Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-DanieDrankwalter-BloodPressureandHeartRate-Standard-0c89f7683df843e893aa83c64fc017a8.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
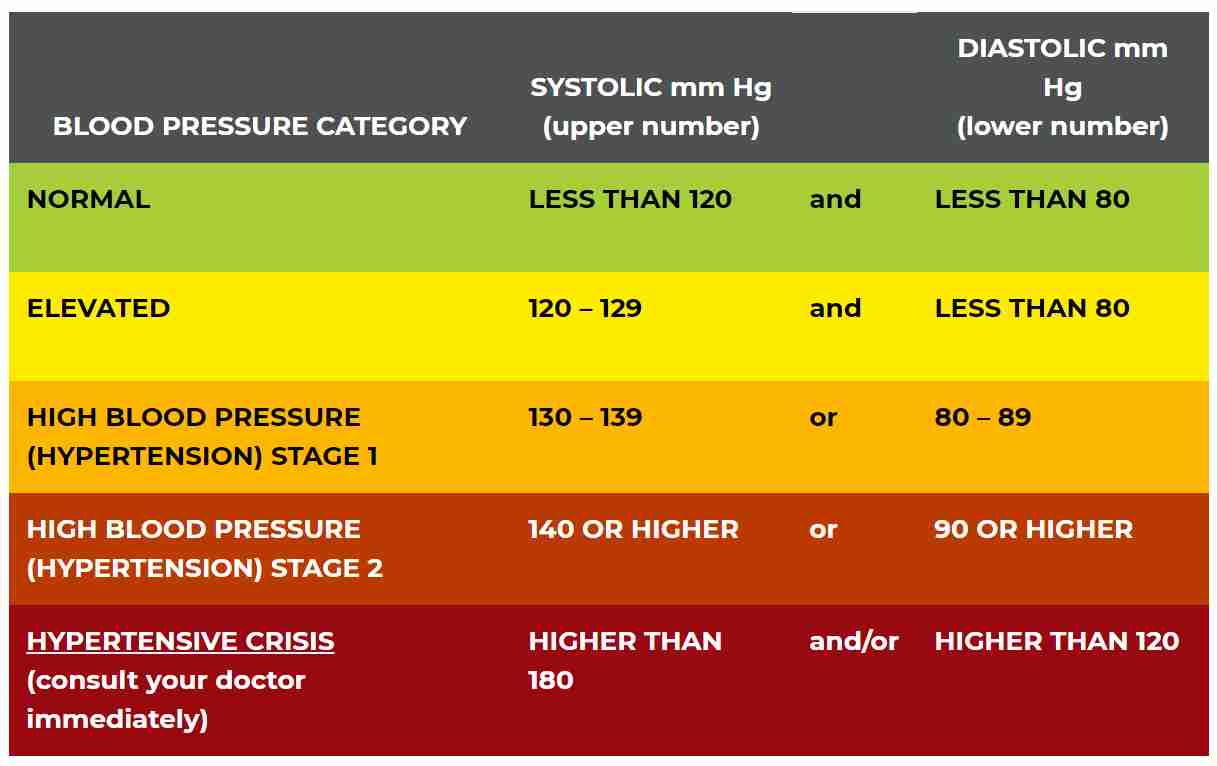 |  |
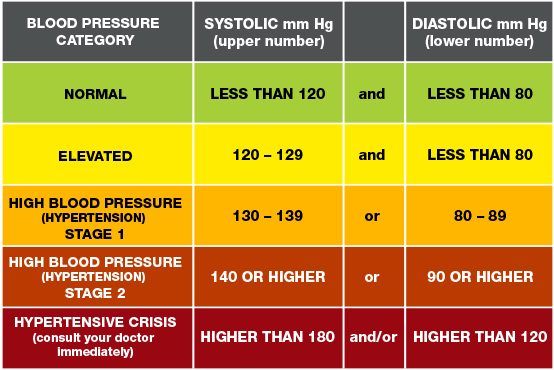
3. Does gabapentin raise blood pressure? While studies suggest that gabapentin can lower blood pressure and heart rate acutely, it is also listed as a potential side effect to cause hypertension, or high blood pressure, particularly with long term use. 4. Can gabapentin cause heart palpitations? Upon arrival to the emergency department, the patient was responsive to pain only and had a blood pressure of 68/40 mmHg and a heart rate of 82 beats per minute. Dopamine 10 mg/kg/min was required to maintain adequate blood pressure. The serum gabapentin concentration was 105 mcg/mL (therapeutic range, 4–8.5 mcg/mL). Does gabapentin lower blood pressure? Research on rats has shown that gabapentin may lower blood pressure in those with high blood pressure ( hypertension ). Does gabapentin cause Gabapentin can affect your heart rate in a few different ways. In a double-blind, observational study, patients undergoing elective surgery were administered different doses of gabapentin. The study found that 400mg of gabapentin resulted in a higher heart rate and blood pressure, whereas 800mg of gabapentin resulted in a lowered heart rate. Gabapentin can help control seizures as well as nerve pain from shingles. a medication used to treat high blood pressure ; ethacrynic acid Its overdose death risk is lower than that of If gabapentin is determined to be the cause, your prescriber may recommend a lower gabapentin dose or that you stop taking the medication altogether. If this isn’t possible, they may recommend that you take medication to decrease edema, like a diuretic. 5. Blurred vision and other eye problems In addition, animal studies have shown that gabapentin can reduce blood pressure, heart rate, vascular function, and left ventricular systolic/diastolic function [31–34], potentially leading to adverse cardiovascular events [35–37]. We observed that unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS whether to change dose-related BP and HR. Then, unilateral microinjection of gabapentin into the NTS before and after N(ω)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment whether to change blood pressure and heart rate. The question of whether gabapentin is bad for blood pressure is complex, with the answer not being a simple yes or no. While research indicates that gabapentin can actually reduce blood pressure and heart rate in some cases, there are also potential risks related to blood pressure, especially with long-term use and withdrawal. The key lies in Gabapentin’s Impact on the Heart. Gabapentin is believed to influence the heart through its actions on the nucleus tractus solitarii in the brain, which helps regulate blood pressure and heart rate. Research indicates that gabapentin can lower both blood pressure and heart rate in some individuals. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Memis D and colleague 19 found that patients receiving 800 mg of gabapentin 1 h before surgery had significantly decreased mean arterial pressure and heart rate during the first 10 min after endotracheal intubation compared with either 400 mg gabapentin or placebo (p<0.05). In addition, animal studies have shown that gabapentin can reduce blood pressure, heart rate, vascular function, and left ventricular systolic/diastolic function [31] [32][33][34], potentially The decreased systolic pressure (SP) and pulse pressure (PP) represent impaired cardiac function and reduced cardiac output, whereas the decreased diastolic pressure suggests vasodilation. Gabapentin has been shown to lower blood pressure acutely in hypertensive models, primarily through mechanisms involving the sympathetic nervous system and central nitric oxide signaling. However, its chronic use does not sustain these hypotensive effects and may even lead to adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of Does Gabapentin Raise Blood Pressure? Understanding the Cardiovascular Effects. The Initial Paradox: Gabapentin and Lower Blood Pressure; The Emerging Concern: Gabapentin and Elevated Blood Pressure. Mechanisms Behind the Possible Increase; Other Cardiovascular Side Effects of Gabapentin. The FDA Warning and Respiratory Depression The evidence suggests that gabapentin can lower heart rate, particularly in acute settings such as anesthesia induction and in hypertensive models. Chronic administration also appears to suppress cardiovascular function, leading to bradycardia. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-DanieDrankwalter-BloodPressureandHeartRate-Standard-0c89f7683df843e893aa83c64fc017a8.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |