Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
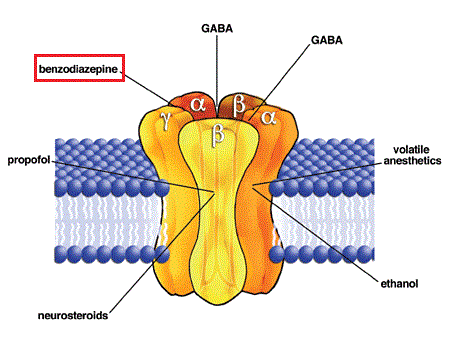
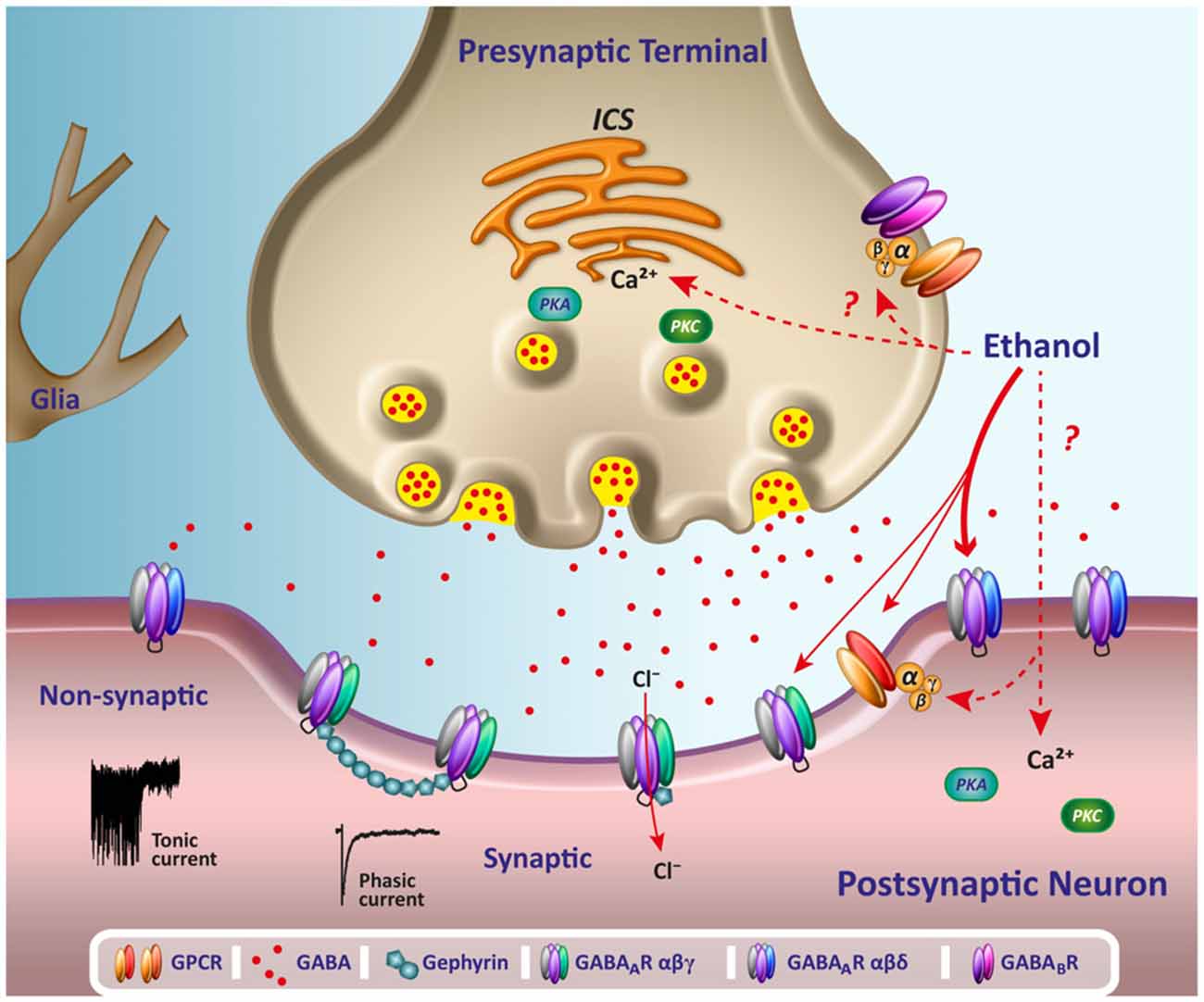
The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells, new research in mice suggests.The experiments mimicked ischemic stroke in humans, which occurs when a clot blocks bloo National Center for Biotechnology Information By altering the flow of calcium in our brain cells, gabapentin might be inadvertently tinkering with the very processes that govern our thinking and memory. It’s a delicate balance, and one that researchers are still trying to fully understand. Chronic administration of gabapentin and carbamazepine may cause increase in neurodegenerative changes in the adult brain. Keywords: Epilepsy, Antiepileptic drugs, Histology, Brain, Rats. Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by intermittent unprovoked seizures. It affects about 65 million people globally. In vitro, pretreatment of PC12 cells with 450 µM GBP significantly reduced cell death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation, increased antioxidant function, and reduced the levels of autophagy and reactive oxygen species via activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. This neuroprotection by GBP was inhibited significantly by 10 µM LY294002. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Many brain regions, such as the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), ventral tegmental area (VTA), and other brain areas, are involved in pain experience, which have important roles in encoding affects and salience. 1, 2 Also, negative emotional experiences, such as depression and anxiety, lead to pain sensation without tissue damage. Neuropathic A2δ is expressed in Purkinje cells, which use gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) as a neurotransmitter. The author states that gabapentinoids inhibit the α2δ subunit and reduce neurotransmitter release, resulting in the induction of cerebellar ataxia. 1,2 Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Does Weed Kill Brain Cells. Ask your friends and loved ones for support. Does Weed Kill Brain Cells. If you’re feeling anxious or depressed, consider joining a support group or seeking counseling. Believe in your ability to take control of the pain Hope you find this article on does week kill brain cells helpful enough to give motivation. Is Gabapentin Bad for the Brain? A Comprehensive Look. The question of whether gabapentin is harmful to the brain is complex, with no simple yes or no answer. While gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication for various conditions, including epilepsy, nerve pain, and restless legs syndrome, mounting evidence suggests it can have significant effects on the brain, both in the short and long term. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning that brain cells release it to slow down the function of other brain cells. Taking too much gabapentin can enhance this slow-down effect, making the drug’s side effects more pronounced. Side Effects of Taking Too Much Gabapentin Gabapentin initiation was significantly associated with cognitive/functional status decline: worsening CDRGLOB at index+1 visit (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.55 [1.07, 2.25]); CDR-SB at index+1 visit (1.94 [1.22, 3.09]); and mean of FAQ at index+2 visit (1.78 [1.12, 2.83]). Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on Gabapentin (GBP), an analgesic, adjunct antiepileptic, and migraine prophylactic drug, reduces neuronal injury induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion (IR). However, the underlying biological molecular mechanism of GBP neuroprotection is not clear. Now, the researchers knew that the tumors were taking advantage of the brain’s networks. So, they turned to gabapentin, which controls seizures by tamping down excess electrical activity in the brain, testing it in mice engrafted with human glioblastoma cells. “Gabapentin actually kept the tumor from expanding,” said Krishna. Intra-LC injection of gabapentin increased withdrawal threshold in the hind paw ipsilateral to SNL in a dose-dependent manner (fig. 6A). Gabapentin showed significant antihypersensitivity effects from 0.3 to 3 μg compared with vehicle (P < 0.05). The peak effect of gabapentin was observed 15 min after injection. Neuroinflammation plays an important role in brain tissue injury during intracerebral hemorrhage. Gabapentin can reduce inflammation and oxidative stress through inhibiting nuclear factor κB (NFκB) signals. Here, we showed that gabapentin reduced brain tissue injury in ICH through suppressing NFκB-m Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. GBP promptly elevates brain GABA and presumably offers partial protection against further seizures within hours of the first oral dose. Patients may expect to experience the anticonvulsant effects of increased homocarnosine and pyrrolidinone with daily therapy.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |