Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hiatal-hernia-surgery-recovery-5086535-v1-f91db9ae2abd415085509102844d901d.jpg) |  |
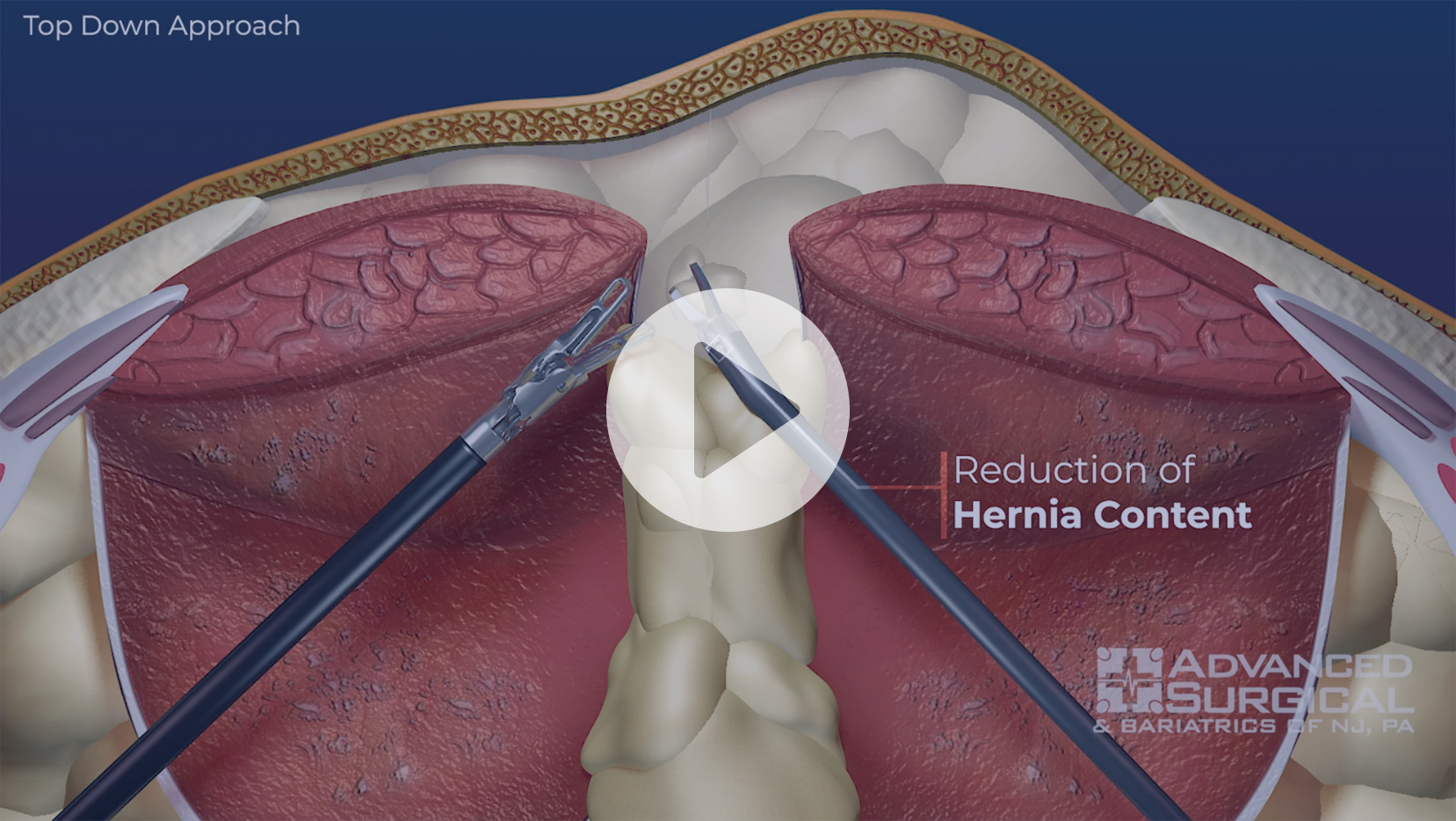 |  |
/GettyImages-157740922-9fa9bf4db6c249799b6aa0c926dc6fcf.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 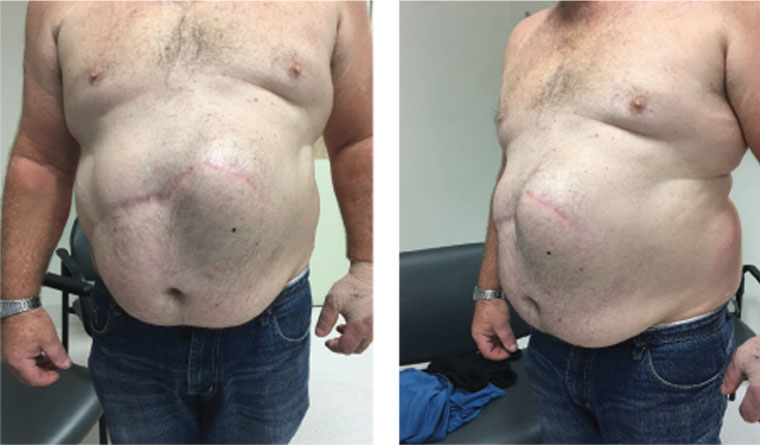 |
According to this review, pre-operative 1200 mg or less gabapentin as a single dose was associated with lesser post-operative pain and opioid demand during first 24 h after surgery, but multiple dosage of gabapentin before and after surgery did not cause a reduction in VAS score for pain, in this regard it suggests single pre-operative dose of They found that gabapentin resulted in a 35% reduction in total analgesic consumption in the first 24 hours following surgery. Gabapentin also resulted in 27% to 39% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores in the first 24 hours postoperatively. Perioperative gabapentin, 1200 mg, administered preoperatively plus 600 mg every 8 hours continued for 72 hours after surgery did not affect time to pain cessation, the rate of pain resolution, or the proportion of patients with chronic pain at 6 months or 1 year following surgery. Similarly, aside from 24 h after surgery, gabapentin significantly reduced pain with movement (25–27,31,34,35,37,38) by 18% to 28% (VAS 8.2 mm to 10.2 mm) after surgery . The pooled effects on VAS pain scores displayed significant heterogeneity, which was not explained by subgroup analyses based on surgical procedure, gabapentin dose or study Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. I began having pain 10 months after laparoscopic mesh surgery. The doctor said it was nerve pain from the ilioinguinal nerve in the groin and put me on gabapentin for a while. He said it’s to be expected and not to worry. We conclude that preoperative single-dose gabapentin decreases the intensity of acute postoperative pain, tramadol consumption and the incidence and intensity of pain in the first 6 months after inguinal herniorrhaphy. A: Doctors are turning to gabapentin for relieving pain after surgery, so that they can prescribe fewer opioids. Dizziness is a fairly common side effect of the drug, and diarrhea has also been We defined new postoperative gabapentin as fills for 7 days before surgery until 7 days after discharge. We excluded patients whose discharge disposition was hospice or death. The primary outcome was prolonged use of gabapentin, defined as a fill>90 days after discharge. Gabapentin has been shown to be effective for postoperative analgesia in a variety of operations. We evaluated the effect of a short course of perioperative gabapentin on chronic pain after IHR. This article explains the causes and risk factors of pain after hernia surgery. It also describes the ways that postoperative pain can be treated, ranging from over-the-counter painkillers to nerve blocks. Types of Pain After Hernia Surgery With an inguinal hernia, a portion of the intestine bulges through a weakness in the muscles of the groin. Yu L, Ran B, Li M, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the management of postoperative pain after lumbar spinal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine 2013; 38:1947–1952. [Google Scholar] 10. Hwang SH, Park IJ, Cho YJ, et al. The efficacy of gabapentin/pregabalin in improving pain after tonsillectomy: a meta-analysis. Multimodal analgesia has been an increasingly adopted strategy in the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery pathway, 1 which aims to reduce opioid use by using nonopioid analgesia, such as regional or epidural analgesia, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen, and gabapentinoids. 2 Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) have demonstrated that More than one-fifth of older adults prescribed gabapentin postoperatively filled a prescription >90 days after discharge, especially among patients with more comorbidities and concurrent prolonged opioid use, increasing the risk of adverse drug events and polypharmacy. The optimal management of chronic pain following inguinal hernia surgery should begin with a thorough clinical examination to rule out other causes of chronic pain and to rule out a recurrence. A scaled approach to treatment is recommended. But gabapentinoids also have risks and there is little evidence to support their use for postoperative pain relief, according to a large new study by a team of Canadian researchers. “No clinically significant analgesic effect for the perioperative use of gabapentinoids was observed. A significant number of RCTs have demonstrated conflicting results in the use of preoperative gabapentin. 19 Bharti et al 20 studied gabapentin administration among patients (n=40) undergoing mastectomy (20 received gabapentin and 20 received placebo) and demonstrated a reduction in the amount of morphine required during the initial 24 hours We evaluated the effect of perioperative gabapentin on chronic pain after IHR. This was a double-blinded, randomized study involving male patients ≥18 years old with an initial inguinal hernia and no chronic pain or psychiatric disorder. It is not uncommon to experience pain after hernia surgery as you might with any other surgery. With inguinal hernia surgery of the groin, however, the pain may be due to the normal healing of the wound, an immune reaction to the mesh used to repair the hernia, or damage caused to local nerves (resulting in a pain condition known as post-herniorrhaphy neuralgia). In this trustworthy systematic review, use of gabapentin for post-operative pain management was scrutinized. In summary, the quality of evidence for a clinically relevant benefit of gabapentin is low, and, importantly, harm may be present.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hiatal-hernia-surgery-recovery-5086535-v1-f91db9ae2abd415085509102844d901d.jpg) |  |
 |  |
/GettyImages-157740922-9fa9bf4db6c249799b6aa0c926dc6fcf.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |