Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
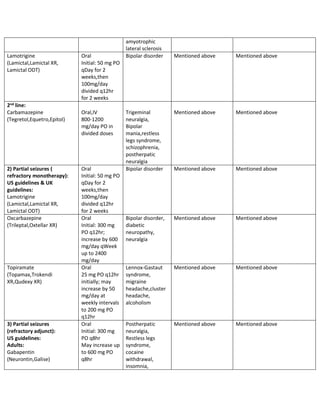 |  |
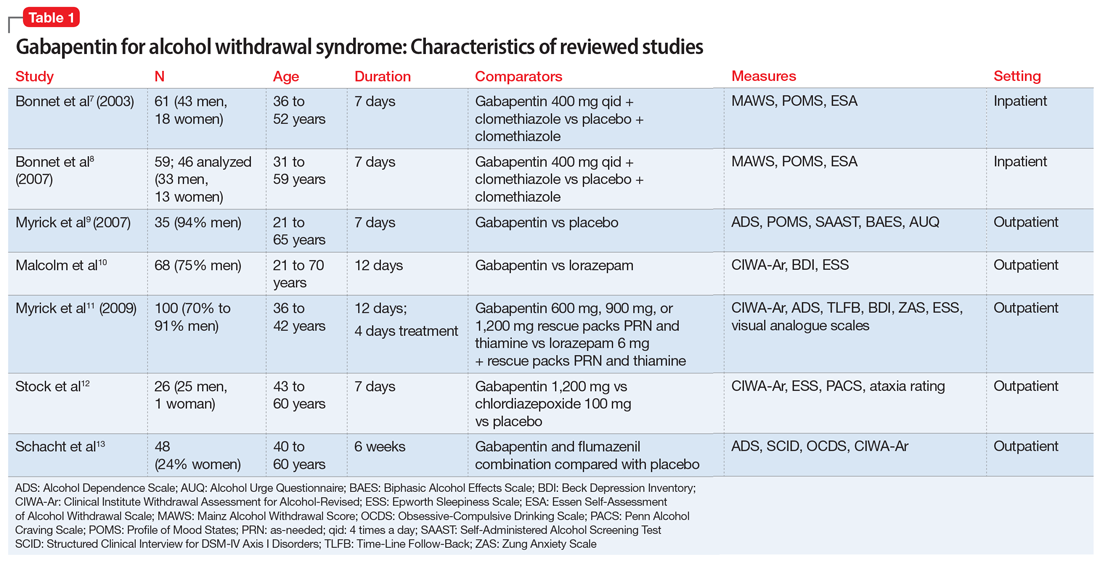
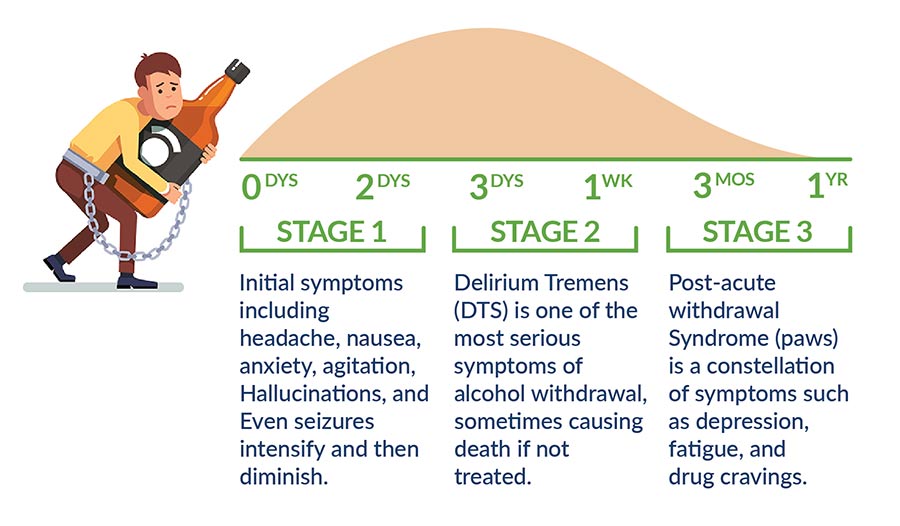
Medically supervised alcohol withdrawal is indicated for patients with current symptoms of withdrawal or at risk of developing alcohol withdrawal. For many individuals with mild symptoms and no history of seizures or DT, supervised withdrawal can be safely and effectively managed in the ambulatory setting. Gabapentin's ease of use, rapid titration, good tolerability, and efficacy in both the withdrawal and chronic phases of treatment make it particularly appealing. In summary, several NBACs appear to be beneficial in treating AWS and alcohol use disorders. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Limited data for gabapentin in alcohol use disorder treatment. Seizure precautions if deemed at risk. Assessment for alcohol use disorder and motivational interviewing. CIWA. CIWA was originally designed as a tool for alcohol withdrawal research and is validated only in mild to moderate alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Another compared valproate (300 mg given 3 to 4 times daily) versus carbamazepine (200 mg 3 times daily) and reported longer hospital length of stay and greater requirement for ICU admission with carbamazepine.55 Limited data suggest a potential benefit for gabapentin (particularly for tapering), although this is primarily based on Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal Benzodiazepine medications are the standard treatment for alcohol use disorder and alcohol withdrawal. They help lower your risk for seizures and Abrupt withdrawal from gabapentin has precipitated seizures and status epilepticus; on- and off-titration of gabapentin is indicated. The overall incidence of adverse events and types of adverse events are similar in men and women across the pivotal trials for approved indications. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that helps to control and reduce severe epileptic seizures. According to a 2020 study, people who took gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal tolerated The propensity score for being treated with gabapentin was estimated using a logistic regression model incorporating the following pretreatment variables: age, sex, number of prior admissions with alcohol withdrawal, prior documented alcohol withdrawal seizures or delirium tremens, prior treatment of alcohol withdrawal with gabapentin, prior One possible form of help in decreasing alcohol withdrawal symptoms is gabapentin, a medicine mostly used to control seizures and neuropathic pain. Here, we explore the function of gabapentin in relation to alcohol withdrawal: how it works, the many conditions it treats, and the important things to keep in mind when thinking about taking it Alcohol withdrawal seizures most commonly occur 12–24 hrs after the individual’s last drink, though the risk for seizures can last for up to 48 hrs following abstinence. 24 Seizures occur in 5–10% of individuals with active AWS and are typically generalized tonic-clonic. 21, 25 Approximately two-thirds of individuals who have an initial Researchers say the medication used for nerve pain and partial seizures can help ease symptoms of alcohol withdrawal. Getty Images. A new study reports the nerve pain reliever This explains its use in treating nerve-related pain such as shingles, as well as epileptic seizures. In fact, seizures are among the more extreme reactions people can have to alcohol withdrawal, and can be prevented by taking gabapentin. For alcohol use disorder (AUD), gabapentin is considered “off-label.” An off-label medication is a drug Patients at minimal risk have none of the following factors: history of alcohol withdrawal–related delirium or seizures, multiple prior withdrawal episodes, comorbid illness, age older than 65 The ambulatory management of mild alcohol withdrawal, the initial diagnosis and treatment of alcohol use disorder, and specific conditions due to alcohol-related organ damage (eg, cirrhosis, pancreatitis) are discussed separately. Secondary outcome measures included total average benzodiazepine and gabapentin dosage used during hospitalization and the development of severe complications of withdrawal including seizures or delirium. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |