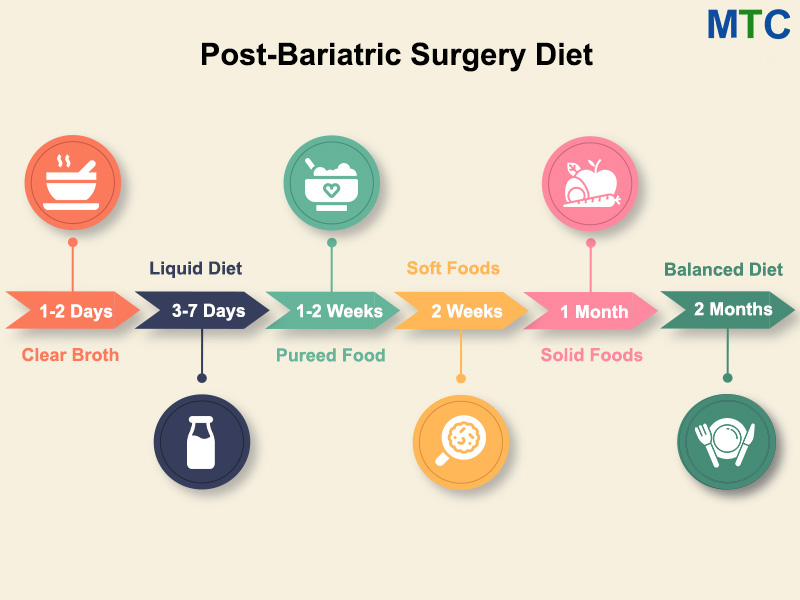
Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
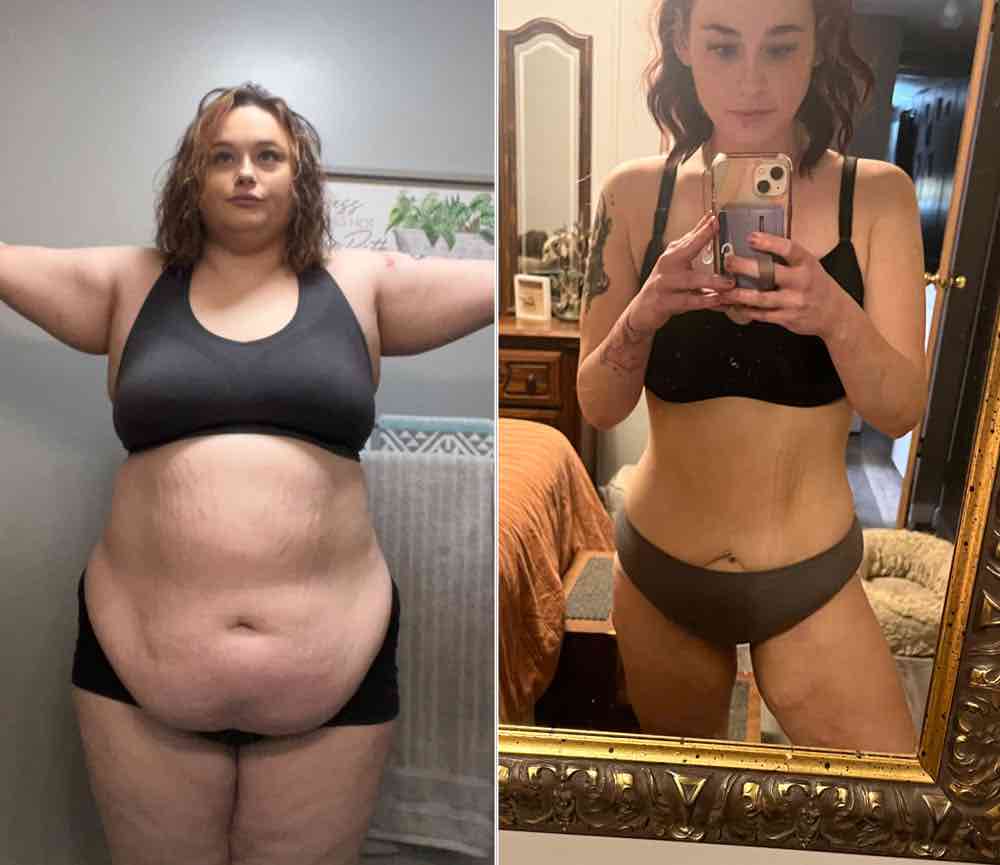
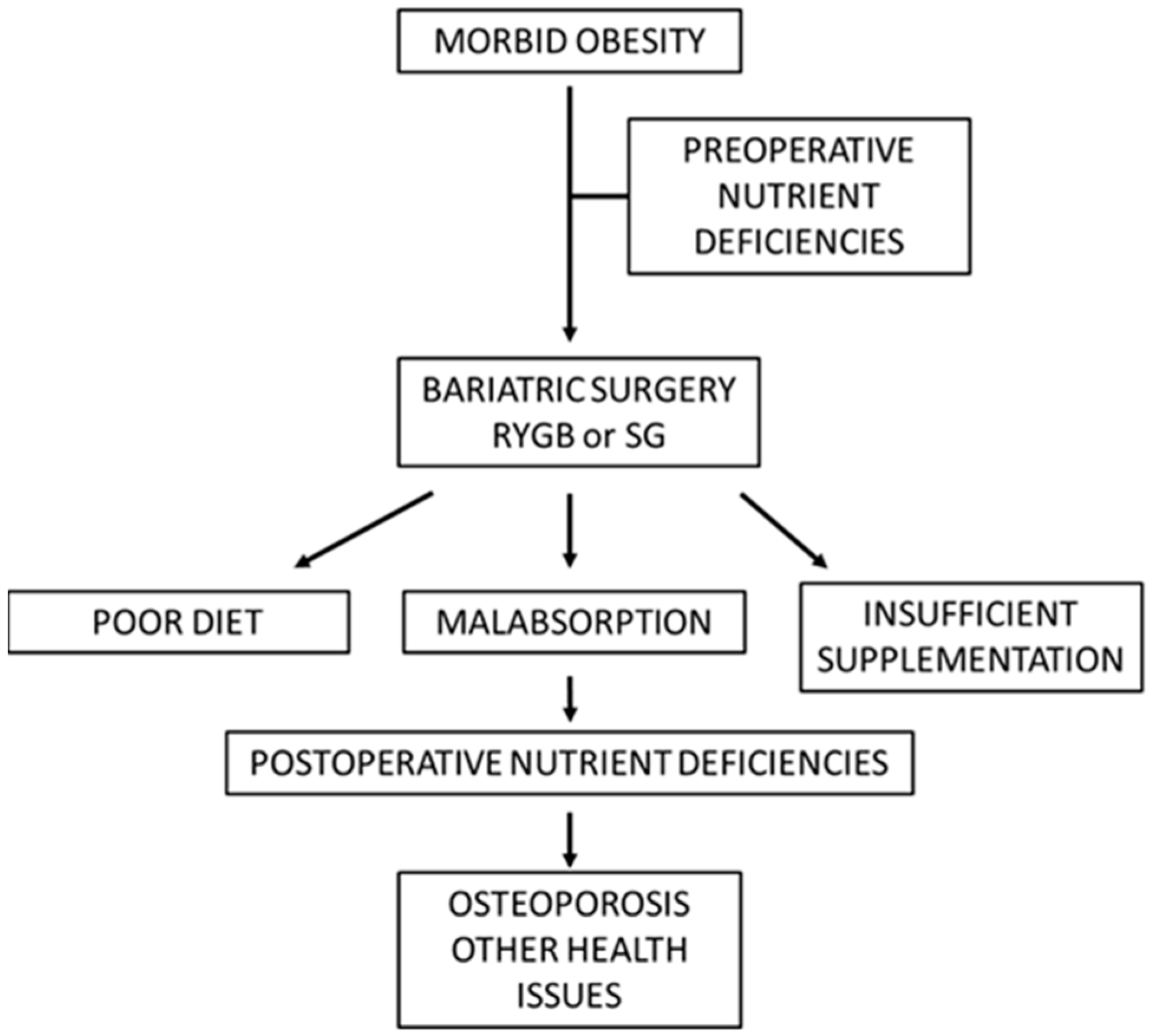
As the number of patients undergoing gastric bypass procedures increases, it is imperative to consider the pharmacokinetic changes in patients with post-surgical malabsorptive states. Pharmacokinetic changes should also be anticipated after non-bariatric surgery resulting in malabsorptive anatomy. Subgroup analyses according to a dose of gabapentin (100 mg and 1,200 mg), the timing of gabapentin administration (1-hour, 2-hours preoperative and intraoperative), and the type of bariatric surgery (gastric sleeve and gastric bypass) did not resolve the high heterogeneity of this outcome. Study authors conclude that presurgical administration of gabapentin was associated with reduced pain and opioid consumption compared with placebo among patients undergoing bariatric What is Gabapentin, and Why is it Prescribed After Bariatric Surgery? Gabapentin is mainly used to treat epilepsy, nerve pain, and restless leg syndrome. It’s also helpful for pain after bariatric surgery. Studies show it cuts postoperative pain and reduces the need for opioids in these patients. Conclusions: The use of gabapentin is effective in the management of postoperative pain in bariatric surgery. However, there is limited data regarding the opioid-sparing effect and adverse effect pro les of gabapentin fi in the bariatric surgical population. 2022 American Society of PeriAnesthesia Nurses. Published by Elsevier Inc. Pain after laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery (LGBP) is a major problem. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that can be effective in postoperative pain control. This study examined the effect of preoperative administration of gabapentin on Background: Pain after laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery (LGBP) is a major problem. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that can be effective in postoperative pain control. Objectives: This study examined the effect of preoperative administration of gabapentin on reducing pain after LGBP in patients with morbid obesity. Study authors conclude that presurgical administration of gabapentin was associated with reduced pain and opioid consumption compared with placebo among patients undergoing bariatric surgery. However, the study authors caution that “there is very limited data on the opioid-sparing effects of gabapentin in bariatric surgery.” Additional Short, Michael, Medications in the bariatric surgery patient. Memorial Bariatric Services presentation – accessed June 2014. 5. Quidley, April. et al., Perioperative management of bariatric surgery patients. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2014; 71:1253-64 6. Schauer, P. et al., Bariatric surgery v ersus intensive medical therapy for diabetes – 3-year Gabapentin [31], [38], [39], [40] 4.6, 9.9 there are numerous pharmacokinetic alterations that may occur after bariatric surgery because of the physiological I take 300mg in the morning & 600mg at night. I had surgery over 2 years ago. I have been on Gabapentin for about 7 years. At one time I took 1800 mg a day. These medications are safe for short-term use after surgery, but you should not take any other NSAID, including ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve). SIDE EFFECTS: Upset stomach SERIOUS RISKS: Stomach bleeding or ulcers. In summary, preoperative oral gabapentinoids optimized postoperative pain outcomes and reduced risk of nausea/vomiting following bariatric surgery. Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Gabapentin; Gabapentinoids; Obesity; Pain; Pregabalin. © 2022. The Author (s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature. There is evidence that gabapentin reduced the pain scores and opioid consumption in the first 24-hours after bariatric surgery. However, there is very limited data on the opioid-sparing effects of gabapentin in bariatric surgery. After any type of bariatric weight loss surgery, there are certain limitations regarding painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications that can be safely used without damaging your small new stomach. These limitations remain for the rest of your life. There is evidence that gabapentin reduced the pain scores and opioid consumption in the first 24-hours after bariatric surgery. However, there is very limited data on the opioid-sparing effects of gabapentin in bariatric surgery. Background Bariatric surgery may affect the pharmacokinetics of medications by altering the gastrointestinal physiology. Pharmacokinetic changes of first-line neuropathic pain medications such as gabapentin and pregabalin following bariatric treatment have barely been investigated. Methods In our prospective five-case study we included gabapentin- or pregabalin-treated patients undergoing Background:: Pain after laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery (LGBP) is a major problem. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that can be effective in postoperative pain control. Objectives:: This study examined the effect of preoperative administration of gabapentin on reducing pain after LGBP in patients with morbid obesity. Preemptive analgesia with gabapentinoids has been demonstrated to lower patient pain scores up to 24 hours following bariatric surgery. Preoperative administration of gabapentin has a significant effect on decreasing opioid consumption postoperatively. Available data indicate up to 33% incidence of pain in patients with neuropathy after bariatric surgery, resulting in significant decreases in quality of life and increases in health care costs. Pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying PBSNP are unclear, and the natural course is variable, with some patients experiencing spontaneous improvement
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |