Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
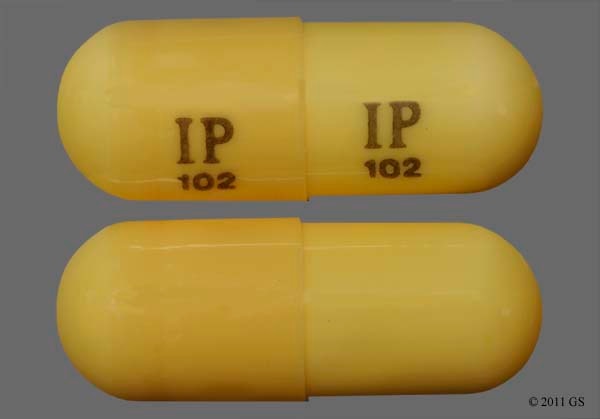
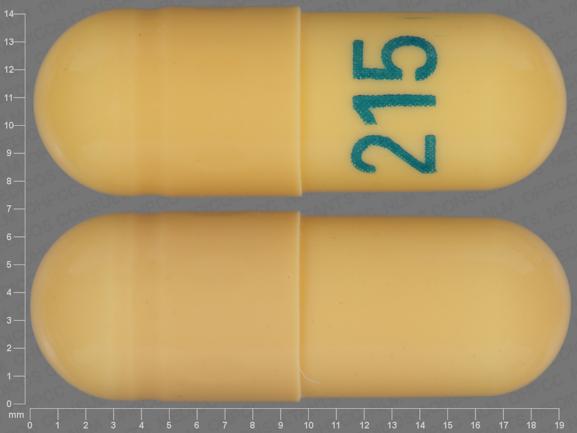
Child 6–11 years 10 mg/kg once daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 1, then 10 mg/kg twice daily (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 2, then 10 mg/kg 3 times a day (max. per dose 300 mg) on day 3; usual dose 25–35 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses, some children may not tolerate daily increments; longer intervals (up to weekly) may be more appropriate, daily dose maximum to be given in 3 divided NEURONTIN is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug or its ingredients. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. CAPD: Probably dialysed. Dose as in GFR: 15 mL/min.: HD: Dialysed. Loading dose of 300– 400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 100–300 mg after each HD session and increase according to tolerability. Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin Capsules Capsules, 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg, Oral 2 CONTRAINDICATIONS TEVA-GABAPENTIN is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to this Day 1: Single 300 mg dose Day 2: 600 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg two times a day) Day 3: 900 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg three times a day) Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures (2.2) Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily The oral TDLo of gabapentin in humans is 2.86 mg/kg and the LD 50 in rats has been found to be >8000 mg/kg. 21 Symptoms of overdose are consistent with the drug's adverse effect profile and involve CNS depression (e.g. dizziness, drowsiness, slurred speech, lethargy, loss of consciousness) and gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea. 18,17 While gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, it may cause side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and coordination problems. It can also interact with certain medications, so it is important to inform the healthcare provider about all current medications and medical conditions before starting treatment. Day 1: Single 300 mg dose; Day 2: 600 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg two times a day) Day 3: 900 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg three times a day) Epilepsy with Partial Onset Seizures (2.2) Patients 12 years of age and older: starting dose is 300 mg three times daily; may be titrated up to 600 mg three times daily Immediate release: Oral: 300 mg once on day 1, 300 mg twice daily on day 2, and 300 mg 3 times daily on day 3, then increase as needed up to 1.8 to 3.6 g/day in divided doses. Additional benefit of doses >1.8 g/day has not been established. Extended release: Oral: Initial: 300 mg once daily; increase by 300 mg each day up to 900 mg once daily It has diverse brand names such as Gralise, Neurontin, Fanatrex and Horizant (National Center for Biotechnology Information). Commercially, gabapentin can be obtained in the forms of capsules or tablets of diverse doses (capsules: 100, 300 and 400 mg; tablets: 300, 600 and 800 mg; webpage of the United States National Library of Medicine). Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. You can take this medication by mouth with a glass of water. Talk to your provider about medications you currently take to avoid drug interaction. What is this medication? where age is in years, weight is in kilograms and S Cr is serum creatinine in mg/dL. The dose of gabapentin should be adjusted in patients with reduced renal function, according to Table 2. Patients with reduced renal function must initiate gabapentin at a daily dose of 300 mg. Gabapentin should be titrated following the schedule outlined in In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). Find medical information for gabapentin on epocrates online, including its dosing, contraindications, drug interactions, and pill pictures. 300 mg, 400 mg; TAB Oral solution: 250 mg per 5 mL (50 mg per mL), clear colorless to slightly yellow solution 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS NEURONTIN is contraindicated in patients who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to the drug Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how gabapentin will affect you. Dizziness or drowsiness can cause falls, accidents, or severe injuries. Do not stop using gabapentin suddenly, even if you feel fine. You should not take gabapentin if you are allergic to it. Gabapentin is a prescription drug most commonly prescribed to relieve nerve pain following shingles in adults and the pain of postherpetic neuralgia. Learn about side effects, drug interactions, dosages, warnings, and more.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |