Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
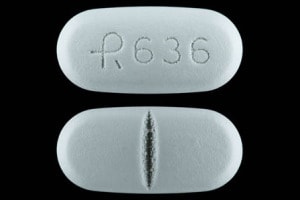
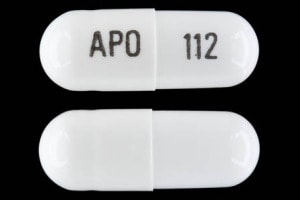
However, individuals with renal impairment experience higher plasma concentrations of gabapentin, as well as an increased elimination half-life. For example, one report documented that among 11 individuals with renal failure, just one 400 mg oral gabapentin dose had a half-life of 132 hours (on average). Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. In elderly patients, and in patients with impaired renal function, gabapentin plasma clearance is reduced. Bioavailability is not proportional to dose (i.e. bioavailability of gabapentin ≅ 60% (900mg), 47% (1200mg), 34% (2400mg), 33% (2600mg), and 27% (4800mg) per day, given in 3 divided doses. In animal models of analgesia, gabapentin prevents allodynia and hyperalgesia. Gabapentin is a drug that modulates the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and is used for various indications. Its half-life is 5 to 7 hours and it is excreted unchanged in urine. Gabapentin Half-Life. Gabapentin comes in immediate-release and extended-release formulations as a tablet. The half-life of gabapentin is between 5 and 7 hours, which is how long it takes for the drug’s concentration in the body to be reduced by half.[3] The liver is responsible for metabolizing most drugs, but gabapentin works differently. Gabapentin (Neurontin) has a short half-life of 5 to 7 hours and a duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. It should be taken consistently three to four times daily for optimal effect. Learn more about gabapentin dosing, side effects and alternatives. Use this tool to estimate how much gabapentin is left in your body after a certain time and how to adjust your doses. Learn about gabapentin half life, factors that affect it, and how to avoid interactions and side effects. Gabapentin is a prescription drug for seizures and nerve pain, but it can also be abused and cause severe withdrawal. Learn about the half-life of gabapentin, how it affects the body, and what to do if you need to stop using it. Gabapentin Half Life. The gabapentin half life is a controlling factor in determining how long the drug remains active in the body. The half life of a drug refers to the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the bloodstream to decrease by 50%. What is the half-life of gabapentin? Adult Patients. In adult patients, the half-life of gabapentin is about 5 to 7 hours. In other words, it takes the body about 5 to 7 hours to eliminate its gabapentin concentration by half. This estimate can be altered by many factors including but not limited to kidney function. Pediatric Patients The half-life of gabapentin in people with kidney failure can be up to 132 hours, meaning it can stay in the body for 28 days without dialysis. How Is Gabapentin Metabolized? When a dose of gabapentin is taken, it is absorbed in the small intestine and then enters the bloodstream. In addition, gabapentin does not undergo hepatic metabolism, unlike most other antiepileptic drugs, and is eliminated almost entirely by renal excretion with a clearance that approximates the glomerular filtration rate. The elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours in patients with normal kidney function. Half-life. The elimination t 1/2 of gabapentin in patients with normal renal function is 5-7 hours. 16,17,5 In patients with reduced renal function, the elimination t 1/2 may be prolonged - in patients with a creatinine clearance of 30 mL/min, the reported half-life of gabapentin was approximately 52 hours. 16,17. Clearance Gabapentin enacarbil (brand name Horizant) is a prodrug of gabapentin that has been designed to overcome the limitations of gabapentin, such as poor absorption and a short duration of action. It requires hydrolyzation in the gastrointestinal tract to become active. Gabapentin belongs to the group of medicines known as anticonvulsants. 2. Upsides In a study in anuric adult subjects (N=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about 132 hours; during dialysis the apparent half-life of gabapentin was reduced to 3.8 hours. Hemodialysis thus has a significant effect on gabapentin elimination in anuric subjects. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly proportional to creatinine clearance. In elderly patients, and in patients with impaired renal function, gabapentin plasma clearance is reduced. The elimination half-life of gabapentin is 5 to 7 hours, and it takes 2 days for the body to eliminate gabapentin from its system. The elimination rate constant, as well as plasma and renal clearance, correlate directly with creatinine clearance. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug that is structurally related to GABA. It has different formulations and dosages for various indications, such as seizure disorders, neuropathic pain, and restless legs syndrome. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication with a half-life of 5 to 7 hours. It is used to treat neuropathic pain, partial seizures, and other conditions, but it has side effects and potential for misuse. Learn how long gabapentin stays in your system, how it is excreted, and how it affects your body. Find out the factors that can alter gabapentin half-life, such as kidney function, dosage, and age.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |