Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
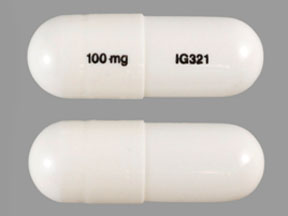
Diabetic Gastroparesis (DGP) Caution: Unclear effects on gastric emptying. Additive risks of HF (pregabalin plus TZDs) . Metabolic acidosis, a contraindication for metformin (topiramate). Loss of glucose control (pioglitazone or glyburide with topiramate). Caution: Loss of glucose control Unclear effects of gastroparesis on absorption of This clinical guideline addresses the definition, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and treatment of gastroparesis, including nutritional supplementation, glycemic control, pharmacological, endoscopic, device, and surgical therapy. Gabapentin as an adjunctive drug could be more effective in reducing the severity of GI symptoms in patients with dyspepsia, especially neurological symptoms (such as pain, reflux, and indigestion). Keywords: Functional dyspepsia, gabapentin, gastrointestinal disorders. Also, neurokinin antagonists are approved for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced emesis. 126 Among these drugs, aprepitant, increases gastric accommodation 127 and improves some digestive symptoms in patients with gastroparesis, 128 but does not affect GE. 127 Although the APRON trial failed to show positive results on the primary endpoint Gabapentin was observed to reduce chemotherapy-induced nausea and hyperemesis gravidarum in uncontrolled native ghrelin is impractical for gastroparesis treatment. Gastroparesis is a syndrome defined by symptomatic delay in gastric emptying in the absence of mechanical obstruction. 1 Typical gastroparesis symptoms of nausea, vomiting, early satiety, bloating, postprandial fullness, abdominal pain, and/or weight loss overlap to a significant degree with functional dyspepsia (FD). 1–5 With an estimated prevalence per 100,000 persons of 37.8 for women and If possible, however, try to use Gabapentin, Pregablin or tricyclics such as Nortriptyline for the abdominal pain in gastroparesis. There are patients who are refractory to all types of treatment and cannot even take in sufficient calories and fluids. I'm on gabapentin (ostensibly) for my gastroparesis and have been for a number of years. I started at 25 mg three times a day, and gradually bumped up. My current dose is 800 mg once a day. It is structurally related to gabapentin but has no activity at GABA or benzodiazepine receptors, though both pregabalin and gabapentin are frequently used to treat neuropathic pain. There are a number of medications available to treat gastroparesis. Your doctor will discuss with you the benefits and risks of each one before deciding on a medication regimen. Prokinetic medications are drugs that promote gastric emptying and are an important part of managing gastroparesis. Two commonly used medications are: The medications also can delay gastric emptying and worsen gastroparesis. Commonly used alpha-2-agonists: Clonidine (Catapres) Methyldopa (Aldomet) Tizanidine (Zanaflex) – used as a muscle relaxer. Clonidine (Kapvay) – used to treat ADHD. Guanfacine (Intuniv) – used to treat ADHD. Lofexidine (Lucemyra) – FDA-approved to treat opiate Given the limited efficacy of treatment options and serious side effects, significant research continues for therapeutic options for gastroparesis. Promising investigational pharmacologic therapies include relamorelin, prucalopride, and aprepitant. Gastroparesis is a syndrome of objectively delayed gastric emptying in the absence of a mechanical obstruction and cardinal symptoms of nausea, vomiting, early satiety, belching, bloating, and/or upper abdominal pain. This topic will review the treatment of gastroparesis. Several medications can delay gastric emptying and should be avoided with gastroparesis. However, most of the below-listed medications are vital to treat or prevent serious diseases. Don’t stop or change your medications without consulting your health care provider. Common medications to avoid with gastroparesis include: Gastroparesis can be a serious problem where the GI tract literally “slows down”. This issue is common in patients with diabetes. Bloating, abdomnial pain, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness are all possible symptoms of gastroparesis. There are also medications that can worsen gastroparesis. The case: KD is a 62 year old female who [] This could be exceeded in cases where gabapentin is well tolerated but there has not been complete improvement. 52 % of patients with functional dyspepsia responded to gabapentin based on change in total PAGI-SYM score. 61 % of patients with functional dyspepsia responded to gabapentin based on change in PAGI-SYM postprandial fullness subscore An accurate diagnosis is necessary to treating gastroparesis, since the treatment depends on the cause.If your doctor diagnosed an underlying disease or condition that is causing the gastroparesis, the treatment will focus on correcting or reversing that condition; if there is no underlying cause or if it is not possible to treat it, then the goal of treatment is to promote gastric emptying Key takeaways: Gastroparesis is a delay in food emptying from the stomach. It can be an uncomfortable and painful condition. Some common medications used to treat gastroparesis include metoclopramide (Reglan), erythromycin, and domperidone. Delayed gastric emptying on objective testing defines gastroparesis, but symptoms overlap with functional dyspepsia and do not correlate well with gastric emptying delay. This review outlines a strategy for defining, diagnosing, and managing refractory gastroparesis. Metoclopramide is the only medicine the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) has approved for the treatment of gastroparesis. The metoclopramide pill (Reglan) has a risk of serious side effects. But the FDA recently approved a metoclopramide nasal spray (Gimoti) for treating diabetic gastroparesis.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |