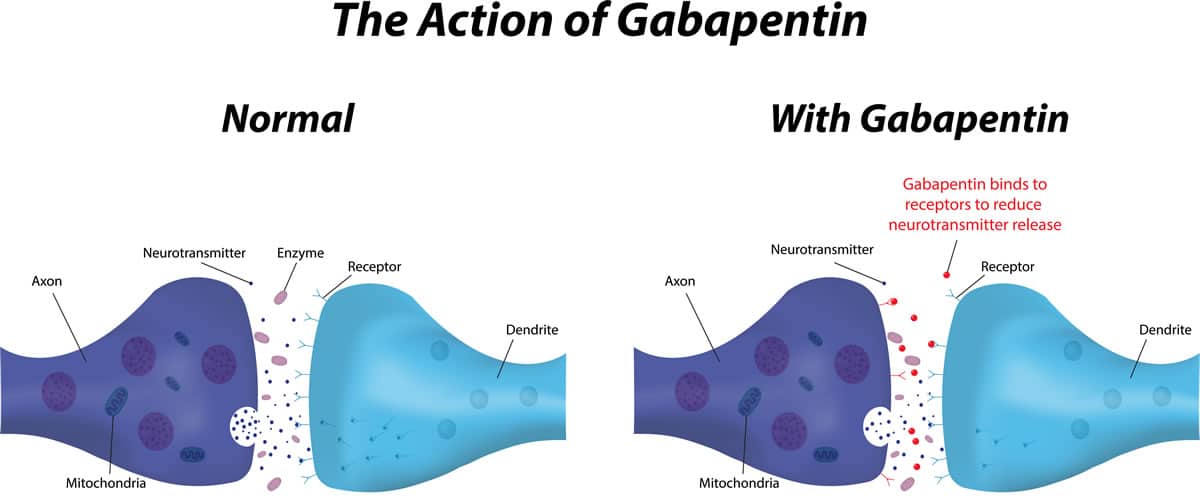 |
Overall, gabapentin was found to reduce the frequency of hot flushes at both 4 and 12 weeks (mean difference: -1.62 [95% CI: -1.98 to -1.26], and -2.77 [95% CI: -4.29 to -1.24], respectively). 28 Among the two crossover studies reported in the meta-analysis, there was no statistically significant difference between the use of gabapentin and Older nonhormonal means of treating hot flashes (eg, a combination of belladonna alkaloids, ergotamine tartrate, and phenobarbital [Bellergal], clonidine, α-methyldopa, and vitamin E) are associated with limited efficacy and/or toxicity. 4 Recently, one of the newer antidepressants, venlafaxine, was proved to be helpful in substantially Hot flashes happen in about 80% of menopausal women and on average, last for more than seven years. Though some women continue to experience them longer than 10 years. Dr. Kling says that treating hot flashes and having another option to help women during these years creates a ripple effect. Lifestyle modifications should be the first-line approach for women with menopausal symptoms. Nonapproved alternative agents include venlafaxine, fluoxetine, paroxetine, gabapentin, soy products, and herbs such as black cohosh. A 2005 study by Pandya et al. randomized 420 women with breast cancer and experiencing at least 2 hot flashes in 24 hours to one of three groups: gabapentin 300 mg daily, gabapentin 900 mg daily, or placebo 23. After 8 weeks, the 300 mg dose group showed a modest 20% reduction in hot flashes, but the 900 mg dose group showed a reduction of The frequency and severity of hot flashes decreased by 75% vs a 30% response with placebo. 30 Clearly not as effective as estrogens for hot flashes, these agents provide substantial relief of symptoms in women in whom estrogens are contraindicated or unacceptable. These agents also relieve the symptoms of mild depression, which may accompany Although pregabalin is not listed by the SOGC as one of the options for treating hot flashes, preliminary data supporting its use for this indication are available. 10,11 This investigational use of pregabalin stems from past evidence that shows the benefit of gabapentin, 12,13 an agent of the same class, for the treatment of hot flashes. Clonidine (Catapres) is an effective option for treating hot flashes. Fluoxetine (Prozac) is an effective option for treating hot flashes, based on limited evidence. Paroxetine (Paxil) is Gabapentin and hot flashes. Gabapentin is commonly used in neurology but rarely in gynecology. As it’s mainly used to prevent seizures, it’s difficult to see how it could help with hot flashes or night sweats. To understand how it could relieve your hot flashes, let’s look at what causes menopause. Bottom Line: Evidence supports the nonhormonal treatment of menopausal hot flashes with paroxetine, clonidine, gabapentin, and soy isoflavone extract. The overall effect size of all nonhormonal The SSRIs or SNRIs, clonidine, and gabapentin trials provide evidence for efficacy; however, effects are less than for estrogen, few trials have been published and most have methodological deficiencies, generalizability is limited, and adverse effects and cost may restrict use for many women. Multiple randomized controlled trials have shown that when compared with placebo, gabapentin is effective at reducing hot flash frequency by 54% and hot flash composite score (combined hot flash frequency and severity score) by 31% to 51%. 28–30 Clonidine is the only non-hormonal drug with a licenced indication for control of hot flushes in the UK. 21 Clonidine 25 mcg is prescribed twice daily for 2 weeks, increased up to a maximum of 50 mcg three times a day. Menopausal hormone therapy is the most effective tool for treating hot flashes and night sweats associated with menopause. It also can help to prevent osteoporosis. "This new medication shouldn't replace hormone therapy," says Dr. Kling. Two fair-quality trials of gabapentin (Neurontin) reported significantly reduced hot flash frequency compared with placebo. One of six trials of red clover isoflavones reported reduced hot Conclusion. Women who suffer from hot flashes but who cannot or will not take hormone therapy can be offered nonhormonal therapies. Nonpharmacological therapies, such as acupuncture, soy, vitamin E, black cohosh, (which have not been proven to be any more efficacious than placebo), or pharmacological therapies, such as SSRI, SNRI, clonidine, or gabapentin, either IR or ER – all have to reduce hot flushes? The non-hormonal medicines used to reduce hot flushes in women include gabapentin, clonidine, venlafaxine or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). The treatment option depends on the individual. Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® available as 100mg, 300mg and 400mg capsules. Also available in generic brand. Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, others). This antiseizure medicine helps ease hot flashes. Side effects can include being drowsy, dizzy or tired and swelling in the arms and legs, called edema. Pregabalin (Lyrica). This is another anti-seizure medicine that can help ease hot flashes. The most effective nonestrogenic agents for treating hot flashes, studied to date, are progesterone analogs. Low doses of megestrol acetate (20-40 mg orally/d) or medroxyprogesterone acetate (400-500 mg intramuscularly as a single dose, that can be repeated months later if effects wear off) decrease hot flashes to a similar degree to what is seen with estrogen. 20,22,31,32 Clinically, these Step-wise approach to management of menopausal hot flashes. M ANAGEMENT. The management of HFs is guided by their frequency and severity. The severity of HFs can be graded as (a) mild (no interference with usual daily activities), (b) moderate (interfere with usual daily activities to some extent), and (c) severe (when usual daily activities cannot be performed).[]
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |