Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
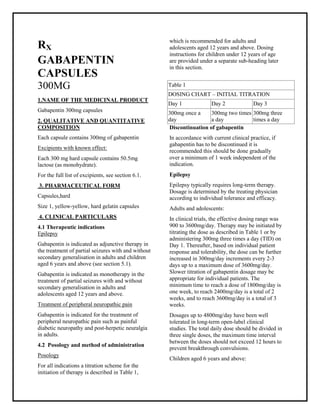 |  |
In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1,800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Gabapentin comes as an immediate tablet or capsule and is typically doses 2-3 times a day. This translates to dosing of every 8 to 12 hours. Gabapentin also comes in an extended release formulation in the name of Gralise or Horizant. Both extended release formulations are dosed once daily. 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. The inactive ingredients for the capsules are lactose, cornstarch, and talc. The 100 mg capsule shell contains gelatin and titanium dioxide. The 300 mg capsule shell contains Estimates of steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters for phenobarbital or gabapentin (300 mg three times a day; N=12) are identical whether the drugs are administered alone or together. Naproxen . Coadministration (N=18) of naproxen sodium capsules (250 mg) with gabapentin (125 mg) appears to increase the amount of gabapentin absorbed by 12% to It may vary from 300 mg per day to up to 3,600 mg per day. Another reason gabapentin takes time to work is that the dose is usually started low and gradually increased over time to reach an effective dose. -Initial dose: 300 mg orally on day one, 300 mg orally 2 times a day on day two, then 300 mg orally 3 times a day on day three -Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg orally in 3 divided doses; the dose may be increased up to 1800 mg/day. It is usually taken once daily around 5 pm. Gabapentin is available as a generic; however, not all generics are interchangeable with some branded versions of gabapentin. The duration of gabapentin's effectiveness can vary based on several factors, including the dose, the condition being treated, and individual patient characteristics. Typically, gabapentin's effects can last between 5 to 7 hours for immediate-release forms. The reported half-life (the time it takes for 50% of the drug to be metabolized) is 5 to 7 hours, which necessitates a dosing frequency of 3 to 4 times daily for it to be effective. Most studies report that gabapentin has a duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, GABARONE may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Immediate release: Oral: 300 mg once on day 1, 300 mg twice daily on day 2, and 300 mg 3 times daily on day 3, then increase as needed up to 1.8 to 3.6 g/day in divided doses. Additional benefit of doses >1.8 g/day has not been established. Estimates of steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters for phenobarbital or gabapentin (300 mg three times a day; N=12) are identical whether the drugs are administered alone or together. Naproxen. Coadministration (N=18) of naproxen sodium capsules (250 mg) with gabapentin (125 mg) appears to increase the amount of gabapentin absorbed by 12% to 15%. In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Peak plasma concentrations are seen within an hour as compared to 3 hours with gabapentin. 12 Oral bioavailability for pregabalin is more than 90% as compared to 30–60% for gabapentin. These differences can be explained by the mechanism of absorption. Initial dose: 300 mg once daily, with gradual increases as needed. Maintenance dose: 900-3600 mg per day, divided into three doses. The duration of treatment depends on the patient’s response. Initial dose: 300 mg on day one, 300 mg twice daily on day two, and 300 mg three times daily on day three. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. The precise mechanism through which gabapentin exerts its therapeutic effects is unclear. 16,17 The primary mode of action appears to be at the auxillary α2δ-1 subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels (though a low affinity for the α2δ-2 subunit has also been reported). 10,8,14 The major function of these subunits is to facilitate the If you have impaired kidney function, taking a lower dose or spacing out the dosing time is essential to prevent unwanted side effects.; Taking gabapentin with opioids (e.g., morphine, hydrocodone) can cause respiratory depression and sedation, and lead to fatal outcomes. 300 mg, and 400 mg of gabapentin, elliptical film-coated tablets containing 600 mg and 800 mg of gabapentin or an oral solution containing 250 mg/5 mL of gabapentin. The inactive ingredients for the capsules are lactose, cornstarch, and talc. The 100 mg capsule shell contains gelatin and titanium dioxide. The 300 mg capsule shell contains Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. It is important to consult with a doctor to determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on individual circumstances and medical history. Mechanism of Action
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |