Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
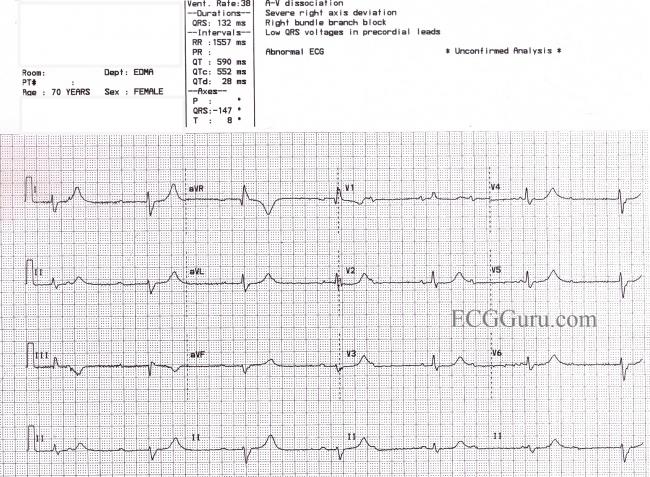 | 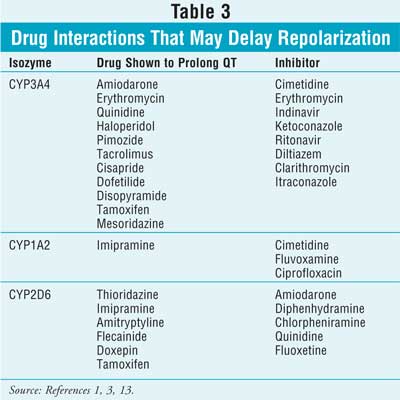 |
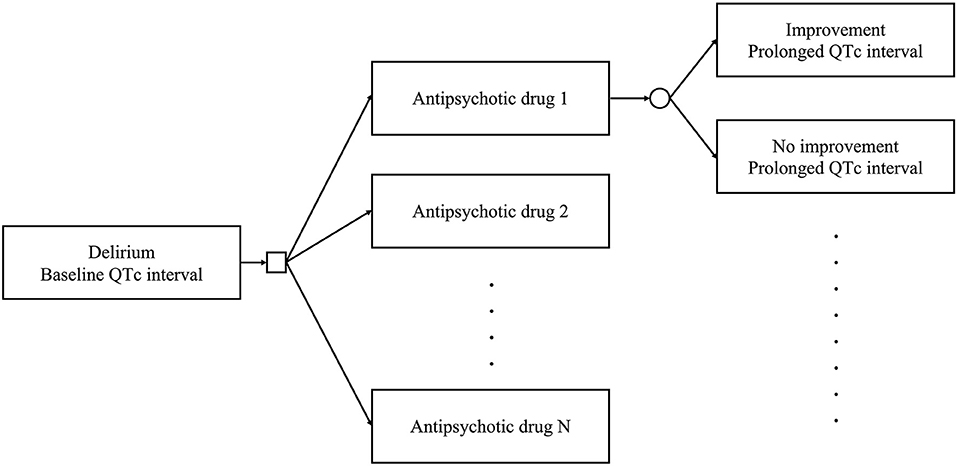
o Reference ranges for prolonged QTc interval (men QTc >440 msec, women QTc >470 msec) & age-related differences (children/older adults) o Patient and drug-specific risk factors for Torsade de Pointes to enable completion of following risk assessment when initiating new medication: Does the Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. Anxiolytic drugs and sedatives Does gabapentin prolong QTc? Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation . The risk of QT interval prolongation was evaluated in a thorough QTc trial in 247 healthy individuals following treatment with LCM at 400 or 800 mg/day. Exposure to LCM did not appear to cause QT prolongation, nor does it seem to have important effects on QRS duration {UCB, Inc., data on file}. Halogenated volatile anesthetics (Halothane, Enfluorane, Isoflurane, Desflurane and Sevoflurane) prolong the QTc interval, even if data is controversial for some of them[39-43]. Isoflurane has been used safely in patients with LQTS[13,44]. Medication-induced QT prolongation commonly occurs through alterations of intracellular ion channels. Prolonged depolarization is associated with increased function of inward sodium channels (I Na). 7 More often, medications reduce repolarization by inhibiting the outward potassium channels (I Kr). Drugs associated with QT Prolongation, QTc prolongation including Antipsychotics, antiarrhythmics, antidepressants, and antihistamines QT prolongation is a rare medication side effect. It can cause your heart to beat abnormally. In severe cases, it can cause life-threatening arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms). Notable QT-prolonging drugs include antiarrhythmics such as amiodarone (Pacerone) and antipsychotics such as chlorpromazine (Thorazine) and ziprasidone (Geodon). For people with LQTS there are specific medications that can have a serious effect by further prolonging the QT interval. We give a list of these medicines below. This list includes drugs that can stimulate and irritate the heart by causing adrenaline-like effects. When studied along with the administration of ketoconazole, a 3A4 inhibitor, the QTc interval increased by 82 milliseconds. 9 Renal impairment may also increase a patient's risk for QT interval prolongation by the accumulation of drug. Despite their relative safety, they also cause QT prolongation. Similar to other QT-prolonging antiemetic classes, serotonin receptor antagonists cause QTc prolongation by inhibiting the IKr potassium efflux channels, thus prolonging cardiac repolarization (8). Different forms of medication delivery may mitigate QTc-prolonging effects. A comprehensive list of conditions and drugs that may prolong the QT interval, and cause torsade de pointes (TdP) and long QT syndrome (LQTS) is presented below. With regards to drugs, the risk of QT prolongation and TdP varies markedly across the list but tends to be rather similar within a drug class. Pregabalin use has been associated with QTc prolongation in patients taking other QTc–prolonging agents, although the relative contributions of pregabalin to QTc prolongation may be minimal. Pregabalin and gabapentin have been associated with a dose-related increased risk of atrial fibrillation. ¶ The "high risk" category includes drugs with evidence of likely or probable association with TdP or clinically significant QT prolongation typically defined as a mean QTc increase of >60 msec from baseline and/or a QTc increased to >500 msec in a significant proportion of patients. Prolongation of the QT interval can lead to a life threatening ventricular arrhythmia known as torsades de pointes which can result in sudden cardiac death. The risk of torsades de pointes depends on patient factors and current medication. QT prolongation is an extended corrected QT (QTc) interval seen on an ECG at rest. 2 Because the QT interval is dependent on heart rate, the QTc interval is calculated to control for this factor. 2 QTc can be calculated by a variety of methods. 3 Definitions of QTc prolongation vary, but often this condition is described as a QTc interval of or changing to an alternative non QT prolonging drug. Prolonged QTc Interval >500 ms in males and females A QTc interval >500 ms is clinically significant and likely to confer an increased risk of arrhythmia. Any drugs which prolong the QT interval should be reviewed immediately. 6,8,9,10 Interpretation of the QT interval on an ECG is not In this population of healthy adults, gabapentin enacarbil at doses of 1200 and 6000 mg was not associated with QT prolongation and was generally well-tolerated. Evaluation of gabapentin enacarbil on cardiac repolarization: a randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, crossover thorough QT/QTc study in healthy adults Long QT syndrome is a cardiac repolarization disorder and is associated with an increased risk of torsades de pointes. The acquired form is most often attributable to administration of specific medications and/or electrolyte imbalance. Among the mood stabilizers, lithium has a moderate risk of QTc prolongation while the antiepileptics used for this purpose such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, valproate, pregabalin, gabapentin, and lamotrigine are reported to be safe with a low risk of QTc prolongation. Anxiolytic drugs and sedatives
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |