Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
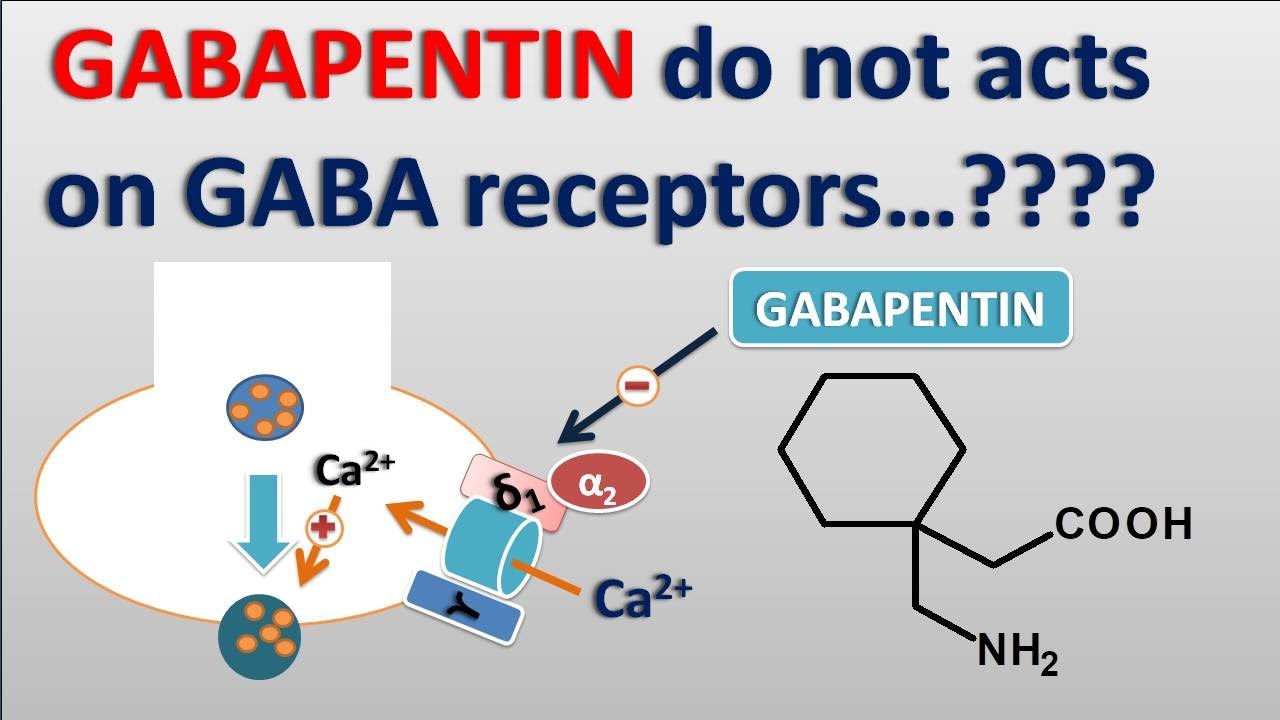
Gabapentin use has been associated with memory loss and cognitive decline. Studies suggest that the risk of dementia may be higher in patients treated with gabapentin. It is important for patients and healthcare providers to be aware of the potential cognitive side effects of gabapentin. Factors like age, overall health, and genetic predispositions can all influence how gabapentin affects cognitive function. Some people might sail through treatment with minimal mental fog, while others find themselves struggling with noticeable changes. Therapeutic Concentration appears to be around 5.9-21 mcg/mL (34.5-123 µmol/L). Toxic Concentration appears to be around > 85 mcg/mL (> 327 µmol/L). Again, it would be pretty rare to have blood levels drawn. Gabapentin is usually started low and titrated up to an effective dose. Below is the most common dosage for neuropathy: While the evidence suggests that gabapentin alone does not cause memory loss, it can lead to brain fog or minor confusion. However, combining gabapentin with other drugs like baclofen can result in significant memory loss and impairment. Neurontin (gabapentin) is associated with memory loss in a dose dependent fashion, meaning the higher doses you take, the more chance there is of having some sort of memory loss, or cognitive impairment. Gabapentin, a medication commonly prescribed for nerve pain and seizures, has been linked to potential cognitive side effects, including memory loss. While its therapeutic benefits are well-documented, some individuals report experiencing forgetfulness or difficulty concentrating during its use. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that helps manage seizures due to epilepsy. It can also treat nerve pain and restless leg syndrome (RLS). Gabapentin appears to work by altering How Gabapentin Affects the Brain Neurochemical Mechanisms. Gabapentin’s primary mechanism of action involves interacting with GABA, a crucial inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. It increases the concentration and potentially the rate of synthesis of GABA, potentially enhancing non-vesicular GABA release during seizures. It is hypothesized that gabapentin increases the concentration of GABA in the brain and reduces the release of several monoamine neurotransmitters . The pharmacokinetics of gabapentin vary widely among patients, but the average time to reaching mean maximum plasma concentration is 2–3 h following a 300 mg dose, with a drug half-life of 5–7 Although GABA concentration changes were small both within day (average 5.6%) and between day (average 4.8%), gabapentin administration was associated with an average increase in GABA concentration of 55.7% (6.9-91.0%). Importantly, drug-induced change in GABA levels was inversely correlated to the individual's baseline GABA level (R²=0.72). Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analog that may also affect glutamate (Glu) production, can normalize GABA and Glu tone during early abstinence from alcohol, effectively treating withdrawal symptoms and facilitating recovery. 4. Gabapentin reduces the release of several monoamine neurotransmitters. 5. Electrophysiology suggests that gabapentin inhibits voltage-activated Na+ channels, but other results contradict these findings. 6. Gabapentin increases serotonin concentrations in human whole blood, which may be relevant to neurobehavioral actions. 7. Although GABA concentration changes were small both within day (average 5.6%) and between day (average 4.8%), gabapentin administration was associated with an average increase in GABA Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication that doctors often prescribe to prevent seizures in people with epilepsy. concentration problems; crying; Gabapentin can also affect specific Gorman et al. showed that gabapentin compounded for topical use with other drugs degraded rapidly in their many active ingredient formulation. 10 Because compounding bases may affect drug stability, we investigated the stability and potency of gabapentin compounded as a single active ingredient formulation with Lipoderm cream, Versabase gel No detrimental effect on attention, concentration or psychomotor speed. Aldenkamp et al. [1997] OL, comparing LTG + CBZ with CBZ only: 25 adults with partial epilepsy: There were no significant differences for measures of motor and mental speed, and short-term memory with add-on LTG. Small changes were in the direction of improvement. Bootsma Does Gabapentin Affect Memory? Like Lyrica, gabapentin can cause cognitive side effects, including memory issues. Patients may experience difficulties in concentration, attention, and short-term memory recall. However, the severity and frequency of these side effects can differ between individuals. Mechanistic Comparisons Although designed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, gabapentin does not bind to GABA receptors, nor does it affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA. In fact, the precise mechanism by which it exerts its analgesic and anticonvulsant effects is unknown. Today, gabapentinoids such as Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) are widely used as painkillers. This may alter the function of the nervous system; hence their results may include a difference in memory and processes that end in memory formation.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |