Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
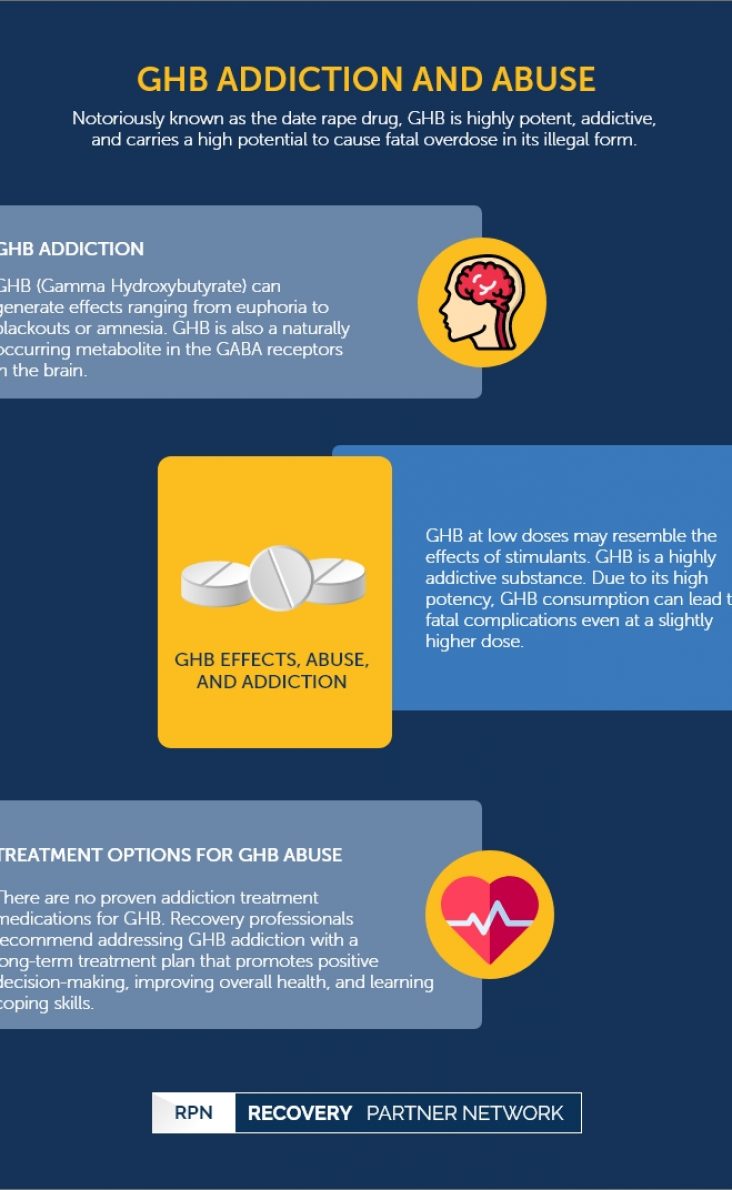 |  |
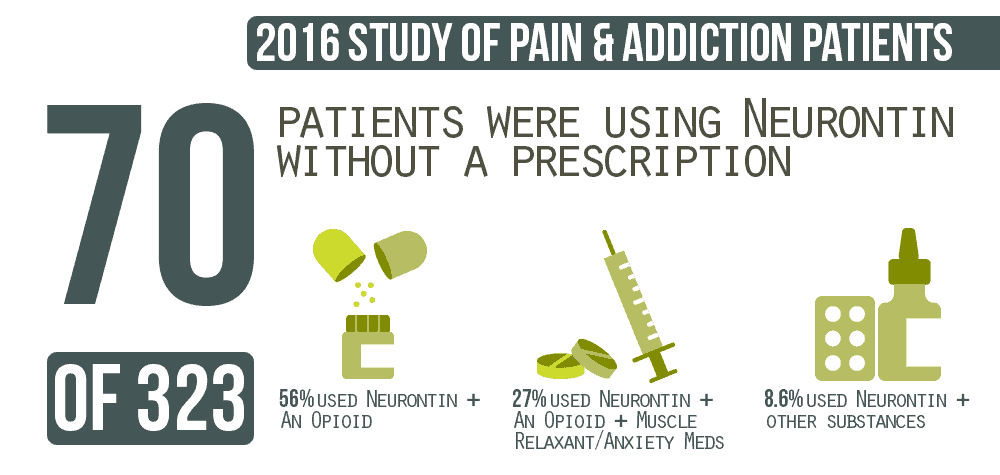
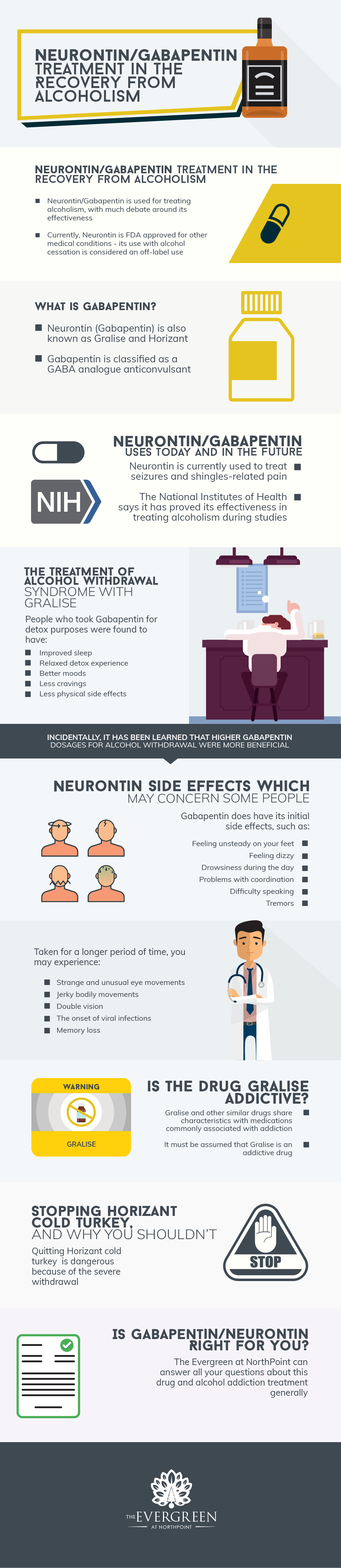
When taken as prescribed for an intended medical condition, gabapentin is well-tolerated and not considered addictive. However, addiction can occur or worsen when misused illicitly, at higher doses, or combined with opioids. Gabapentin Abuse Potential. While gabapentin isn’t a controlled substance at the federal level, some states have chosen to make it a Schedule V controlled substance as evidence for certain drug risks accumulates. For a long time, researchers didn’t believe gabapentin held potential for misuse. Despite initial views that gabapentin had no abuse potential (19–23), there have been numerous published case reports of gabapentin abuse by substance abusers in the community and penal system (24–36). The purpose of this review is to describe the international scope of gabapentin abuse (i.e., prevalence, risk factors, motivations behind In addition to their approved indications, both pregabalin and gabapentin are frequently prescribed off-label for restless legs syndrome and diabetic neuropathy.³˒⁷ Gabapentinoid use for patients with these indications is currently supported only by small studies.³ Gabapentin has also been found to significantly reduce the number of alcoholic drinks a person has in a week, leading to its When combined with opioids, the risk of respiratory depression and opioid-related mortality increases significantly. In the US, gabapentin was approved by the Food and Drug Administration as a non-controlled substance. Gabapentin, while not currently listed as a controlled substance, still has a potential for abuse and addiction. Gabapentin works by binding to neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. There, it works like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is a natural chemical in the brain, to affect the central nervous system. These states recognize gabapentin as a Schedule V drug. This classification is considered to have a lower potential for abuse and addiction, but there’s still a possibility. Signs and Symptoms of Gabapentin Addiction. Gabapentin addiction can cause behavioral changes similar to those of opioid addiction. These include: 12 In response to increased abuse of gabapentin,some statesare classifying gabapentin as a Schedule V controlled substance. While gabapentin appears to have low abuse potential, it is often used in conjunction with other, more addictive, drugs. Gabapentin Warnings Gabapentin, a prescription painkiller, can be a valuable alternative to opioids due to its lower addictive potential. Nevertheless, addiction and abuse of the medication can still occur, and there is also a risk of gabapentin overdose. Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substances. Illegal diversion of gabapentin has led to its illicit availability on the streets, as well. Using gabapentin with opioids can be dangerous. On the street, gabapentin is sold under various nicknames, including “gabbies.” 4 One study found that gabapentin is used as a cutting agent in street heroin, increasing the potential for abuse and the development of dangerous health effects. 4 . Nonmedical use of gabapentin may be fueled by: 4 Although research shows that gabapentin has lower abuse and addiction potential than other medications, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and prescription stimulants like Adderall, some people should proceed with caution based on their medical conditions and history. Abstract. This review summarizes current evidence on the abuse and misuse of the gabapentinoids pregabalin and gabapentin. Pharmacovigilance studies, register-based studies, surveys, clinical toxicology studies, and forensic toxicology studies were identified and scrutinized with the goal to define the problem, identify risk factors, and discuss possible methods to reduce the potential for Gabapentin is not likely to cause addiction, but it may lead to dependence or misuse under certain conditions. As such, doctors prescribe gabapentin carefully to avoid withdrawal symptoms and Gabapentin is easily prescribed without restriction, and escalating doses are recommended. 3,4 It is therefore easy to facilitate any misuse and addiction potential, and to stock the black market. Though gabapentin was initially marketed as a medication with low potential for abuse and is commonly thought to be safe and effective, a growing body of evidence highlights the potential risks of overprescribing the medication. Though an off-label use, gabapentin has also been found useful in treating certain mental health disorders. 3 So, during addiction treatment, a person could be prescribed gabapentin to help with symptoms of cannabis, opioid, or alcohol use disorders or to help with co-occurring mental disorders such as anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder Background and aims: Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. There is no clear evidence that gabapentinoid drugs disrupt these pathways (McAnally, Bonnet, & Kaye, 2020). Historically, gabapentinoids have been prescribed as a treatment for neuropathic pain instead of opioids to avoid abuse potential and addiction. Gabapentin abuse tends to occur in people who already have an addiction to opioids or other drugs. The effects of gabapentin intoxication have been described as a sense of calm, euphoria, and a high similar to marijuana.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |