Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
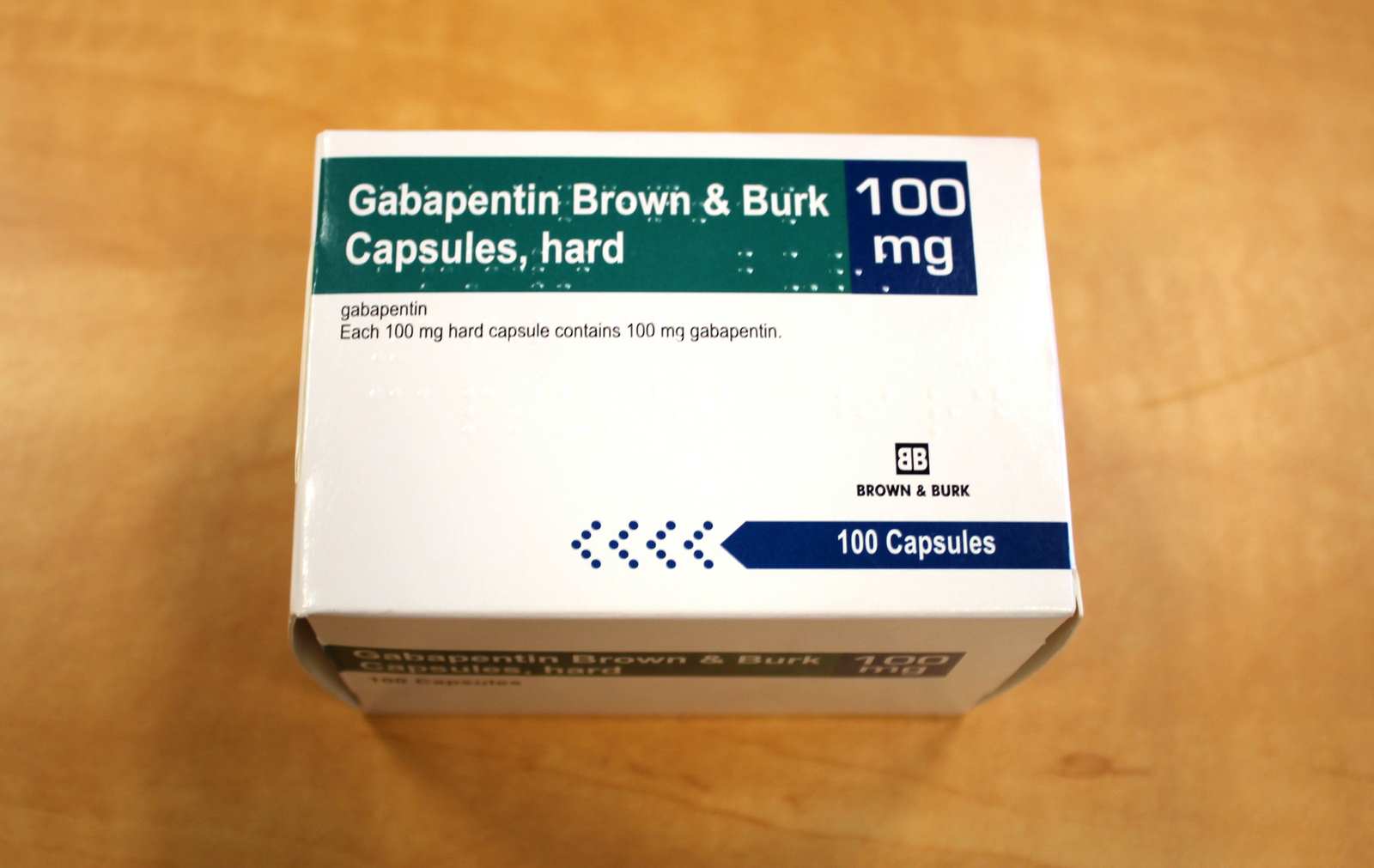
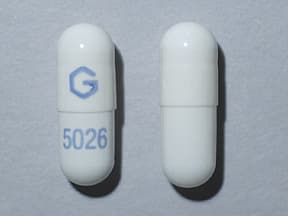
Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. A Cochrane review reported that 3 to 4 patients out of every 10 with either of these conditions experienced at least a 50% reduction in pain intensity when prescribed gabapentin at dosages of 1800mg-3600 mg/day (gabapentin encarbil: 1200mg-3600 mg/day). This compared with only 1 or 2 out of every 10 given a placebo (an inactive treatment). Gabapentin is also used as an adjunct to more potent anticonvulsants and for the management of certain types of neural pain. Definition and uses of gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant with pain-relieving effects that may be used to treat partial-onset seizures or relieve nerve pain. Research has shown gabapentin binds strongly to a specific site (called the alpha2-delta site) on voltage-gated calcium channels and this is thought to be the way gabapentin works to relieve nerve pain and lower 2.1 Dosage for Postherpetic Neuralgia In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day The typical starting dosage of gabapentin for seizures is 300 mg by mouth three times a day, with or without food. Your prescriber may adjust your gabapentin dosage to up to 600 mg 3 times a day (1,800 mg per day). The maximum gabapentin dosage is 3,600 mg per day, but higher doses are more likely to cause side effects.Restless legs syndrome Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Gabapentin is taken by mouth and is available either as a capsule (100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg) or a tablet (600 mg and 800 mg). Gabapentin can be taken with or without food. When used for pain, gabapentin is prescribed at a lower "loading dose" and gradually increased to the optimal "therapeutic dose." Gabapentin is a remedy for nerve pain that’s also prescribed for back pain. See how it works and if it can help back pain from sciatica, shingles, and more. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain from shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. The 100 mg capsule shell contains: gelatin and titanium dioxide. The 300 mg capsule shell contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide. The 400 mg capsule shell contains: gelatin, red iron oxide, titanium dioxide and yellow iron oxide. The imprinting ink contains: FD&C Blue #1 Aluminum Lake, propylene glycol, shellac, and titanium Gabapentin is a prescription medicine. It's important to take it as advised by your doctor. Dosage and strength. Each capsule of gabapentin contains 100mg, 300mg or 400mg of gabapentin. Each tablet contains 600mg or 800mg of gabapentin. If you're taking gabapentin as a liquid, 2ml is usually the same as taking a 100mg tablet or capsule. For oral dosage forms (capsules, liquid, and tablets): For epilepsy: Adults and children 12 years of age and older—At first, 300 milligrams (mg) 3 times per day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. However, the dose is usually not more than 1800 mg per day (600 mg 3 times per day). If your back pain is nerve-related, then the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin may be a good choice for you. This article will explain how gabapentin works, detail its uses, and go over potential side effects, so that you can assess with your doctor whether this drug may be right for you. The role of gabapentin for back pain works in the following way: Reduces the release of several neurotransmitters, decreasing the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system Prevents pain responses in animal models of hyperalgesia, indicating its ability to modulate the perception and processing of pain Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Prescribing gabapentin for chronic, non-specific low back pain is not recommended. Patients who suffer from nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in the legs from sciatica or have Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |