Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
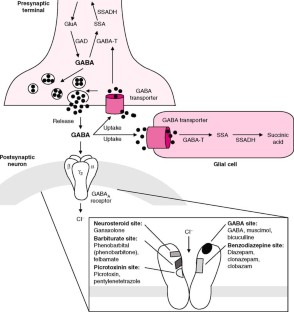
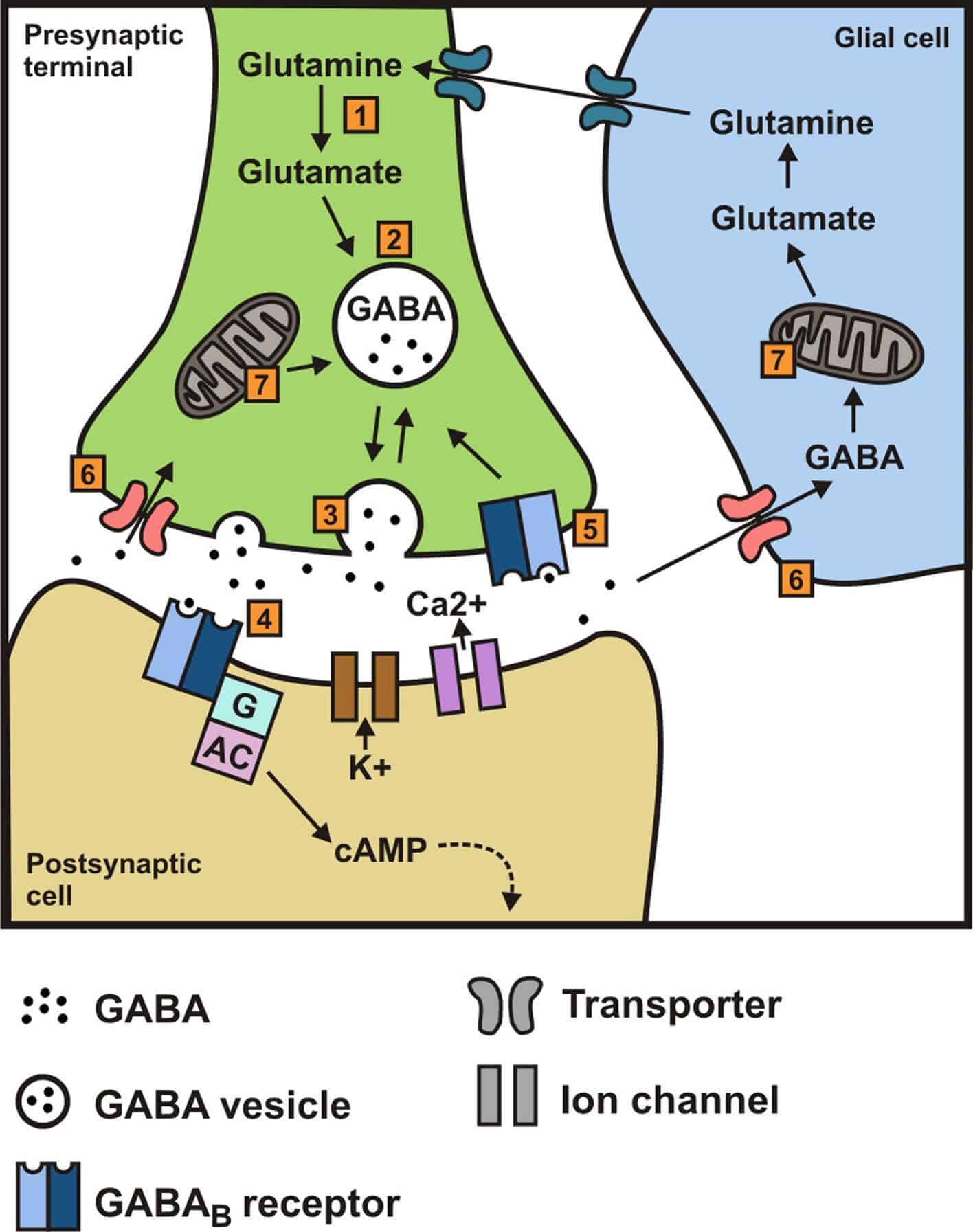
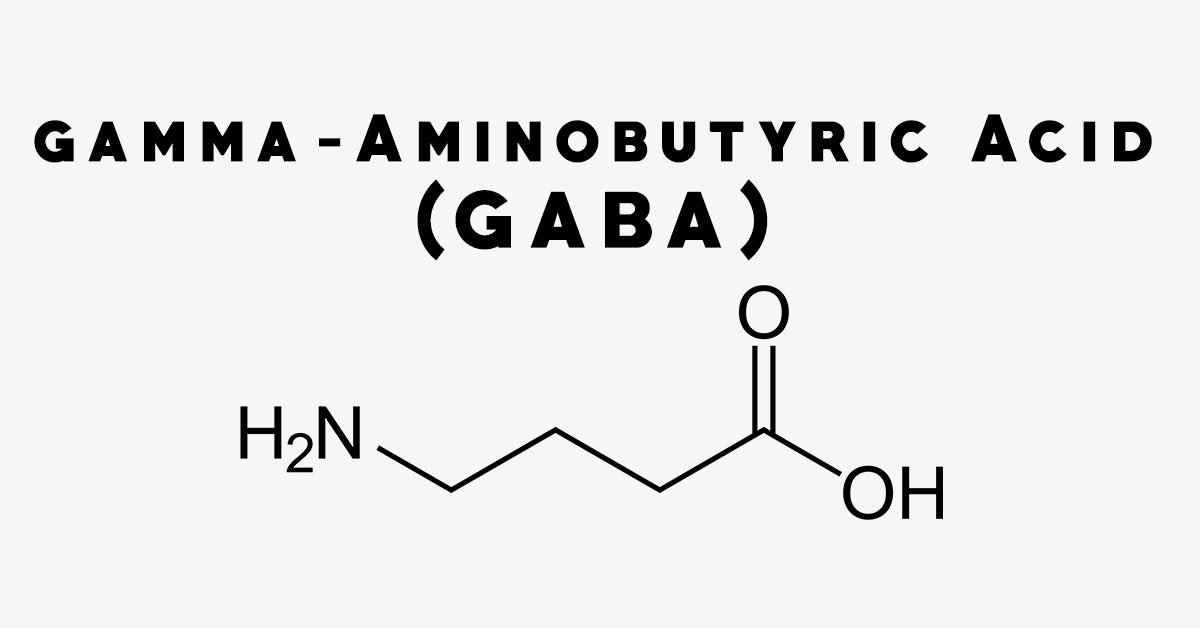
Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects We reported that daily dosing increased brain gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in patients with epilepsy. This study was designed to determine how rapidly brain GABA and the GABA metabolites, homocarnosine and pyrrolidinone, increase in response to the first dose of GBP. GABA was elevated in patients taking gabapentin compared with 14 complex partial epilepsy patients, matched for antiepileptic drug treatment. Brain GABA levels appeared to be higher in patients taking high-dose gabapentin (3,300-3,600 mg/day) than in those taking standard doses (1,200-2,400 mg/day). 5-HTP: Your body converts 5-HTP into serotonin, and serotonin can enhance GABA activity. 5-HTP is a synthetic form of tryptophan, which is found in turkey. However, tryptophan from food-based sources (like turkey, soybeans, and milk) is not thought to cross the BBB the way 5-HTP does. The results showed that gabapentin failed to modify the levels of GABA, taurine and alanine (Fig. 5b), suggesting that gabapentin does not increase agonist concentrations after chronic treatment. Fig. 5 Levels of GABA A receptor agonists are not increased by gabapentin. GABA rose 48% at 6 hours with gabapentin but not with lamotrigine. With long-term dosing and once target doses were achieved at 4 weeks, significant elevations in GABA were observed compared with baseline for all three drugs (topiramate 46%, gabapentin 25%, lamotrigine 25%). Common brand names for gabapentin include Gralise, Horizant, Neuraptine, and Neurontin. This drug works by stimulating the release of neurotransmitters in the brain, specifically GABA and serotonin. Usually, drugs that affect serotonin levels come with the risk of producing serotonin syndrome. But can gabapentin cause serotonin syndrome? However, in other studies [7,12,13], gabapentin increases GABA levels in both rodents and humans, either by increasing GABA synthesis via the activation of GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase or by decreasing GABA metabolism via the inhibition of GABA transaminase. While gabapentin was designed as a GABA analogue, its GABA-like properties are not as straightforward as initially believed. The drug does not directly bind to GABA receptors or increase GABA levels in the brain. However, it may indirectly enhance GABAergic neurotransmission through its effects on calcium channels and other neuronal processes. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Does Gabapentin Increase GABA Levels? Gabapentin is a medication that has been widely studied for its potential to increase GABA levels in the brain. GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, is a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in regulating neuronal excitability and promoting relaxation. Background: Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin increases the concentration and probably the rate of synthesis of GABA in brain, which may enhance non-vesicular GABA release during seizures. 3. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to a novel binding site in brain tissues that is associated with an auxiliary subunit of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Gabapentin has been shown to increase GABA levels in the brain, as evidenced by magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in both humans and animals. This increase in GABA concentration is thought to enhance inhibitory neurotransmission, contributing to gabapentin's anticonvulsant and anxiolytic effects. Certain types of tea, particularly varieties of tea made from Camellia sinensis leaves (such as green tea), have been reported to contain GABA. GABA tea is often processed in a way that enhances GABA levels. Sprouted Grains. Sprouting grains, seeds, and legumes may increase GABA content. Treatment of mice with gabapentin resulted in an increase in surface, but not total, expression in cerebellum and hippocampus. There was no change in expression of α1- or α5-subunits. Treatment of mice with gabapentin did not increase GABA, taurine, or alanine levels, or neurosteroids in the brain. Glutamine is the precursor of GABA. A dose of 2000 mg or more of glutamine a day when taken on an empty stomach with vitamin B6 (2mg or more), will increase your natural level of GABA and probably reduce your pain levels. Pure GABA is available as a tablet, capsule or in sublingual (under-the tongue) form in most health food stores or online.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |