Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) | |
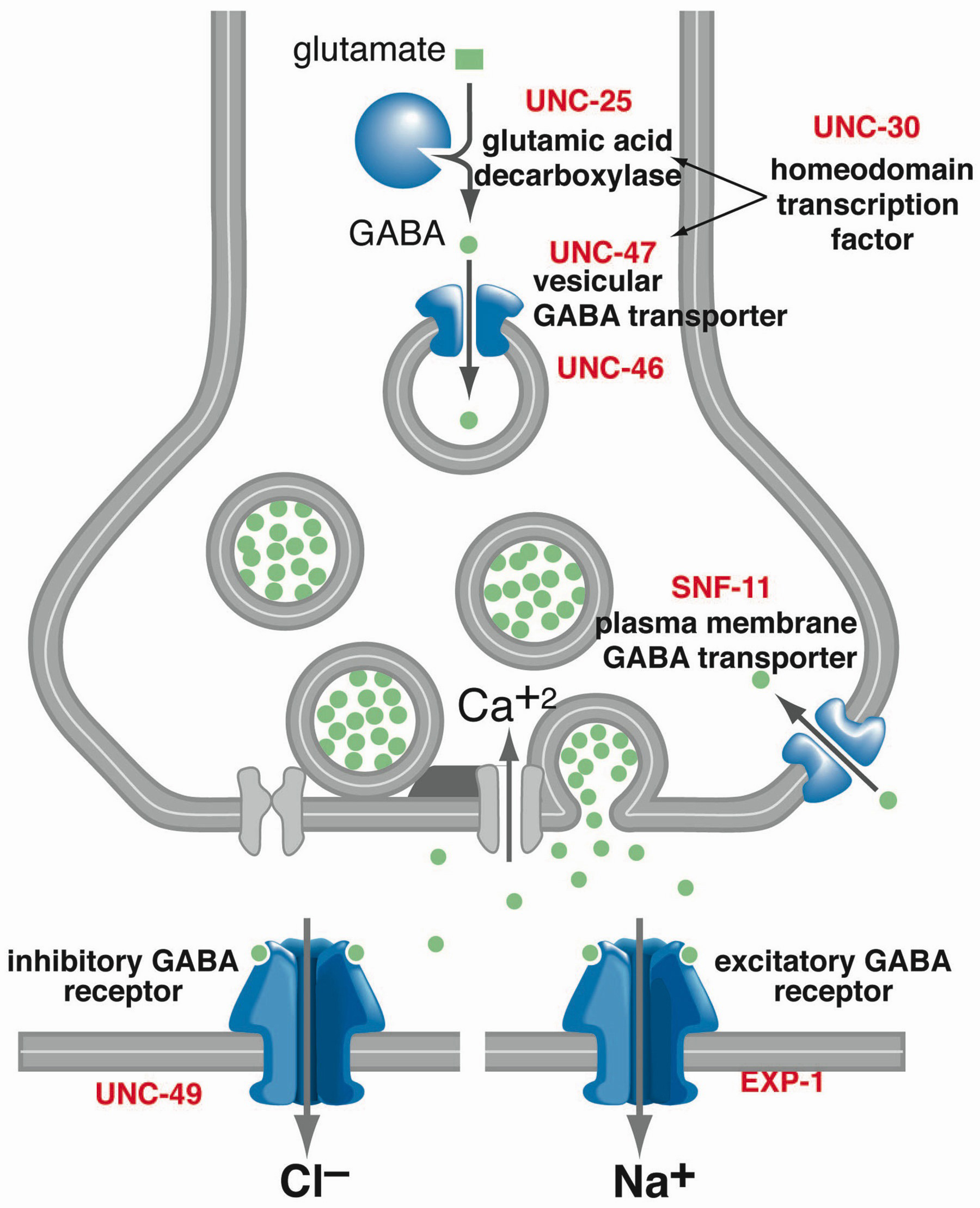 |  |
Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. acid (GABA), gabapentin does not appear to bind to GABA-A or GABA-B receptors or to high affinity GABA transporters (Taylor et al., 1998; Jensen et al., 2002). While still incompletely understood, gabapentin’s anticonvulsive and analgesic mecha-nisms of action are thought to involve the inhibition of Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Originally designed as analogs of GABA (Fig. 1), neither gabapentin nor pregabalin has any significant agonist‐like effect on GABA A or GABA B receptors, nor obvious effects on levels of GABA (Lanneau et al. 2001; Jensen et al. 2002). Although it is rapidly absorbed, readily crosses the blood–brain barrier and is orally active in several animal models of epilepsy, gabapentin neither binds to GABA A or GABA B receptors nor is it metabolized to GABA (Goa and Sorkin, 1993; Kammerer et al, 2011; Taylor et al, 1992). It is concluded that gabapentin is not an agonist at GABA (B) receptors that are functional in baclofen-induced antiallodynia in the postoperative pain model in vivo and in GIRK channel It is concluded that gabapentin is not an agonist at GABA B receptors that are functional in baclofeninduced antiallodynia in the postoperative pain model in vivo and in GIRK channel activation in ventrolateral PAG neurons in vitro. In the present study, we examined whether gabapentin is an agonist at native GABA(B) receptors using a rat model of postoperative pain in vivo and periaqueductal gray (PAG) slices in vitro; PAG contains GABA(B) receptors, and their activation results in antinociception. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Applies to gabapentin: oral capsule, oral solution, oral suspension, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release 24 hr. Serious side effects of gabapentin. Along with its needed effects, gabapentin may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Additionally, while GABA from food sources is generally considered safe, its effectiveness in exerting physiological effects in the body may be influenced by various factors, including its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Incorporating a variety of GABA-rich foods into a balanced diet can contribute to overall GABA intake. This inhibitory effect is rapid and short-lived. GABA-B receptors, on the other hand, are metabotropic. They work through second messenger systems to produce slower, longer-lasting inhibitory effects. Activation of GABA-B receptors can lead to the opening of potassium channels, which also results in hyperpolarization of the neuron. Here we report that gabapentin was completely inactive at recombinant GABA (B) heterodimers expressing either GABA (B1a) or GABA (B1b) receptor subunits in combination with GABA (B2) receptor subunits. We conducted a gabapentin (900 mg) challenge in healthy human subjects to confirm and explore its effects on GABA and glutamate concentrations, respectively, and to test the ability of single Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. We conducted a gabapentin (900mg) challenge in healthy human subjects to confirm and explore its effects on GABA and glutamate concentrations Research about the effects of gabapentin on gamma -aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter levels has reported inconsistent results, i.e., increase in GABA levels based on human studies, 10 but no effects have been reported in in vitro studies. 11 Moreover, gabapentin affects GABA (A), but not GABA (B) receptor responses, based on in vitro stu GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is a second-generation antiepileptic drug widely used for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is also used to treat anxiety, insomnia, bipolar disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Although first introduced as an adjunct therapy for epilepsy, gabapentin became a blockbuster drug for the management of chronic pain from many nerve conditions [8]. Side effects are usually
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) | |
 |  |