Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
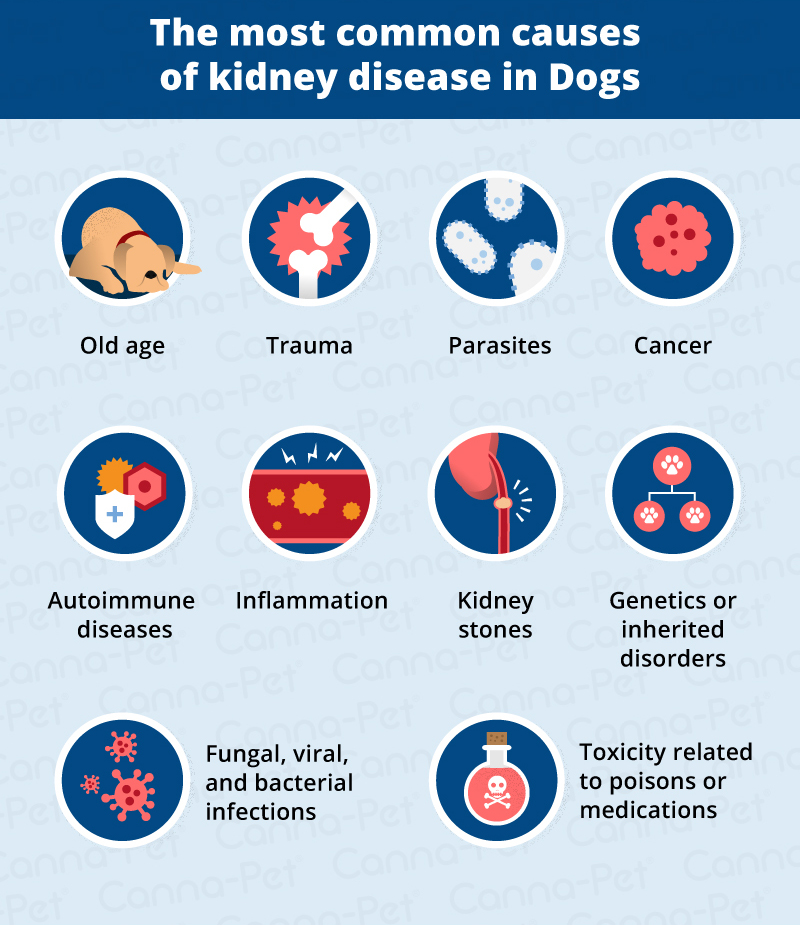 |  |
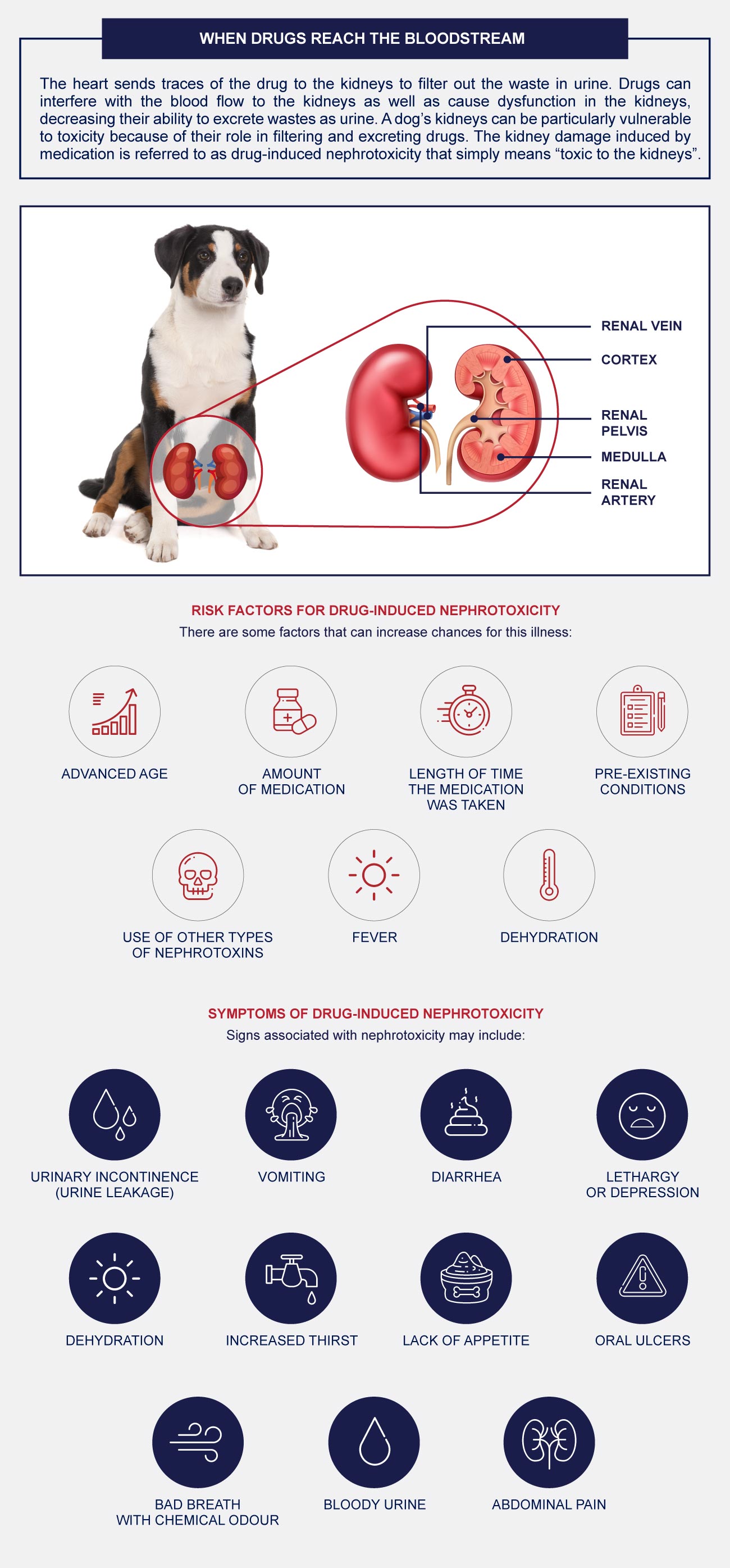
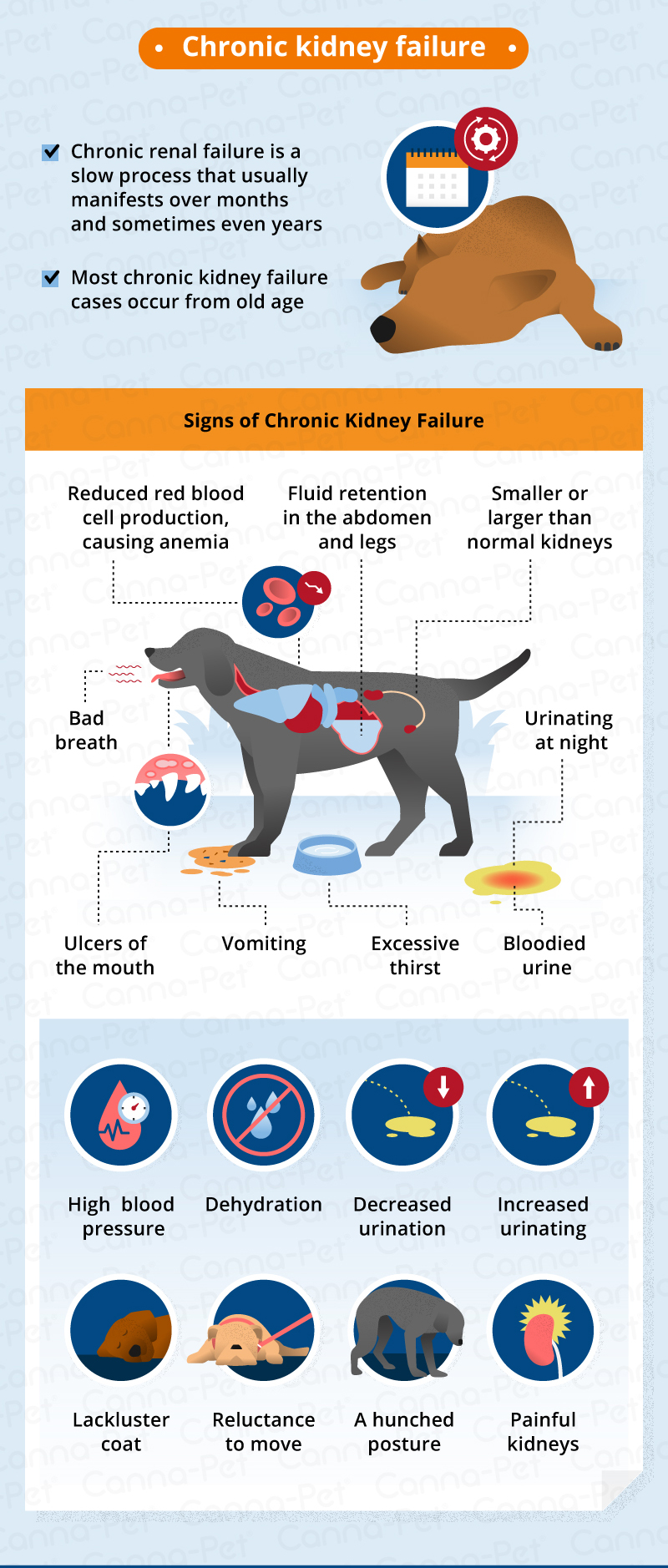
9. Can gabapentin cause liver or kidney damage in dogs? Gabapentin does not typically cause direct liver or kidney damage. However, it’s metabolized by the kidneys, so dogs with kidney disease may require lower doses to avoid side effects. 10. What happens if you stop gabapentin suddenly in dogs? 2. Is Gabapentin Safe for Dogs with Kidney Issues? 🩺. Gabapentin can be safely used in dogs with kidney impairments, but dosage adjustments are often necessary. Renal Clearance: Reduced kidney function can slow the elimination of gabapentin, increasing its concentration in the bloodstream. Monitoring: Regular blood tests to assess kidney In conclusion, gabapentin is generally not considered directly bad for dogs’ livers, particularly when used appropriately under veterinary guidance. However, it is essential to consider factors such as pre-existing kidney or liver conditions, monitor for side effects, and never abruptly stop treatment. Although dogs with kidney disease may need a lower dose due to slower excretion, gabapentin does not seem to have adverse effects on the kidneys like NSAIDs do. One of the drawbacks to gabapentin as a pain medication, however, is that it does not have anti-inflammatory effects like NSAIDs do. Does gabapentin damage the kidneys? Gabapentin itself is not known to directly cause kidney damage in dogs. However, it’s essential to understand that the way gabapentin is processed in a dog’s body means that kidney health plays a vital role in how the drug works and whether dose adjustments are necessary. 1. Is gabapentin a strong painkiller for dogs? 2. How long does gabapentin take to work in dogs? 3. Can gabapentin make a dog unable to walk? 4. Is gabapentin hard on a dog’s kidneys? 5. What organs can gabapentin damage in dogs? 6. Can gabapentin make dogs sleepy? 7. What is better than gabapentin for dogs? 8. How does gabapentin make a dog Gabapentin is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys in dogs, so it is important to monitor kidney function in dogs receiving long-term gabapentin therapy. Liver damage is rare but can occur in some cases. When Is It Contraindicated to Use Gabapentin in Dogs? Because gabapentin is predominantly excreted by the kidneys, dogs with kidney disease should not be treated with gabapentin. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Is Gabapentin OK for Dogs’ Kidneys? A Comprehensive Guide. The short answer is: generally, yes, gabapentin is considered safe for dogs’ kidneys at appropriate doses. However, there are nuances to this answer that every dog owner should understand. Gabapentin should start to take effect fairly quickly, and relief should be noticed within one to two hours of administration. It’s a short-acting drug, and the effects will be gone in 24 hours. That said, the medication may last longer in dogs with kidney or liver impairment. The two most important factors include breed and individual reaction to the medication. Another important factor is the health status of the dog’s kidneys. Since gabapentin is eliminated from the body through the kidneys, dogs with damaged or impaired kidneys need modified doses of gabapentin. If you are getting your dog’s gabapentin from a human pharmacy, If your dog now or ever has had liver or kidney disease 1,3. Any history of a bad reaction to So dogs with kidney or liver problems may have more prolonged side effects. Your veterinarian may want to monitor kidney and liver blood values when using gabapentin long-term. Recommended Most dogs are prescribed gabapentin to manage chronic pain associated with arthritis and cancer as well as neural and post-operative pain. It’s often prescribed alongside NSAIDs or opiates. It’s thought to amplify their effect on pain management despite potential side effects. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is often used for nerve pain and is safe for dogs with kidney disease. It is typically used to manage conditions like arthritis, spinal issues , and post-surgical pain. It does not have significant effects on kidney function, making it a reliable option. While generally considered safe, it’s crucial to understand that gabapentin can interact with certain other drugs, potentially leading to adverse effects. Combining gabapentin with certain medications can alter its effectiveness or even pose a risk to your dog’s health. Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication for dogs, used primarily to manage chronic pain, especially from conditions like arthritis or neuropathic pain, and to help control seizures. It can be a highly effective treatment option, but when given long-term, some pet owners wonder about the potential side effects. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the long-term effects of Background: Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Although dogs with kidney disease may need a lower dose due to slower excretion, gabapentin does not seem to have adverse effects on the kidneys like NSAIDs do. One of the drawbacks to gabapentin as a pain medication, however, is that it does not have anti-inflammatory effects like NSAIDs do.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |