Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
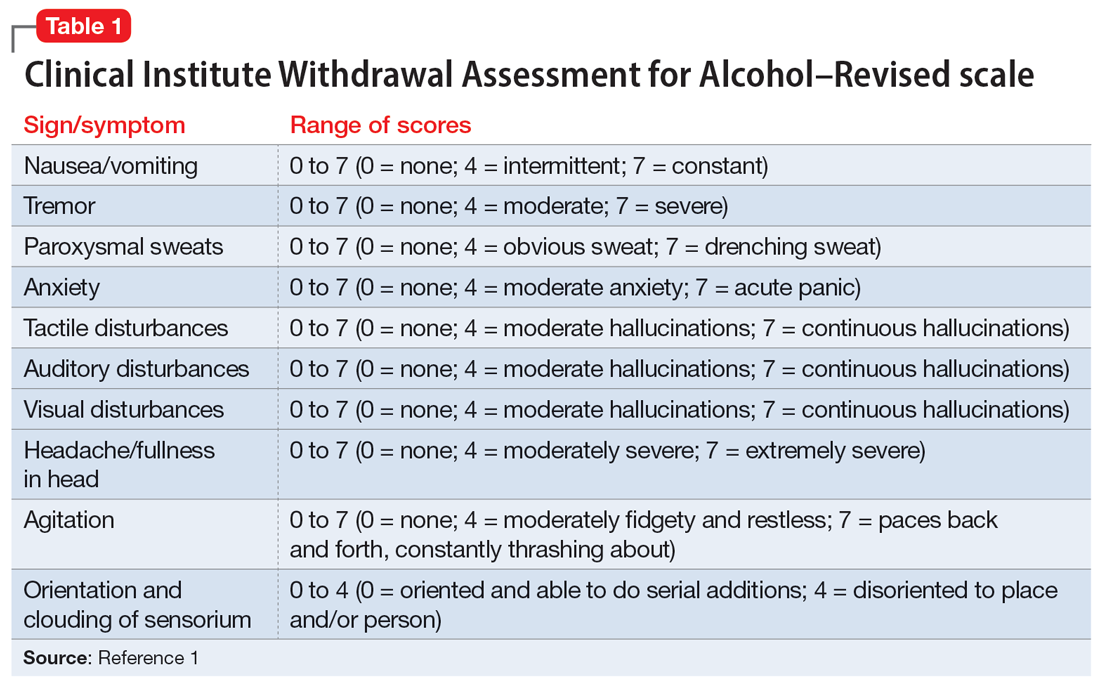
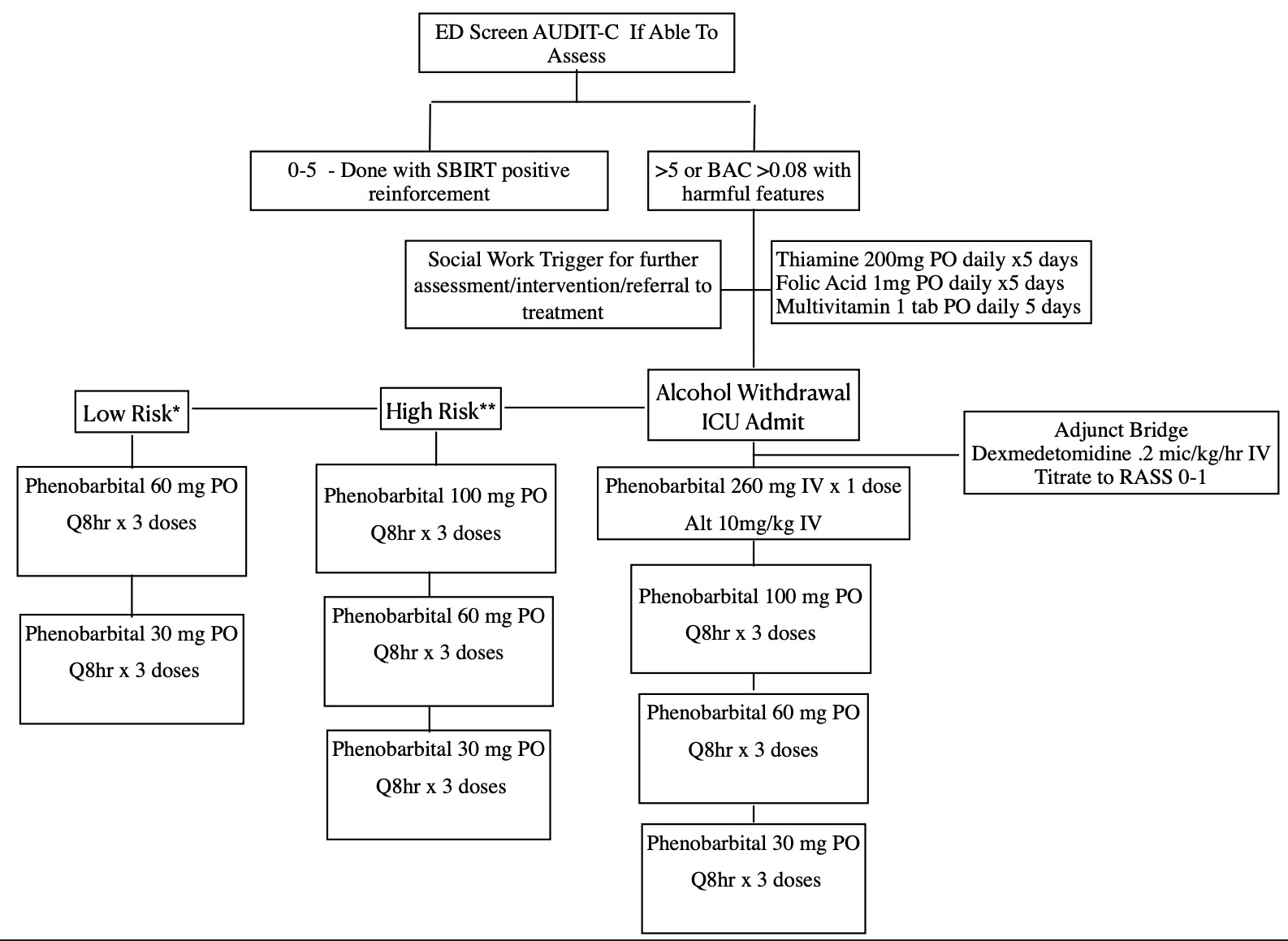
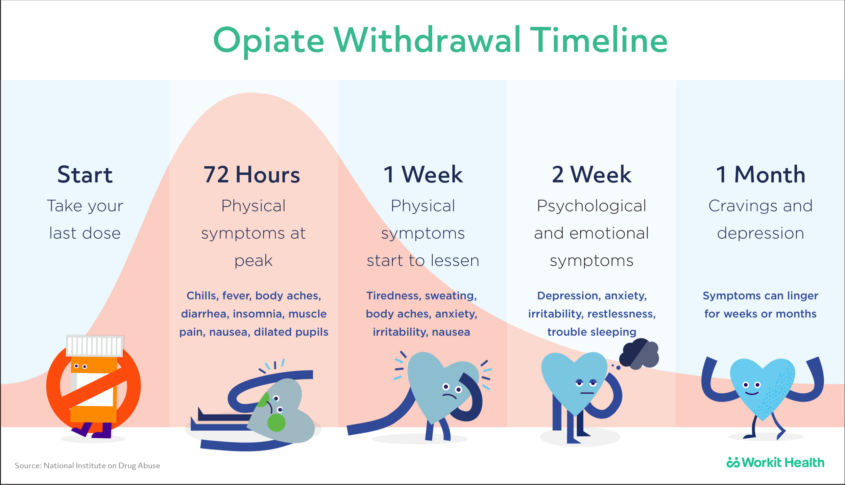
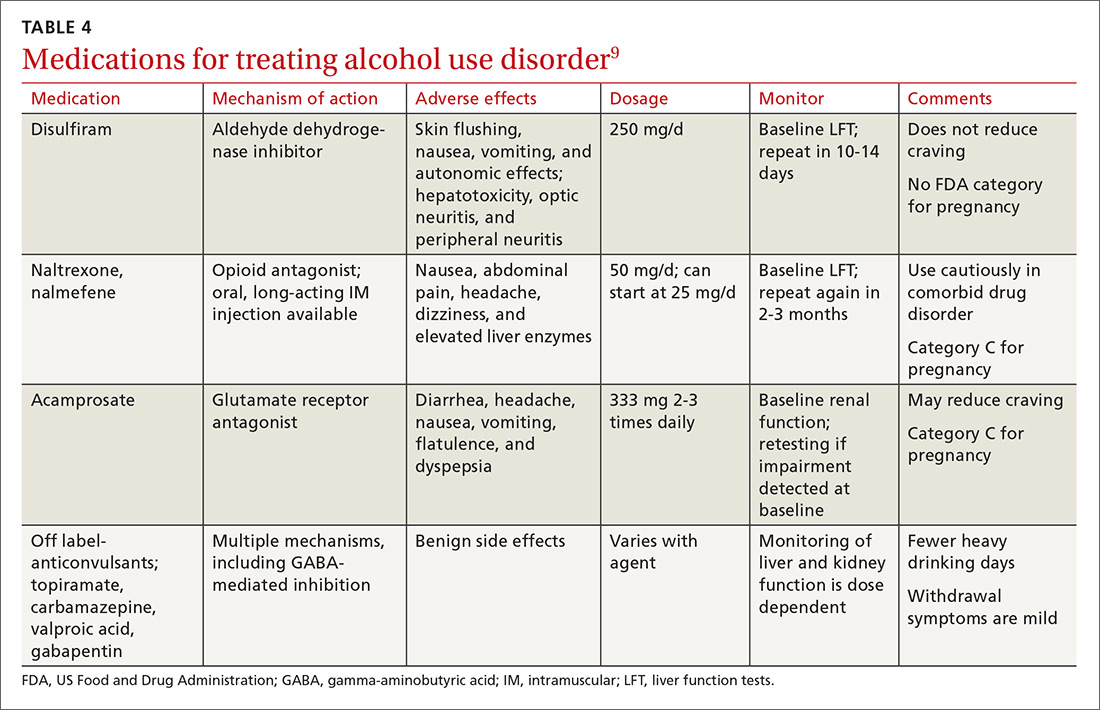
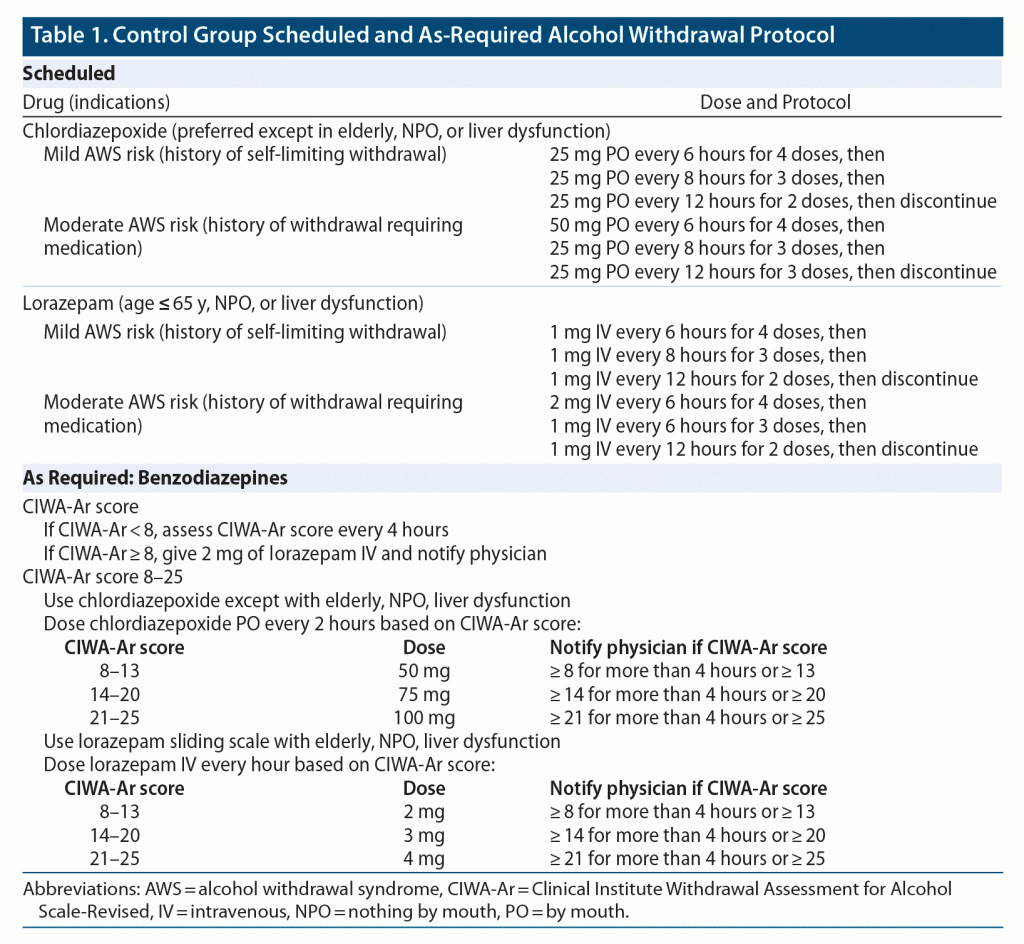
Gabapentin appears to be more beneficial for mild rather than severe alcohol withdrawal. High dose Gabapentin (1800 mg/day) is also associated with decrease in percentage of heavy drinking days. CIWA protocol adapted from San Francisco General Hospital CIWA protocol form. Severe or complicated alcohol withdrawal treatment. Severe and complicated alcohol withdrawal requires treatment in a hospital — sometimes in the ICU. While receiving treatment, healthcare providers will want to monitor you continuously to make sure you don’t develop life-threatening complications. Objectives: Recent literature suggests that gabapentin may be an alternative treatment to standard management of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, The weight of the evidence now suggests that gabapentin might be most efficacious after the initiation of abstinence to sustain it and that it might work best in those with a history of more severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms. History of severe alcohol withdrawal < 1 year ago: Voronin K, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol use disorder in patients with alcohol withdrawal symptoms: a randomized Experiments in 1955 demonstrated that alcohol-naïve volunteers given continual alcohol for longer periods developed more severe withdrawal than those who drank for shorter periods . These results imply that most people are vulnerable to the effects of the abrupt cessation of prolonged, sustained ethanol intake. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. The propensity score for being treated with gabapentin was estimated using a logistic regression model incorporating the following pretreatment variables: age, sex, number of prior admissions with alcohol withdrawal, prior documented alcohol withdrawal seizures or delirium tremens, prior treatment of alcohol withdrawal with gabapentin, prior Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29, 30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32, 33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or naltrex Another compared valproate (300 mg given 3 to 4 times daily) versus carbamazepine (200 mg 3 times daily) and reported longer hospital length of stay and greater requirement for ICU admission with carbamazepine.55 Limited data suggest a potential benefit for gabapentin (particularly for tapering), although this is primarily based on Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Sep; 33(9): 1582–1588. PMID: 19485969; ↑ Myrick, H et al. A double-blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009 Sep;33(9):1582-8. PMID: 19485969; ↑ Barrons R et al. The role of carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine in alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. CONTENTS Rapid Reference Preamble & disclaimer Diagnosis Alcohol withdrawal vs. hepatic encephalopathy Therapeutic target (CIWA vs RASS) Treatment: Phenobarbital monotherapy Phenobarbital pharmacology Advantages of phenobarbital over benzodiazepines Contraindications to phenobarbital ️ Phenobarbital guideline Checking phenobarbital levels? ️ Pitfalls of phenobarbital Alternative agents additional risk factors for developing severe or complicated withdrawal should be treated as outpatients Mild symptoms can be treated with carbamazepine or gabapentin. Benzodiazepines are Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal–related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Time to alcohol withdrawal symptom resolution, amount of benzodiazepines administered, rate of resolution of alcohol withdrawal symptoms, serious withdrawal-related complications, and hospital length of stay (LOS) were examined. Results: Eight retrospective studies (n = 2030) were included in this meta-analysis. There were no studies that Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |