Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
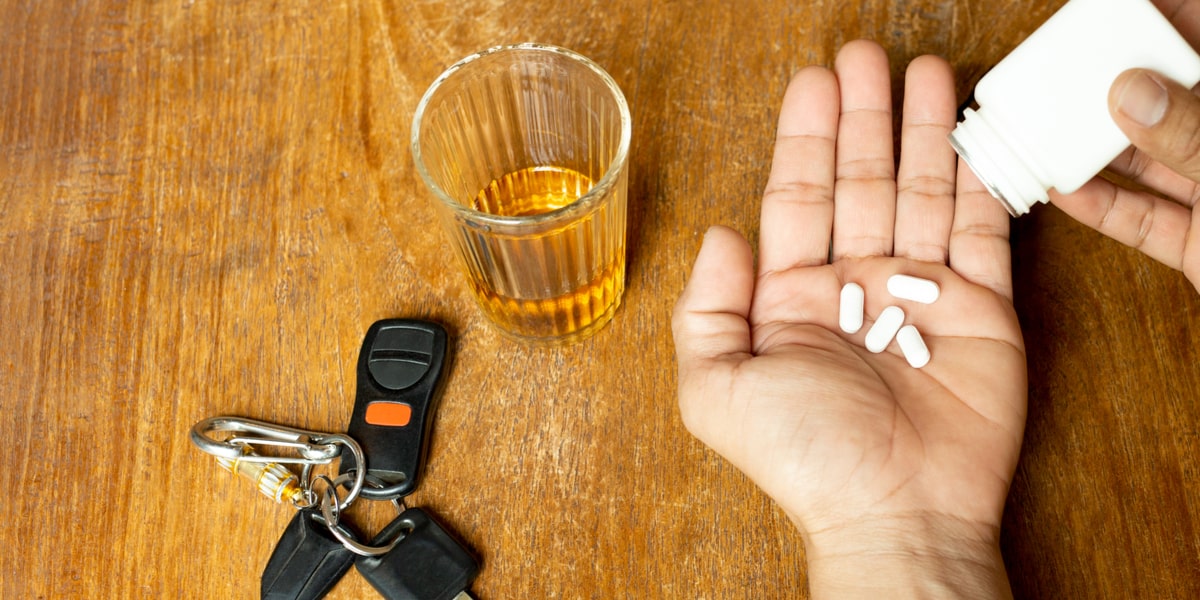
Gabapentin and alcohol already depress the central nervous system, so adding other sedatives, like opioids, benzodiazepines, or sleep aids, can be extremely dangerous. Avoiding these substances decreases the cumulative risk of respiratory depression, unconsciousness, and overdose. In addition to alcohol, those taking gabapentin should completely avoid real and synthetic opioids and many other substances. Side Effects of Gabapentin and Alcohol: Why Mixing Them Can Be Dangerous. Gabapentin is a widely prescribed medication for many conditions, including restless leg syndrome, hot flashes, epilepsy, and neuropathic pain. Patients who have just started taking gabapentin are highly advised to avoid drinking alcohol until the specific side effects of gabapentin are known. Alcohol side effects can mimic, even intensify, those of gabapentin making it difficult to diagnose potentially adverse effects. Alcohol can increase the nervous system side effects of gabapentin such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. Some people may also experience impairment in thinking and judgment. You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with gabapentin. Alcohol can increase the nervous system side effects of gabapentin such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. Some people may also experience impairment in thinking and judgment. You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with gabapentin. Mixing alcohol and gabapentin can cause the effects of the two substances to become heightened. This means that the side effects of gabapentin can become worse while drinking alcohol, and the effects of alcohol can be more severe when drank while taking gabapentin. Mixing prescription drugs like Gabapentin with alcohol can be very dangerous, as both have similar nervous system depressant effects. This combination can be incredibly dangerous, with side effects ranging from mild (drowsiness, dizziness, and stumbling) to more dangerous symptoms (trouble breathing, confusion & impaired mobility leading to Gabapentin carries a significant risk when mixed with alcohol. Both substances act as depressants, and their combined effects can lead to serious health complications. It's crucial to understand the dangers and potential consequences of combining these substances to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Perceptions regarding the use of gabapentin for alcohol use disorder (AUD) have shifted over time. 1–4 Early on, the drug was deemed to be benign and effective. 4–6 But more and more, concerns are being raised about its recreational use to achieve euphoria, 7 and the drug is often misused by vulnerable populations, particularly those with opioid use disorder. 7–9 Like gabapentin, it's taken for epilepsy and nerve pain. It can also be taken for anxiety. But there are differences between pregabalin and gabapentin. Pregabalin can be taken less often and in different doses to gabapentin. If you need to change to pregabalin, your doctor will explain how to swap safely from gabapentin. Alcohol can interact with gabapentin and increase the risk of side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, and difficulty concentrating. In addition, alcohol can increase the risk of kidney damage or other serious side effects. Mixing gabapentin and alcohol can worsen existing side effects and increase their severity. It also increases the risk of overdose or death. 6 Generally, you should avoid any medication that can cause dizziness while taking gabapentin. Alcohol can increase the nervous system side effects of gabapentin such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. Some people may also experience impairment in thinking and judgment. You should avoid or limit the use of alcohol while being treated with gabapentin. When taking gabapentin, consuming alcohol is contraindicated, presenting several potentially disastrous risks and possible complications. These risks only begin with the high chances of experiencing more severe side effects that can result in dangerous behavior like driving while extremely sleepy. Gabapentin is commonly misused with alcohol because the drugs have similar mechanisms. Gabapentin and alcohol target the same receptors in the brain and amplify the effects of the other. Abusing gabapentin and alcohol together is extremely dangerous and vastly increases the risk of side effects and overdose. It is strongly advised not to drink alcohol while taking gabapentin. Alcohol can increase the nervous system side effects of gabapentin such as dizziness, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating. In some cases, it can also lead to impairment in thinking and judgment. What might happen if I mix gabapentin with alcohol? Dizziness, drowsiness, tiredness, fever, and nystagmus (a rapid and uncontrollable movement of the eyes). Drowsiness caused by gabapentin may affect your ability to drive or operate machinery. Alcohol and other drugs with sedative properties enhance this effect. Drinking alcohol with gabapentin could increase sleepiness or dizziness. What else do I need to know about gabapentin? Never stop taking gabapentin without talking to your healthcare provider first. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause serious problems, including increasing your risk of seizures (if you are taking gabapentin to control
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |