Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 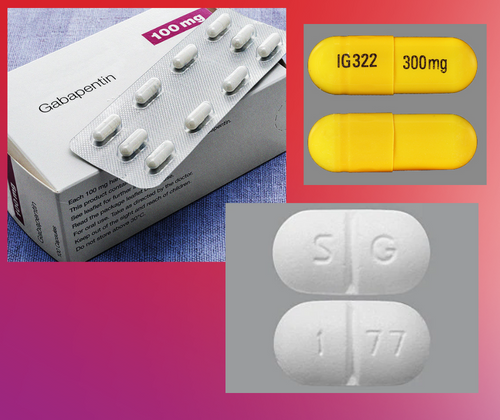 |
Gabapentinoids are opioid substitutes whose elimination by the kidneys is reduced as kidney function declines. To inform their safe prescribing in older adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD), we examined the 30-day risk of serious adverse events according to the prescribed starting dose. Unlike other drugs, gabapentin is not metabolized in the liver and is solely excreted by the kidneys. Therefore, it is crucial to adjust the dosage in patients with renal insufficiency to avoid severe adverse effects. Kidney disease can affect your sexuality in many ways — from hormones, nerves, energy levels, even medicine. Image. NKF Cares. Offering support for people affected The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Gabapentin (Neurontin) usually isn’t bad for your liver or kidneys. In most cases, it has little effect on these organs. In rare instances, gabapentin can cause DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms) syndrome. Does gabapentin have any cardiac side effects I should be aware of with kidney disease? Some studies suggest a potential link between short-term gabapentin use and increased risks of cardiac issues like heart failure, which is more concerning for patients with kidney disease and may further compromise their health. BACKGROUND: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Background: Gabapentinoids (GPs) are frequently prescribed in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD); however, their exclusive renal elimination warrants dose adjustments to decrease risk of toxicity. This study evaluated GP prescribing patterns and whether excessive dosing was associated with increased incidence of gabapentinoid-related How they can affect the kidneys: If taken as directed, most laxatives are safe for those without kidney problems. For those with kidney disease, it’s important to keep well hydrated by drinking lots of water and clear liquids. Dehydration can cause damage to the kidneys by decreasing blood flow to them. However, in stage 3 kidney disease, where kidney function is moderately reduced (typically with an eGFR between 30 and 59 ml/min/1.73 m²), the kidneys’ ability to clear gabapentin is diminished. Potential Risks of Gabapentin Buildup Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily. This case report outlines a significant type of morbidity due to continued use of gabapentin during an episode of acute renal failure. Setting. University teaching hospital. Discussion. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. For patients on dialysis, the recommended dose is 100-300mg post dialysis on dialysis days only. But for people with kidney disease, aspirin can increase the risk of bleeding. And in those with reduced kidney function, aspirin is not recommended unless prescribed by a physician. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |