Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
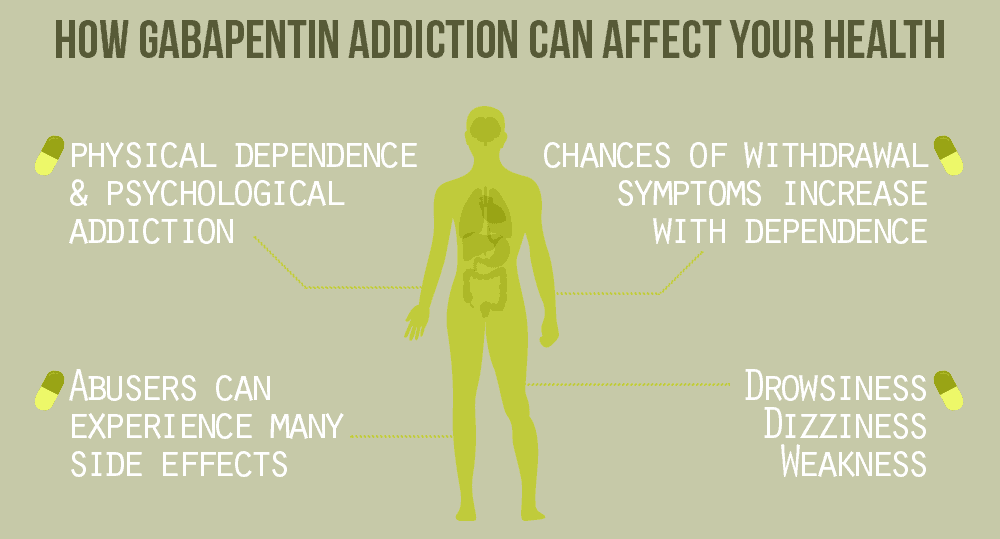
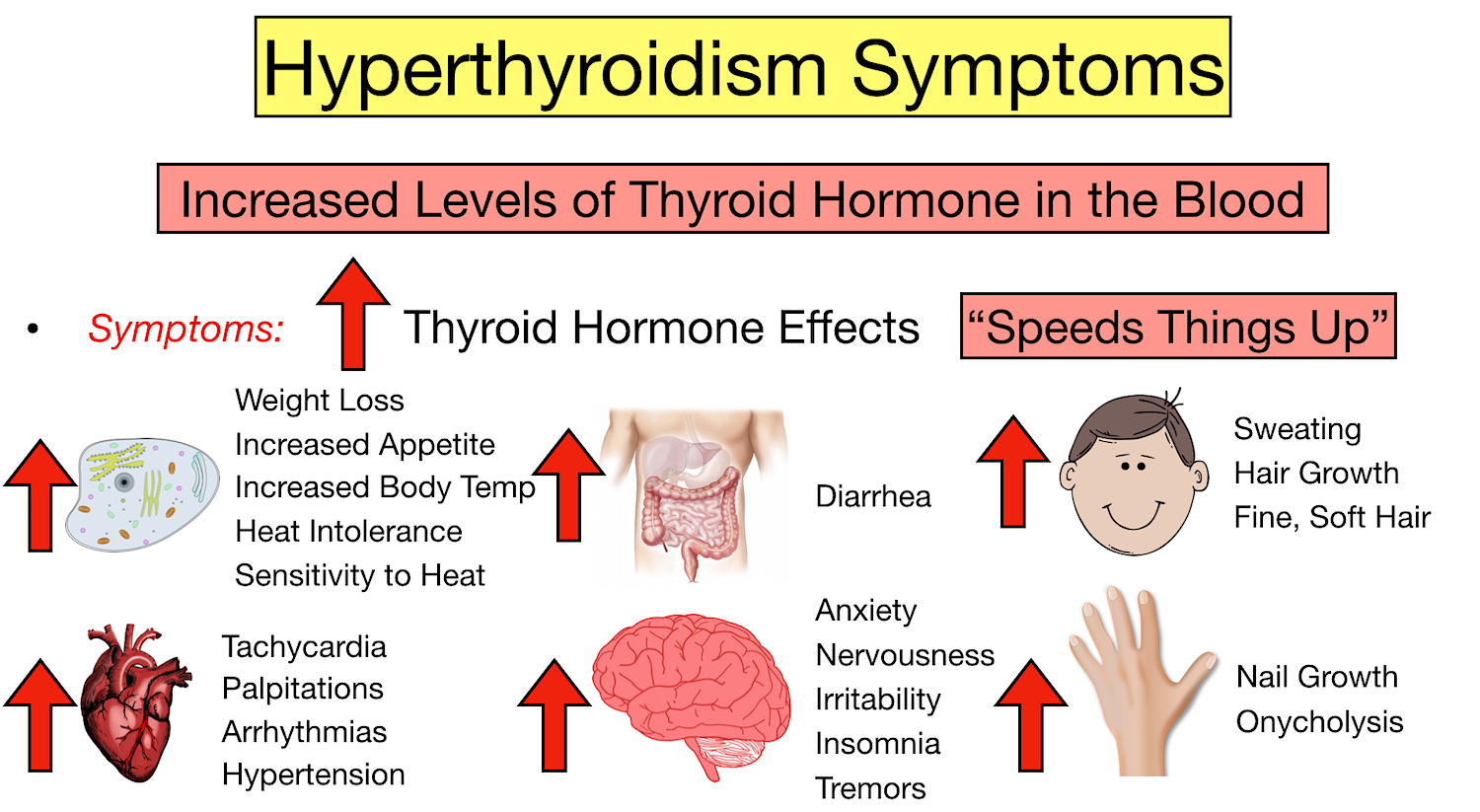
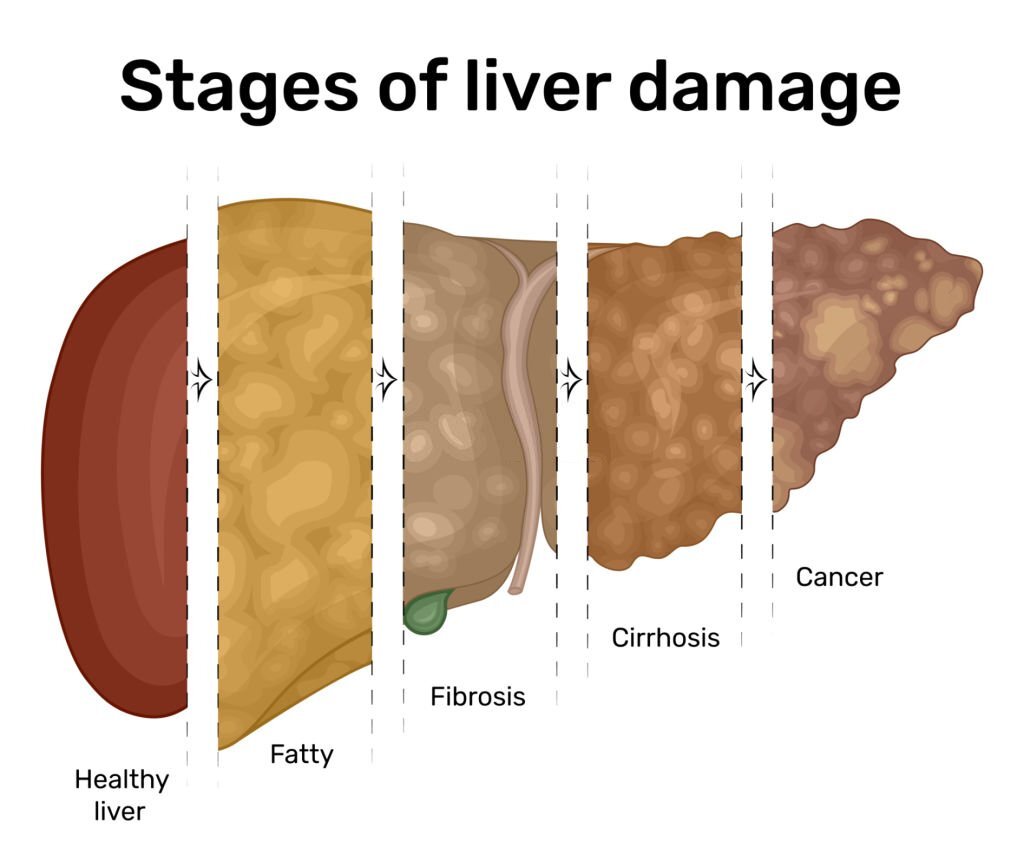
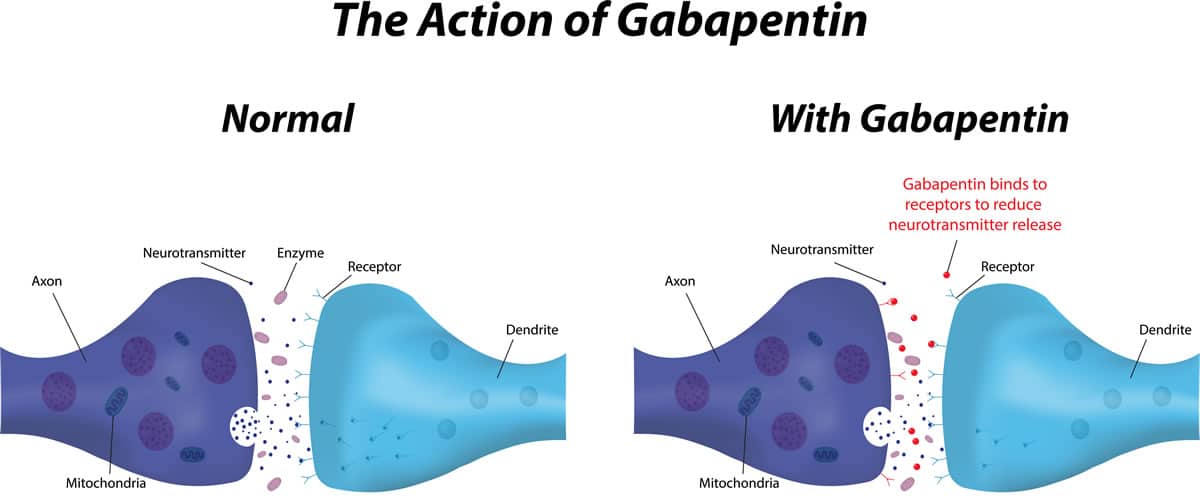
Key Takeaways: Gabapentin Effects on Organs Central Nervous System Impact: Gabapentin modulates neurotransmitter release, affecting mood. Kidney Function Monitoring: Impaired kidneys can lead to toxic gabapentin levels. Liver Health Considerations: Minimal liver metabolism; caution advised with liver issues. Gastrointestinal Side Effects: Common effects include nausea and constipation from Gabapentin and Cirrhosis of the Liver - Fatty Liver Disease Gabapentin enacarbil and gabapentin are associated with a low rate of transient serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent liver injury. Gabapentin enacarbil is a long acting form of gabapentin that is used for restless leg syndrome and for painful postherpetic neuropathy. Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. Keywords: gabapentin, hepatotoxicity, drug-induced liver injury. Our previous and several other studies shows that long term treatment with old or new anti epileptic drugs affect liver function from transient state to a fatal liver damage (1,8-10). But when considered GPN such an effect is quite less and no report of death or fatal liver damage. Liver damage from alcohol: If you’re worried about your liver health, here are some of the earliest symptoms that could indicate a problem. Foods and your liver health: Foods that are high in fat, sugar, and salt put extra stress on the liver. Learn more about how diet affects your liver. Rare cases of liver and kidney damage have been reported with Gabapentin use. Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions may be at a higher risk. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function is essential while taking Gabapentin. When it comes to gabapentin and kidney disease, kidney disease sufferers should be aware of the risks that are involved in taking gabapentin with kidney disease. Gabapentin is actually toxic to the kidneys. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Question. I have a patient with trigeminal neuralgia who was taking 1600 mg of gabapentin and had serious elevations of liver function tests (aspartate transaminase 258 U/L, alanine transaminase Therapy with gabapentin is not associated with serum aminotransferase elevations, but several cases of clinically apparent liver injury from gabapentin have been reported. Changes in liver function may be attributed to free radical damage induced by gabapentin, as documented in this study, where the drug enhanced antioxidant defense systems and elevated liver NO Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term treatment with GPN is not yet clear. It could be concluded the biochemical, morphological, and morphometric findings suggested that vitamin E coadministration is promising in attenuating the placental toxic effect of methotrexate. In this study, VIT E decreased the inflammatory and oxidative stress effect of methotrexate on the placental tissue by enhancing the level of eNOS. Liver enzymes are proteins your liver uses for normal liver functions. When your liver is damaged, these enzymes leak out into your blood and can be measured with blood testing called liver function testing. There are several liver enzymes, but the ones that show liver damage from medications are aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine What is the number one side effect of gabapentin? a high temperature, swollen glands that do not go away, your eyes or skin turn yellow (this may be less obvious on brown or black skin), unusual bruises or bleeding, severe tiredness or weakness, unexpected muscle pain or weakness, with or without a rash – these may be symptoms of a serious reaction. In most cases, gabapentin doesn’t hurt the liver or kidneys, though proper dosing is important to prevent side effects. Learn how gabapentin affects the liver and kidneys here. Gabapentin is not metabolized by the liver. Instead, it is excreted unchanged in your kidneys after circulating in your blood. Gabapentin affects nerves and chemicals in your body that are involved in some types of pain and in seizures. Herein, we report a gabapentin-induced hepatocellular injury in a patient without another identifiable cause for acute liver injury. Discontinuing gabapentin resulted in rapid reversal improvement in hepatocellular injury. Gabapentin, a common over-the-counter pain reliever and fever reducer, has been linked to rare individual case reports of liver injury. The causal relationship between gabapentin and liver damage is unclear, with the latency to onset being 1 to 8 weeks. Gabapentin (GPN) is a new antiepileptic agent currently in used as add-on therapy in adult patients suffering from partial seizures. The extent of liver damage at different dosage and long term
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |