Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
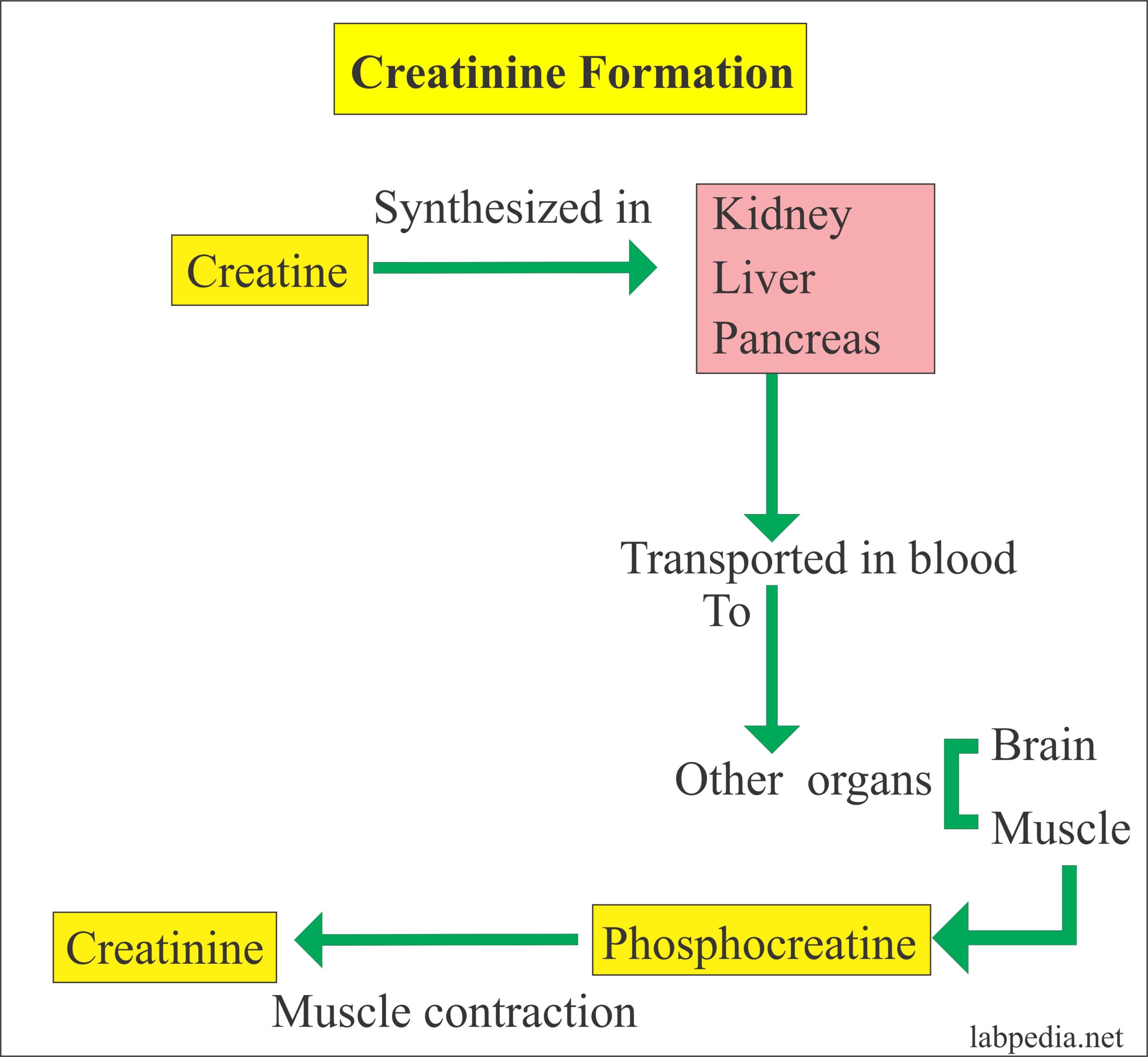
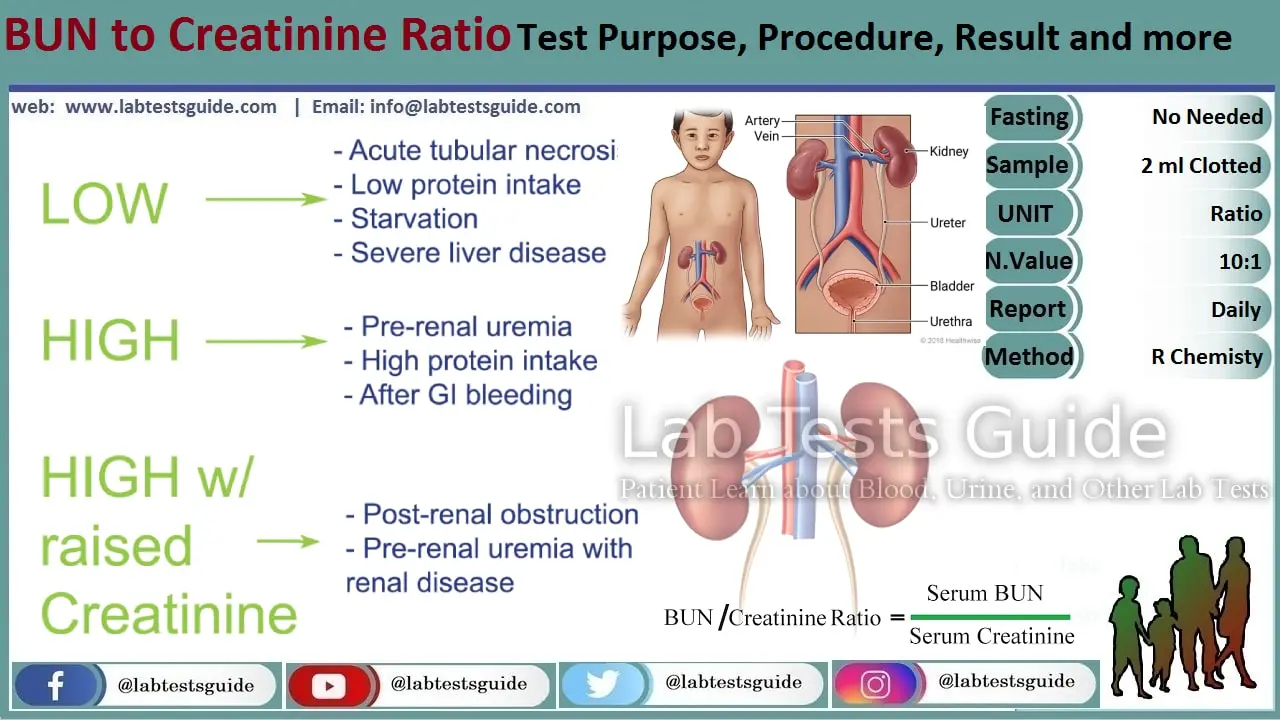
In fact, gabapentin is eliminated through renal excretion only, and since it does not bind to proteins, a single dialysis session will eliminate nearly 35% of the total. 8,9 In our case, this would explain the rapid improvement in symptoms. As in the other 2 cases of gabapentin-induced acute renal failure and rhabdomyolysis, the patients Insulin and certain medications used by people with diabetes are cleared by the kidneys. Because diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease, it's important that those with diabetes control their blood sugar levels. Blood sugar control typically involves a combination of diet, physical activity, and medication. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Laboratory tests showed haematocrit 33.4%, serum creatinine 5.1 mg/dl, sodium 134 mEq/l, potassium 3.7 mEq/l and glucose 154 mg/dl. The clinical impression was dizziness and she was observed in the ED. Four hours later, altered consciousness with lethargy was noted. The Glasgow Coma Scale was E2V3M5. There was no focal neurological deficiency. Objectives The thrombin inhibitor dabigatran is mainly excreted by the kidneys. We investigated whether the recommended method for estimation of renal function used in the clinical trials, the Cockcroft-Gault (CGold) equation and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) modification of diet in renal disease equation 4 (MDRD4), differ in elderly participants, resulting in erroneously Not usually. It’s unlikely that gabapentin will cause liver or kidney damage at normal doses. But doses higher than what’s prescribed are more likely to cause side effects and lead to serious risks. This is especially true if gabapentin is combined with other medications or substances (like alcohol) that make you drowsy. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Abstract. A bipolar I manic patient was treated successfully by adding gabapentin to perazine and clonazepam. Also initially tolerated well, an increase of creatinine after several weeks of GP (2000 mg) was observed which was reversible after discontinuation of GP. It is suggested that the possibility of renal dysfunction should be kept in mind with the usage of gabapentin. Gabapentin’s apparent total clearance is 100 mL/min in adults with normal renal function, which is essentially equivalent to CrCl and does not suggest the involvement of tubular reabsorption. 1 Some evidence suggest that active tubular secretion mediated by organic cation transporter-1 (OCT-1) may play a role in gabapentin’s renal clearance. Of the 729 patients in this study, a significantly higher serum gabapentin level in those with estimated glomerular filtration rate reduction indicates an inappropriate dosing for their kidney clearance, a problem at the level of gabapentin prescription. A high creatinine level in a blood test can be a sign of decreased kidney function or kidney disease. But there are other reasons this level can be high. Some medications can increase the creatinine level without actually hurting the kidneys. Gabapentin (GBP) is a drug which is frequently used in diabetic neuropathy. Common adverse effects of GBP include drowsiness, dizziness, ataxia, somnolence, and fatigue. Rhabdomyolysis is an extremely rare side effect of GBP. In this report we describe a case of GBP-induced rhabdomyolysis in a 63-ye This may be due to one of three factors: decreased creatinine secretion, interference with the serum assay, or enhanced creatinine production. Thus, in patients taking one of the drugs described below, an elevation of creatinine without a concomitant elevation of BUN does not likely reflect a true decrease in GFR. DECREASED SECRETION Reported increased blood creatinine phosphokinase levels and muscle damage caused by inflammation. Antiepileptic drugs increase risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication; monitor for emergence or worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. They lower the amount of acid in your stomach, but studies have shown that taking them for a long time can raise your chances of serious kidney problems and possibly lead to kidney failure. Blood creatinine increased is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Enbrel, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. In individuals with normal renal function, gabapentin clearance is 100 ml/min, which is equivalent to a normal creatinine clearance. On the other hand, in patients with ESRD and on HD, gabapentin clearance with HD is approximately 142 ml/min with an elimination half-life of about four hours with HD, which makes HD an effective treatment option
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |