Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
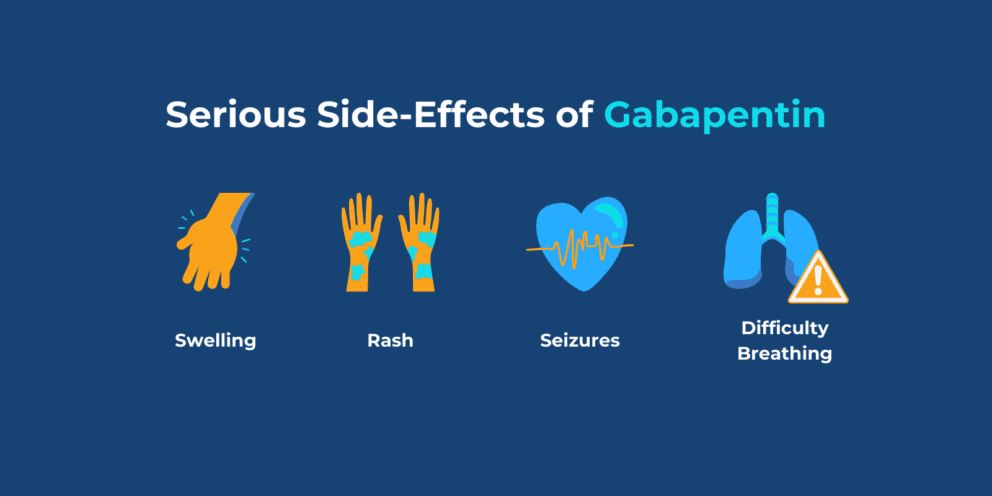 |  |
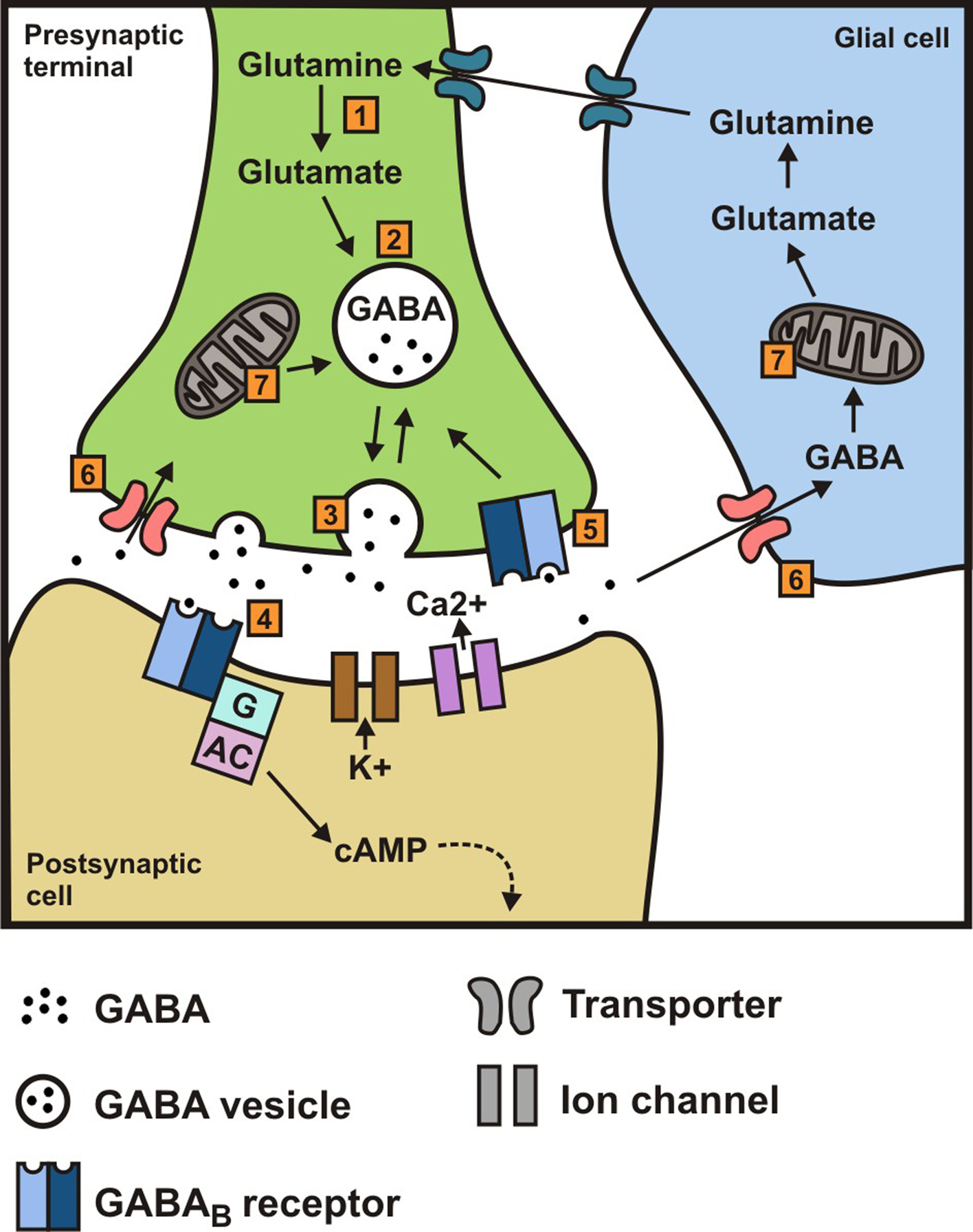
In the present study, we examined whether gabapentin is an agonist at native GABA(B) receptors using a rat model of postoperative pain in vivo and periaqueductal gray (PAG) slices in vitro; PAG contains GABA(B) receptors, and their activation results in antinociception. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Additionally, while GABA from food sources is generally considered safe, its effectiveness in exerting physiological effects in the body may be influenced by various factors, including its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Incorporating a variety of GABA-rich foods into a balanced diet can contribute to overall GABA intake. On the other hand, gabapentin was created to mimic some of the effects of GABA but it does not appear to affect the same receptors in the brain. Another function of GABA is its responsibility for regulating the body’s muscle tone since it is linked to the pituitary glands which affect human growth hormone (HGH) levels. However, in other studies [7,12,13], gabapentin increases GABA levels in both rodents and humans, either by increasing GABA synthesis via the activation of GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase or by decreasing GABA metabolism via the inhibition of GABA transaminase. We reported that daily dosing increased brain gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in patients with epilepsy. This study was designed to determine how rapidly brain GABA and the GABA metabolites, homocarnosine and pyrrolidinone, increase in response to the first dose of GBP. Gabapentin (GBP), a GABA analog that may also affect glutamate (Glu) production, can normalize GABA and Glu tone during early abstinence from alcohol, effectively treating withdrawal symptoms and facilitating recovery. Using in vivo magnetic The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. We conducted a gabapentin (900 mg) challenge in healthy human subjects to confirm and explore its effects on GABA and glutamate concentrations, respectively, and to test the ability of single Contrary to its name, gabapentin does not directly interact with GABA receptors or influence GABA levels in the brain. Instead, its primary mode of action involves modulating voltage-gated calcium channels. Calcium channel modulation is at the heart of gabapentin’s therapeutic effects. Research about the effects of gabapentin on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter levels has reported inconsistent results, i.e., increase in GABA levels based on human studies, 10 but no effects have been reported in in vitro studies. 11 Moreover, gabapentin affects GABA(A), but not GABA(B) receptor responses, based on in vitro Applies to gabapentin: oral capsule, oral solution, oral suspension, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release 24 hr. Serious side effects of gabapentin. Along with its needed effects, gabapentin may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. GABA is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter in the brain that inhibits or slows down nerve activity, helping to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation. On the other hand, Gabapentin is a medication that is structurally similar to GABA but does not directly bind to GABA receptors. The chemical structure of gabapentin (Neurontin) is derived by addition of a cyclohexyl group to the backbone of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentin prevents seizures in a wide variety of models in animals, including generalized tonic-clonic and partial seizures. Gabapentin has no activity at Although gabapentin does not directly modify GABA-A receptor function, it may indirectly increase tonic inhibition via enhanced expression of extrasynaptic receptors in specific brain regions including the cerebellum and hippocampus. Gabapentin Side Effects in Cats. The most common side effects seen in cats with gabapentin are lethargy and abnormal walking/movement, which is called ataxia. It is important to note that some of these effects may be expected or even desired when gabapentin is used intentionally as a sedative. Effects typically start to wear off within 12 hours. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_Illustration_What-to-Know-About-Gaba_Illustrator_Jessica-Olah_Final-ea5963205783442fa62455edbc5851ef.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |