Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
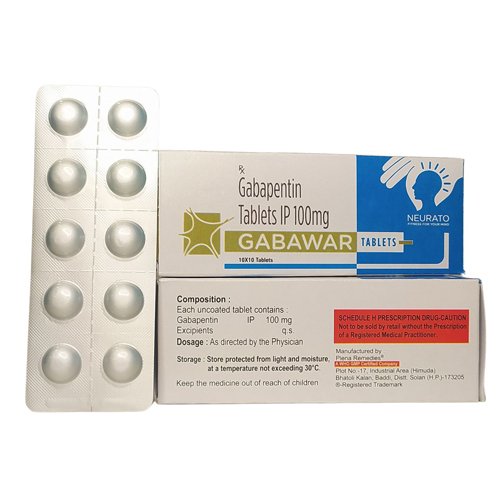
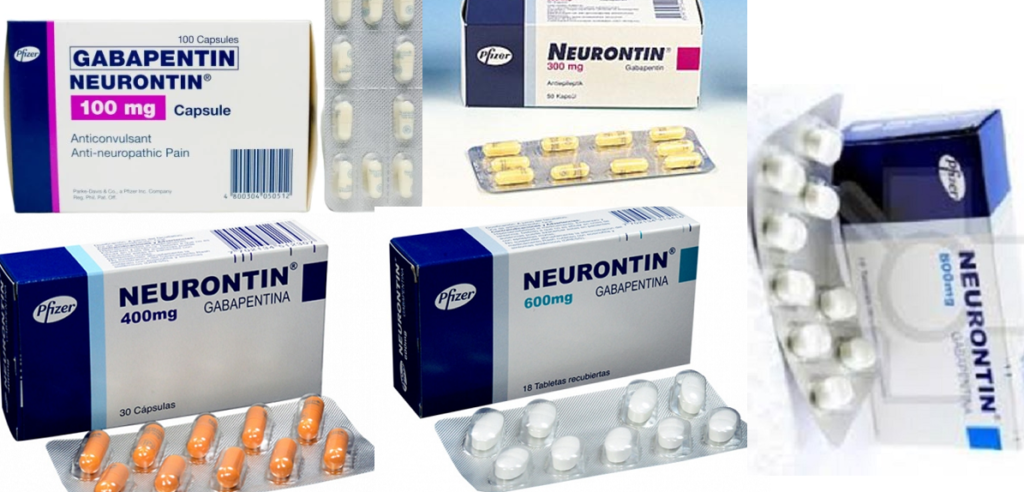
Studies have shown that gabapentin 100mg can significantly reduce pain after abdominal surgery, making recovery a smoother ride for patients. Gabapentin is like a superhero cape for postoperative pain – it not only reduces pain intensity but also helps decrease the need for other pain medications. Gabapentin for dogs is commonly prescribed for pain, anxiety, or seizures. It's generally safe, but there are some known side effects to be aware of. After-Surgery Pain: Gabapentin 100 mg treats after-surgery pain by reducing the activity of certain chemicals in the brain and spinal cord that are involved in pain signalling. Gabapentin can be used to treat after surgery pain from a variety of surgical procedures, including: Yu L, Ran B, Li M, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of postoperative pain after lumbar spinal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine 2013; 38:1947–1952. [Google Scholar] 10. Hwang SH, Park IJ, Cho YJ, et al. The efficacy of gabapentin/pregabalin in improving pain after tonsillectomy: a meta-analysis. The use of gabapentin significantly lowered the cumulative pain score in the first 24 hours after surgery by an average of 1.04 (MD, –1.04; 95% CI, –1.45 to –0.63; P < .00001). Gabapentin also reduced the overall morphine equivalent consumption by 7.89 mg (MD, –7.89; 95% CI, –13.56 to –2.2; P = .006). We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. Perioperative gabapentin upped the risk of delirium, new antipsychotic use, and pneumonia in older adults after major surgery, a retrospective study showed. pain relief. In rare cases, I may recommend avoiding ibuprofen or aleve after surgery – this will be made clear at the time of surgery. Motrin or Advil (ibuprofen) 600mg every 6 hours OR Celebrex 100mg every 12 hours. Tylenol (acetaminophen) 650mg every 6 hours. Neurontin (gabapentin) 300mg every 8 hours for the first 3 days only. Postoperative opioid consumption was reduced when using gabapentin within the initial 24 hours following surgery (standard mean difference −1.35, 95% confidence interval [CI]: −1.96 to −0.73; P <0.001). There was a significant reduction in morphine, fentanyl, and tramadol consumption (P <0.05). Their findings, recently published in the journal Anesthesiology, indicate that the analgesic benefits of pregabalin and gabapentin after surgery are negligible, regardless of the dose or type of operation. Gabapentinoids were also ineffective in preventing chronic pain from developing after surgery, one of the primary justifications for using Surgery was performed while patients were supine. After surgery, the muscle relaxants were reversed using neostigmine (40 μg/kg) and atropine (20 μg/kg). After extubation and ensuring adequate ventilation, patients were transferred to the recovery care unit for 2 h and then to the ward. All patients received 100 mg suppository diclofenac The purpose of this review is to critically appraise the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids for acute pain management and its impact on the development of chronic pain after surgery. Recent findings: Recent meta-analyses have revealed that prior data likely have overestimated the beneficial effects of gabapentinoids in acute perioperative Pre-operative gabapentin (600-1200 mg) reduces the amount of narcotics required in the post-anesthetic care unit (PACU). Pre-operative gabapentin does not decrease long-term narcotic use and is associated with increased side effects of respiratory depression, sedation, and falls. Studies have not shown gabapentin to be as effective for acute pain in cats as some other medications like buprenorphine, and so it is less commonly prescribed for a sudden onset of a painful condition, or after surgery. Gabapentin Side Effects in Cats Similarly, aside from 24 h after surgery, gabapentin significantly reduced pain with movement (25–27,31,34,35,37,38) by 18% to 28% (VAS 8.2 mm to 10.2 mm) after surgery . The pooled effects on VAS pain scores displayed significant heterogeneity, which was not explained by subgroup analyses based on surgical procedure, gabapentin dose or study According to this review, pre-operative 1200 mg or less gabapentin as a single dose was associated with lesser post-operative pain and opioid demand during first 24 h after surgery, but multiple dosage of gabapentin before and after surgery did not cause a reduction in VAS score for pain, in this regard it suggests single pre-operative dose of They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication but demonstrates benefits in neuropathic and chronic pain. 28 In patients undergoing ambulatory hand procedures, preoperative gabapentin was shown to reduce postoperative pain medication consumption significantly and prolong the time to the patient’s first postoperative pain medication request versus
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |