Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
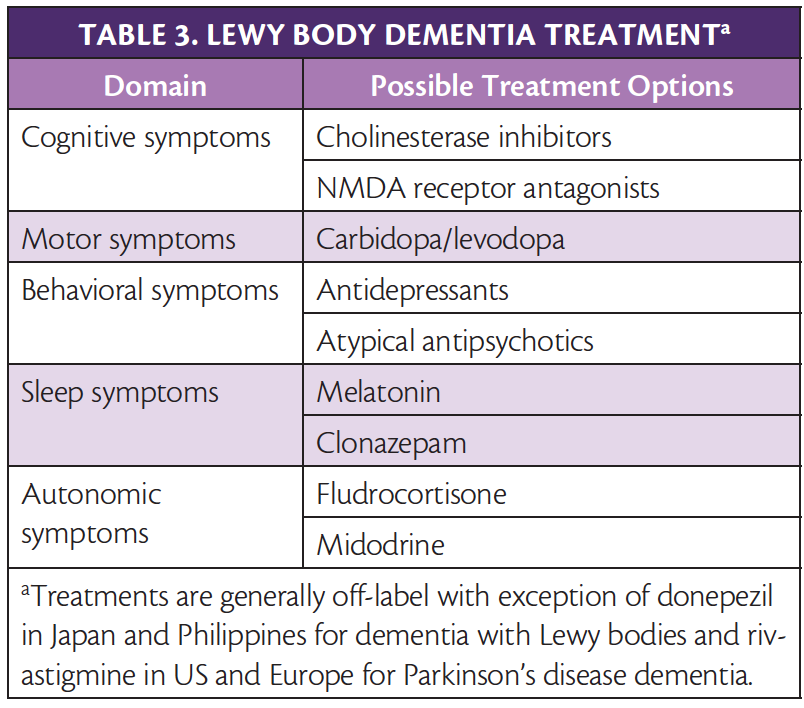
Management of the patient with dementia; Patient education: Caring for someone with Alzheimer disease or dementia (The Basics) Patient education: Dementia (including Alzheimer disease) (The Basics) Prognosis and treatment of dementia with Lewy bodies; Schizophrenia in adults: Guidelines for prescribing clozapine Descriptive summaries provide some evidence of benefits for galantamine, modafinil, levodopa, rotigotine, clozapine, duloxetine, clonazepam, ramelteon, gabapentin, zonisamide, and yokukansan. Piracetam, amantadine, selegiline, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone, and citalopram do not appear to be effective. Aim: To evaluate low dose gabapentin in treatment of disruptive behavioral symptoms in patients with moderate- severe dementia with Lewy bodies. Findings: Improvement in symptoms seen by clinician and caregivers supported by changes on respective scales. Dementia with Lewy bodies is an under-recognized disease; it is responsible for up to 20 % of all dementia cases. Accurate diagnosis is essential because the management of dementia with Lewy bodies is more complex than many neurodegenerative Lewy body dementia is a common cause of degenerative dementia in older people, accounting for some 3%–15% of cases (1, 2). It is characterized by impairments and fluctuations in cognition, recurrent visual hallucinations, and motor features of parkinsonism. We present the case of a patient with incipient vascular dementia accompanied by nocturnal agitation, which was successfully treated with gabapentin. Gabapentin appears to be useful and well-tolerated in this indication. Lewy body dementia (LBD) is the second most common neurodegenerative dementia, and it causes earlier mortality and more morbidity than Alzheimer’s disease. Reviewing current evidence on its pharmacological management is essential for developing evidence-based clinical guidelines, and for improving the quality of its clinical care. Cholinesterase inhibitors are important drugs for managing patients in all stages of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), since they improve global cognitive function and reduce visual hallucinations and other behavioral symptoms. Sakakibara R, et al. Lower urinary tract function in dementia of Lewy body type. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76(5):729–32. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2004.046243. [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 95. McKeith IG, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. In most of the reviewed cases, gabapentin was reported to be a well tolerated and effective treatment for BPSD. However, two case reports in which gabapentin was used in the context of agitation in dementia with Lewy bodies questioned the appropriateness of gabapentin for all types of dementia-related agitation. Dementia syndromes associated with Lewy body pathology are subdivided into dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson disease with dementia (PDD), arbitrarily based on the timing of cognitive decline in relation to motor symptoms. DLB is an underdiagnosed cause of dementia in the elderly. Lewy body dementia is a common cause of degenerative dementia in older people, accounting for some 3%–15% of cases (1, 2). It is characterized by impairments and fluc-tuations in cognition, recurrent visual hallucinations, and motor features of parkinsonism. Gabapentin-induced worsening of neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia with lewy bodies: case reports Clinical trials and meta-analyses now provide an evidence base for the treatment of cognitive, neuropsychiatric, and motor symptoms in patients with Lewy body dementia. discrepant findings. The first patient with Alzheimer’s Dementia was followed for months while the second patient with mixed dementia patient was only followed for three weeks. Next, it is unclear whether gabapentin is equally efficacious in Alzheimer’s dementia versus concomitant Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia. Dementia is an umbrella term that describes impaired memory loss and changes to cognition in various medical conditions. While it’s commonly associated with older people, dementia isn’t a part We describe a case where gabapentin was used to treat a patient with mixed Alzheimer's/vascular dementia presenting with severe aggression requiring hospitalization. The case is followed by a systematic review of current literature of the use of these drugs in aggression in patients with dementia. Caution should be noted about the use of gabapentin in Lewy-body dementia, where dramatic worsening of neuropsychiatric symptoms has been reported after its use to treat behavioral symptoms. 23 A review of the literature yielded no reports of an increased risk of cerebrovascular events in patients with vascular dementia treated with gabapentin. Lewy body dementia (LBD) is situated at the convergence of neurodegenerative disorders, posing an intricate and diverse clinical dilemma. The accumulation of abnormal protein in the brain, namely, the Lewy body causes disturbances in typical neural
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |