Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
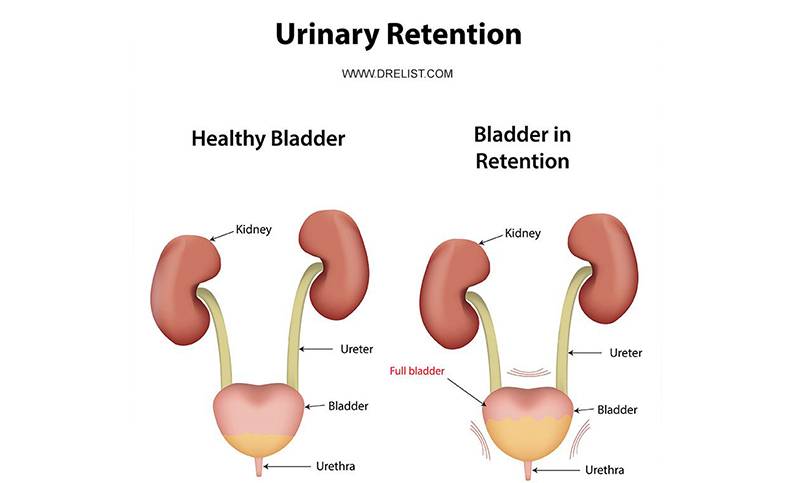
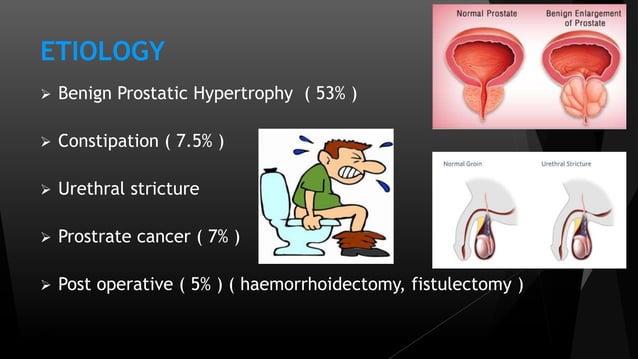
Clinical features and evaluation Signs and symptoms of AUR include bladder/suprapubic pain and tenderness and new onset overflow incontinence. The presence of AUR should be assessed in older patients who develop delirium, particularly if they have underlying dementia. Drugs that may cause Urinary Retention IV. CARDIOPULMONARY AGENTS 1. Antirrhythmics i. Disopyramide ii. Procainamide (Pronestyl) iii. Quinidine 2. Antihypertensives i. Hydralazine ii. Dihydropyridine CCBs 1. Nefedipine 2. Amlodipine (Norvasc) 3. Sympathomimetics i. α agonists (oral decongestants) 1. Ephedrine 2. Phenylephrine 3 Table 1: Drug Classes Causing Urinary Retention Drugs causing urinary retention Example medications Mechanism Anticholinergic drugs - TCAs (amitriptyline, nortryptiline) - tiotropium (Spiriva) - diphenhydramine (benadryl) - dimenhydrinate (gravol) Impaired detrusor contraction, leading to poor bladder emptying. Opioids All opioids Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Hematuria, dysuria, urinary frequency, cystitis, urinary retention, vaginal hemorrhage, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia; Frequency not reported: Sexual dysfunction (including changes in libido, ejaculation disorders, and anorgasmia) Hematologic. Common (1% to 10%): Leucopenia, purpura Drug-induced urinary retention is generally treated by urinary catheterization, especially if acute, in combination with discontinuation or a reduction in dose of the causal drug. Gabapentin and Urinary Retention To determine whether there is any evidence to support an (causal) association between the administration of gabapentin and the development of urinary retention. Download PDF Acute urinary retention. Symptoms of acute urinary retention may include. the inability to urinate; pain—often severe—in your lower abdomen; the urgent need to urinate; swelling of your lower abdomen; Chronic urinary retention. Chronic urinary retention develops over time and may cause few or no symptoms, which may make it hard to detect. The prognosis for acute urinary retention and constipation secondary to herpes zoster is generally regarded as benign and selflimiting. 7 Previous reports have shown resolution of voiding abnormalities after 4-6 weeks. In contrast, our patient demonstrated continued neurogenic detrusor underactivity as evidenced by a maximum cystometric Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Acute urinary retention (AUR) is the inability to voluntarily pass urine. It is the most common urologic emergency [1]. In males, AUR is most often secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH); AUR is rare in females [2,3]. Acute urinary retention is a urologic emergency characterized by the sudden inability to urinate combined with suprapubic pain, bloating, urgency, distress, or, occasionally, mild We identified 78 drugs associated with urinary retention, including Mirabegron, Tiotropium, Quetiapine, Amlodipine, etc. MR analysis indicated genetic markers (SNPs rs10500326, rs4815689, and rs1216743) of Amlodipine were associated with an increased risk of urinary retention. Urinary retention is the acute or chronic inability to voluntarily pass an adequate amount of urine. The condition predominantly affects men. The most common causes are obstructive in nature, with Following administration of gabapentin, the patient's paresthesia was greatly reduced; however, 10 days after starting the therapy, she experienced daily urge urinary incontinence. Incontinence was mix type urinary incontinence. Urinary retention means that you are having problems emptying the bladder completely. It may occur suddenly (acute urinary retention) or it may develop over a longer period of time (chronic urinary retention). Acute urinary retention is a medical emergency. Urinary retention is more common in men than in women. Spontaneous adverse drug reactions reporting databases are helpful data sources for evaluating safety profiles of and detecting potentially emerging safety signals for different pharmacological classes. Five potentially new signals of urinary retention associated with dapagliflozin, gabapentin, lithium, celecoxib, and piroxicam were found from the Italian spontaneous reporting system database Urinary retention (UR) is a urological syndrome characterized by the patient’s inability to empty all the urine from the bladder. It is usually caused by obstructive diseases of the lower urinary tract (eg, benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH] and urethral stricture), urinary tract infections and/or inflammatory diseases, and neurological disorders (eg, diabetic neuropathy, multiple sclerosis Urinary retention is a condition in which impaired emptying of the bladder results in postvoidal residual urine. It is generally classified into ‘acute’ or ‘chronic’ urinary retention. Because of the complex mechanism of micturition, many drugs can interact with the micturition pathway, all via different modes of action. Although the incidence of urinary retention, in particular acute In this analysis of the Italian spontaneous reporting system database, we found new urinary retention signals, requiring further evaluation, for dapagliflozin, gabapentin, lithium, celecoxib, and piroxicam. Treatment for urinary retention can depend on whether you have the acute form or the chronic form, as well as the cause. Treatment for acute urinary retention. Since the acute form of urinary retention is a medical emergency, your healthcare provider will insert a catheter to drain your bladder. This should provide almost immediate relief.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |