Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 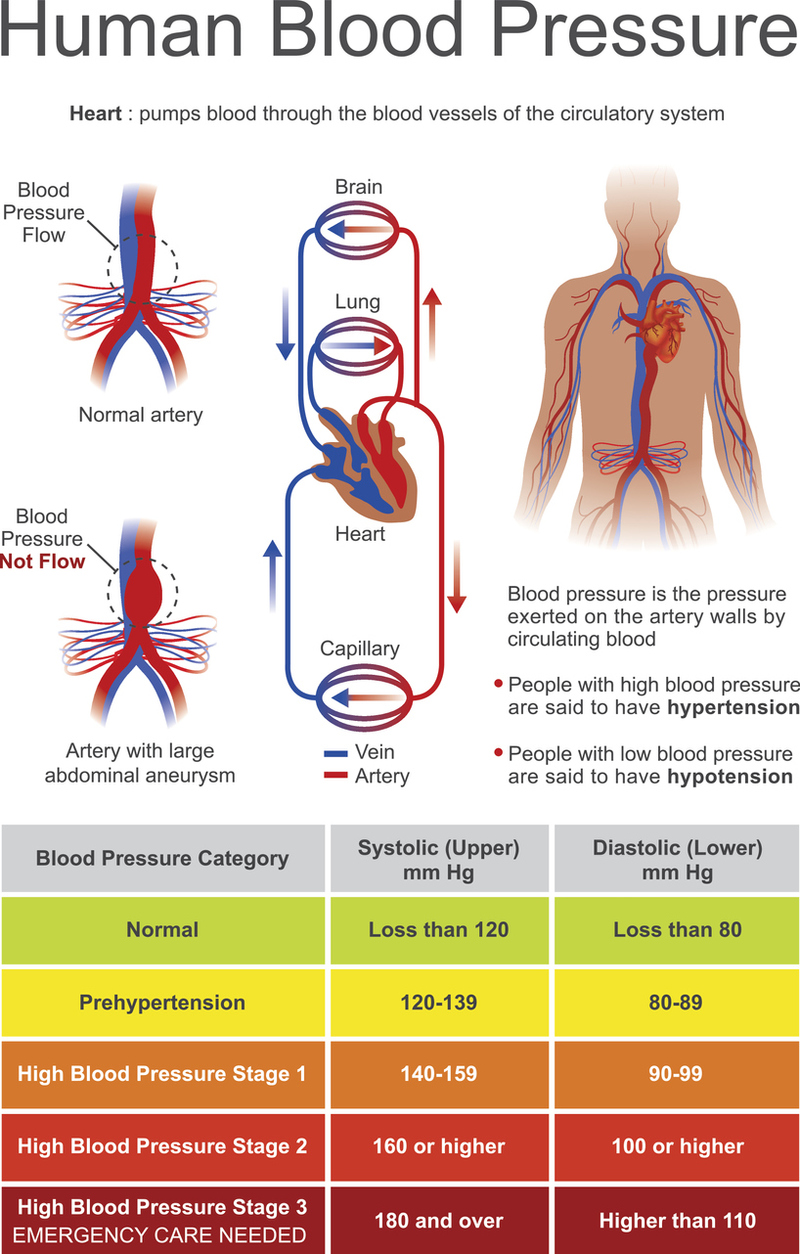 |
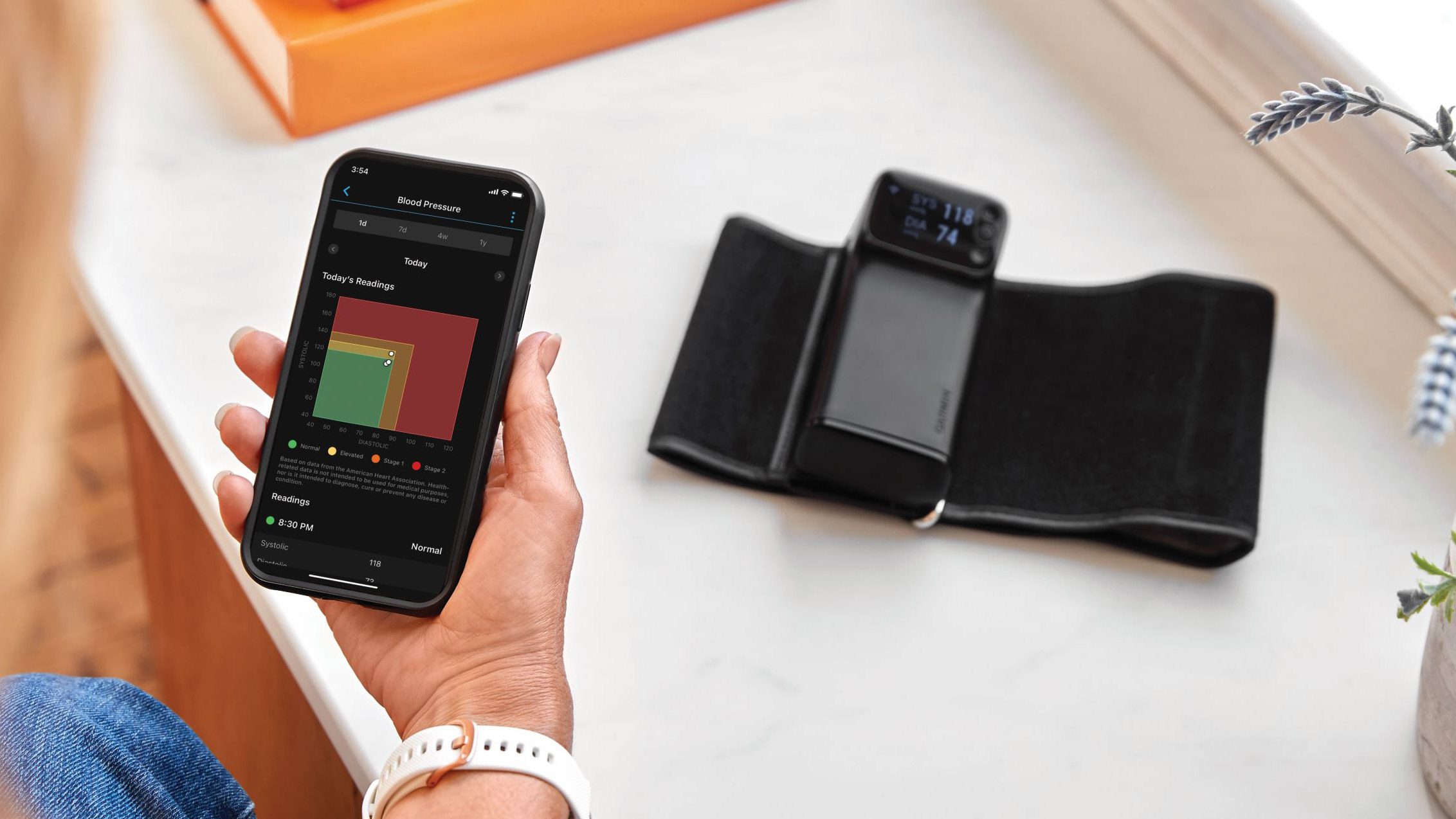
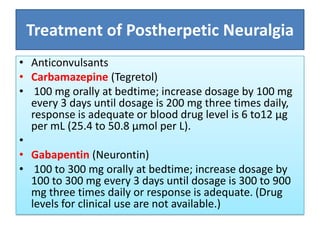
Not everyone who takes gabapentin will experience changes in blood pressure. However, certain factors may increase your risk, including: * Age: Older adults may be more susceptible to blood pressure changes. * Existing blood pressure issues: If you already have high or low blood pressure, gabapentin may exacerbate these issues. Some other blood pressure medications, such as thiazide diuretics and thiazide-like diuretics, can have a similar effect. Like beta blockers, hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) and metolazone can increase blood sugar levels. They can also cause new Type 2 diabetes in as little as 9 to 18 weeks. Gabapentin is not known to raise the blood pressure. The only time it may increase the blood pressure is if the patient stops Gabapentin abruptly and they start to have pain. In this case, the increase in blood pressure is not due to Gabapentin but due to the patient not taking the medication and being in pain. Oral and intravenous gabapentin can markedly attenuate blood pressure (BP) in hypertensive rats. The nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS) is the primary integrative center for cardiovascular control and other autonomic functions in the central nervous system. Gabapentin is taken by mouth and comes in capsule, tablet, and liquid form. Conditions treated with gabapentin. Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. The question of whether gabapentin is bad for blood pressure is complex, with the answer not being a simple yes or no. While research indicates that gabapentin can actually reduce blood pressure and heart rate in some cases, there are also potential risks related to blood pressure, especially with long-term use and withdrawal. The key lies in But that doesn’t mean one can suffer high blood pressure when taking gabapentin. Here’s what happens. When an individual withdraws abruptly from gabapentin and uses the drug for nerve pain regulation, there’s a chance the pain could return. Severe pain alone can drive up one’s blood pressure. Ligands of auxiliary α2δ subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) decrease elevated L-type VDCCs surface expression in arterial myocytes and arterial constriction in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). However, their effect on blood pressure (BP) is unclear. In this study, we investigated the hemodynamic response to acute and chronic administration of gabapentin, a ligand of Summary: High blood pressure is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Tylenol, and have Rheumatoid arthritis. In conclusion, while Gabapentin can potentially cause a slight increase in blood pressure, this side effect is generally manageable and does not pose a significant risk to most individuals. However, it is important to be aware of the potential connection and to monitor your blood pressure regularly while taking Gabapentin. The current body of research indicates that gabapentin does not increase blood pressure. Instead, it generally lowers BP, particularly in hypertensive conditions, by modulating sympathetic nervous system activity and central cardiovascular control mechanisms. Estrogen may increase blood pressure by raising levels of a protein called angiotensinogen. Angiotensinogen eventually turns into angiotensin II, which can raise blood pressure. In most cases, birth control doesn’t raise blood pressure by a significant amount. Research suggests that gabapentin can lower blood pressure by reducing the body’s production of certain hormones that can increase blood pressure. It may also help to relax blood vessels, making it easier for blood to flow through them. Yes, it can cause High Blood Pressure (hypertension) Cardiovascular side effects including hypertension have been reported to occur in more than one percent of patients taking gabapentin. Read more at: Pain and blood pressure appear to be strictly related. According to available evidence, both pain and analgesic therapies may induce a clinically significant destabilization of blood pressure values. The subsequent implications on hypertension incidence and blood pressure control remain unclear and should be explored in future studies. Funding The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Can I drink alcohol while taking gabapentin? Avoid drinking alcohol while taking gabapentin. Drinking alcohol with gabapentin could increase sleepiness or dizziness. What else do I need to know about gabapentin? Never stop taking gabapentin without talking to your healthcare provider first. One possible explanation for the findings is that gabapentin and pregabalin can alter arterial myogenic tone and cause fluid retention . Fluid retention causes either an increase in cardiac output or an increase in blood pressure . Velocity of blood flow increases either way, thereby increasing turbulence of blood flow . Yes, gabapentin can lower blood pressure. However, in the vast majority of people taking gabapentin, it does not lower blood pressure to a worrisome extent. A blood pressure of 113/64 is below average, but it is not at a worrisome level unless it is associated with any lightheadedness or dizziness. Overall, gabapentin does not raise blood pressure; in fact, it tends to lower BP, particularly in hypertensive models and during stress-inducing procedures like surgery. Its hypotensive effects are primarily mediated through the sympathetic nervous system and central mechanisms involving the NTS.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |