Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
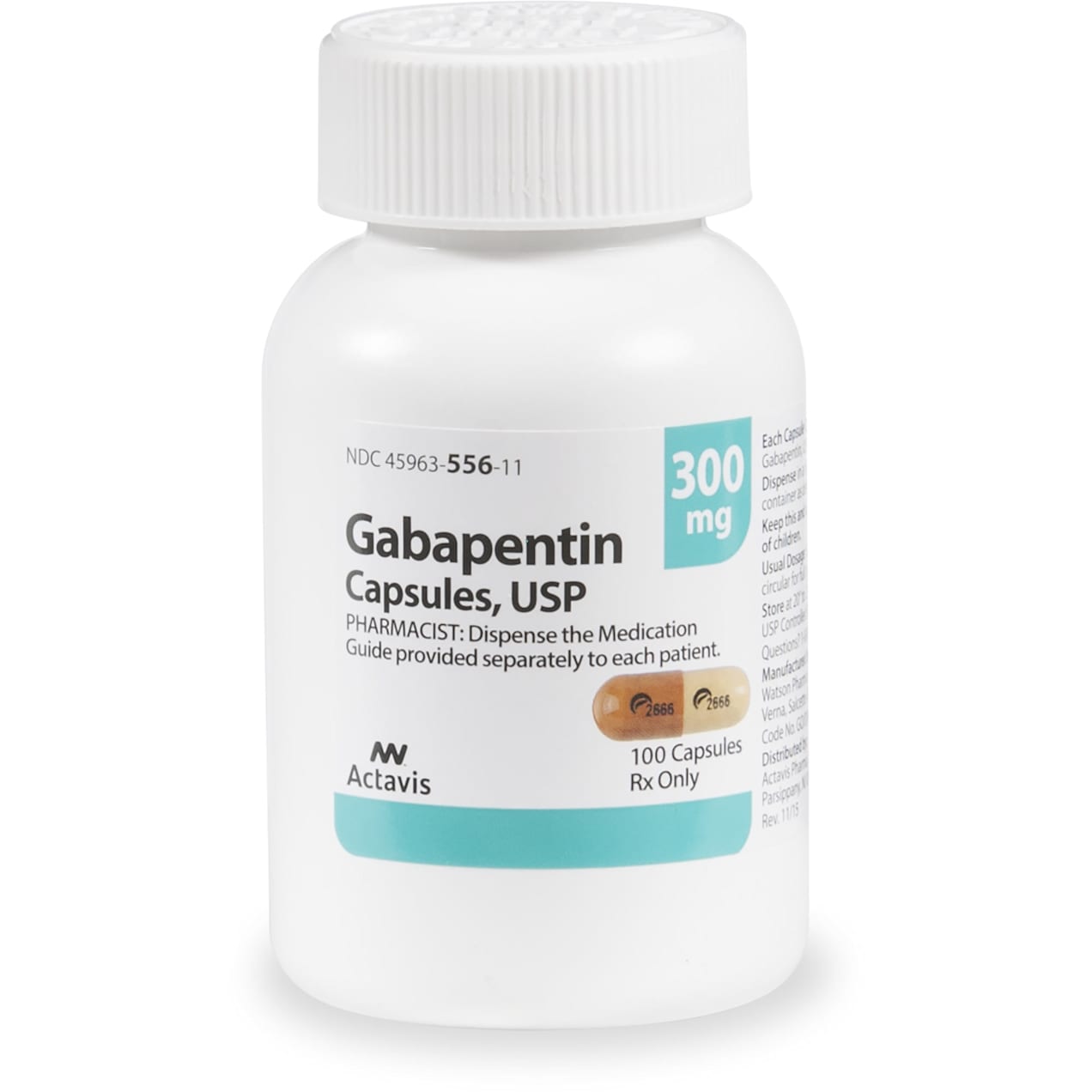
Gabapentin (Neurontin) is not a narcotic or federally controlled substance by the DEA as of November 2022, but it is classified as a Schedule V controlled substance in certain states. Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. Gabapentin is not a narcotic. It's not classified as a controlled substance in most states. (Kentucky, West Virginia, Michigan, Tennessee, and Virginia have reclassified gabapentin as a Schedule V controlled substance). Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Opioids (narcotic analgesics) are a class of medicines that are used to provide relief from moderate-to-severe acute or chronic pain. They may also be called opiates, opioid analgesics, or narcotics. They may also be called opiates, opioid analgesics, or narcotics. Typical starting dosage: 900 mg per day (300 mg, three times per day, spaced evenly throughout the day). The usual maintenance dose is 900–1,800 mg per day, divided into three doses daily. Adults and children 12 years of age and older—At first, 300 milligrams (mg) 3 times per day. Your doctor may adjust your dose as needed and tolerated. However, the dose is usually not more than 1800 mg per day (600 mg 3 times per day). Children 3 to 11 years of age—Dose is based on body weight and must be determined by your doctor. The simple and direct answer is: there is no narcotic in gabapentin. Gabapentin is not a narcotic, nor is it an opioid. No, gabapentin isn’t an opioid. Gabapentin belongs to a group of medications called gabapentinoids. These medications have a similar structure to a chemical in the brain called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). But researchers aren’t exactly sure how gabapentin works. Liquido - Narcotic (Official Video)From the album "Liquido"Stream here: For adults‚ the usual starting dose of gabapentin is 300 mg three times a day. The dose may be increased gradually as needed‚ up to a maximum of 1‚800 mg per day. For children aged 6 to 12 years‚ the usual starting dose of gabapentin is 10 to 15 mg/kg/day‚ divided into three doses. Initial dose: 300 mg orally on day one, 300 mg orally 2 times day on day two, then 300 mg orally 3 times a day on day three Maintenance dose: 300 to 600 mg orally 3 times a day Maximum dose: 3600 mg orally daily (in 3 divided doses)-Maximum time between doses in the 3 times a day schedule should not exceed 12 hours Gabapentin, initially developed for epilepsy, is now widely used for nerve pain and other off-label applications. Rising prescription rates have sparked discussions about whether it should be classified as a controlled substance due to concerns over misuse and dependency. Gabapentin isn’t a controlled substance according to the federal government. But several states have passed their own laws classifying gabapentin a schedule V (schedule 5) controlled substance. Combining gabapentin and opioids can be extremely dangerous. Gabapentin isn’t a controlled substance or narcotic on the federal level, but several states have passed laws to make it a Schedule V controlled substance. Gabapentin has risks and adverse effects, especially when combined with some other substances. The FDA approved gabapentin in December 1993.PRESCRIPTION: YesGENERIC AVAILABLE: YesPREPARATIONS:Capsules: 100, 300, and 400 mg.Tablets: 100, 300, 400, 600, and 800 mg.Solution: 250 mg/5 mlSTORAGE: Tablets and capsules should be stored between 15-30 C (59-86 F). Gabapentin’s potential for abuse, especially in combination with opioids, may have been misjudged — but the drug remains safe for approved uses. It’s not a narcotic, but what it does, is Gabapentin isn’t a narcotic or federally controlled substance, but it is regulated and recognized as a controlled substance in certain states. Gabapentin is approved by the Food and Drug Illicit Narcotic Drugs. Illegal narcotic drugs, such as heroin, do not have any accepted medical use and are extremely addictive. Although illegal, heroin is similar in structure and effects to prescription opioids. Heroin. Heroin is an illegal narcotic that is considered to be extremely addictive. If your doctor has prescribed gabapentin for you to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, or another condition, you may be wondering if it is considered a narcotic and if it is safe for you to take.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |