Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 | |
 |
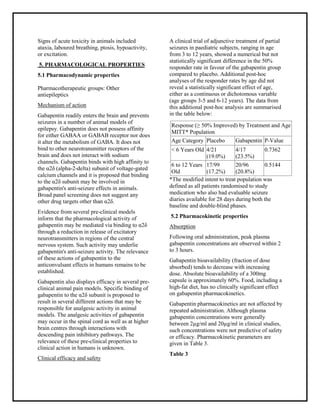
Identify the appropriate indications for gabapentin therapy, including neuropathic pain, partial onset seizures, restless legs syndrome, and other relevant neurological and psychiatric conditions. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems, including increasing your risk of seizures (if you are taking gabapentin to control seizures) or not improving your symptoms (if taking gabapentin for other indications). Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided CONTRAINDICATIONS----- Known hypersensitivity to gabapentin or its ingredients (4) -----WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS----- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (Multiorgan hypersensitivity): discontinue NEURONTIN if an alternative etiology cannot be established (5.1) Neurontin (gabapentin) is used to treat pain you may have from shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It is also used with other seizure medicines for partial onset seizures in patients 3 years and older. Gralise (gabapentin) is only used for pain after having shingles (postherpetic nerve pain). It should not be used for any other medical condition. 4. Contraindications. Gabapentin is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients. Gabapentin is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients and avoid abrupt withdrawal. Reduce dose in renal impairment. Partial seizure: Under 3 years: Safety and efficacy not established. 3-4 years (Maintenance dose): 40 mg/kg/day orally in three divided doses. 5-12 years (Maintenance dose): Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause side effects, including seizures. If you need to stop taking gabapentin, your healthcare provider will give you instructions on how to stop the medicine. This medication contains gabapentin. Do not take Neurontin or Gralise if you are allergic to gabapentin or any ingredients contained in this drug. Keep out of reach of children. In case of overdose, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center immediately. Contraindications. Do not use if you are hypersensitive. Gabapentin can interact with losartan, ethacrynic acid, caffeine, phenytoin, mefloquine, magnesium oxide, cimetidine, naproxen, sevelamer and morphine. Gabapentin use is contraindicated in patients with myasthenia gravis or myoclonus. Acknowledgments Find medical information for gabapentin on epocrates online, including its dosing, contraindications, drug interactions, and pill pictures. Gabapentin can be taken by most adults and children aged 6 and over. Gabapentin is not suitable for some people. To make sure it's safe for you, tell your doctor if you: NHS medicines information on who can take gabapentin and who may not be able to take it. Neurontin (gabapentin) is an anti-eleptic medication used to treat seizures that occur with epilepsy, as well as nerve pain associated with shingles. Learn side effects, dosage, drug interactions, warnings, patient labeling, reviews, and more. Precautions and contraindications for gabapentin and acetaminophen. Before taking gabapentin and acetaminophen, it is important to be aware of certain precautions and contraindications. This will ensure a safe and effective experience with these medications. Pregnancy and breastfeeding Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8 The current work is targeted to review the risks of gabapentin misuse, its potential interactions with other drugs, side effects and use contraindications. This review consists of a total of 99 biographical references (from the year 1983 to 2016). A publication search of PubMed was performed from Ja While gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, it may cause side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and coordination problems. It can also interact with certain medications, so it is important to inform the healthcare provider about all current medications and medical conditions before starting treatment. Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how gabapentin will affect you. Dizziness or drowsiness can cause falls, accidents, or severe injuries. Do not stop using gabapentin suddenly, even if you feel fine. You should not take gabapentin if you are allergic to it. The current work is targeted to review the risks of gabapentin misuse, its potential interactions with other drugs, side effects and use contraindications. This review consists of a total of 99 bio 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
.jpg) |  |
 | |
 |