Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/alcohol-dementia-62980_final-9155b590ac9749fbadc70810f3c9414c.png) |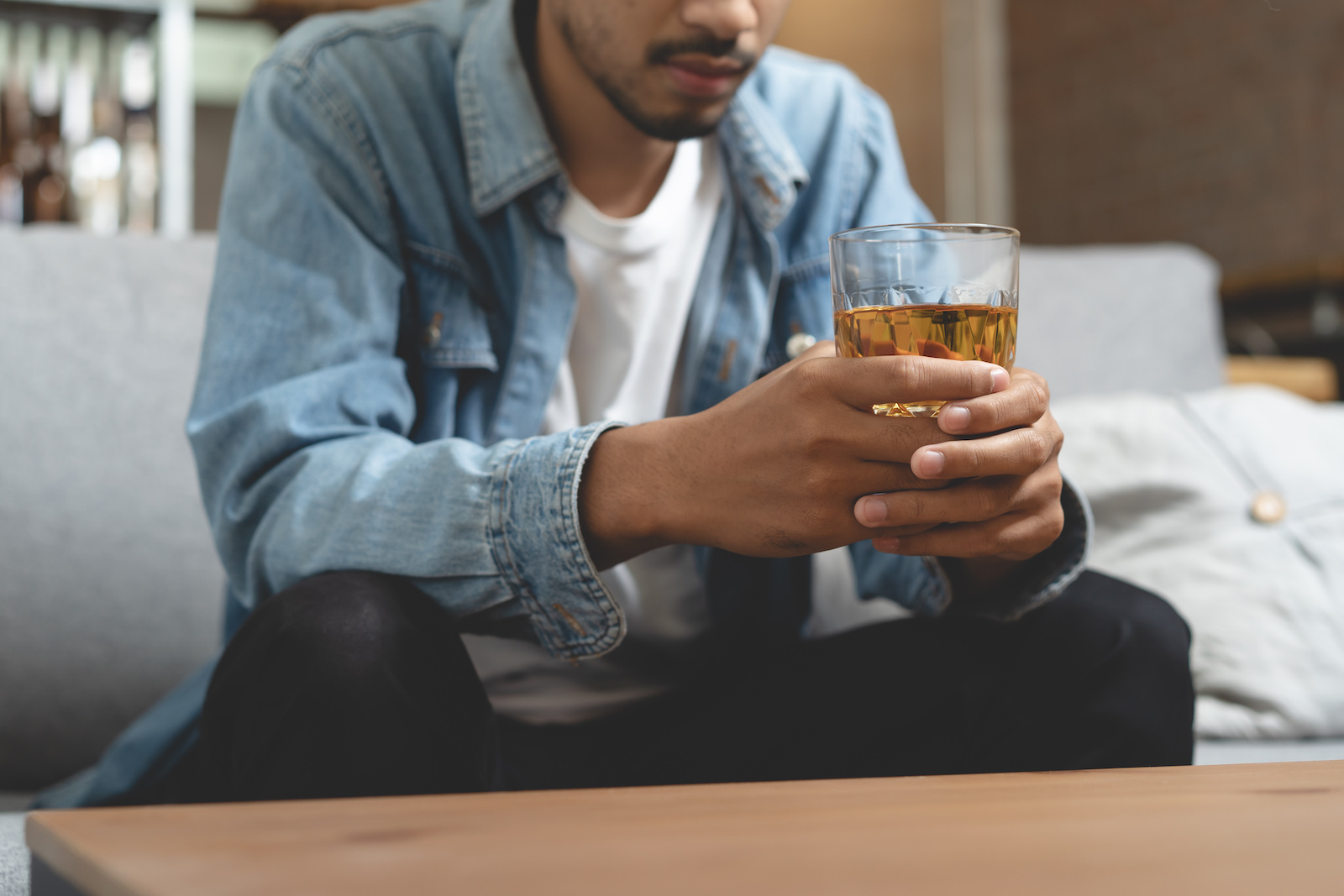  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
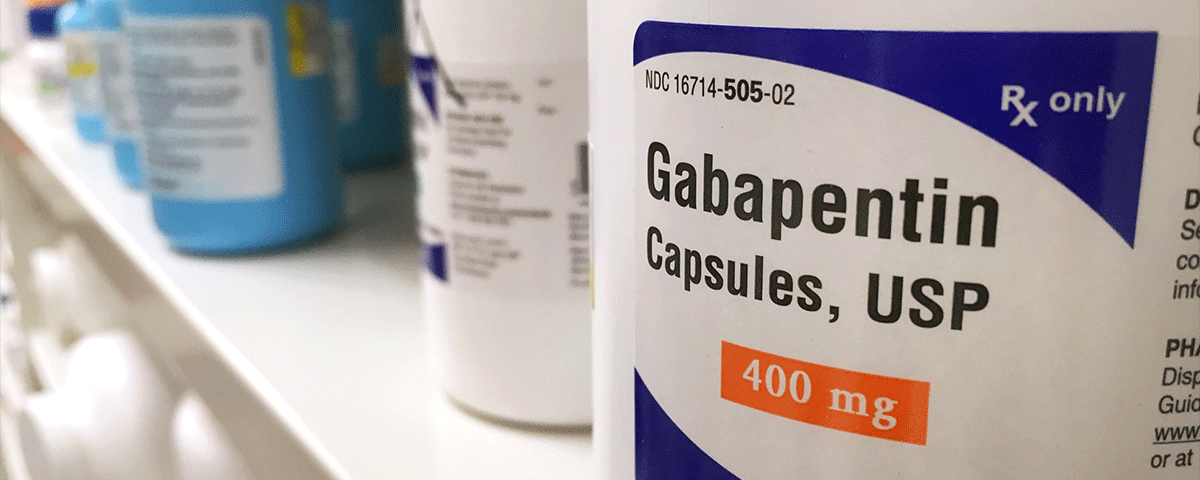
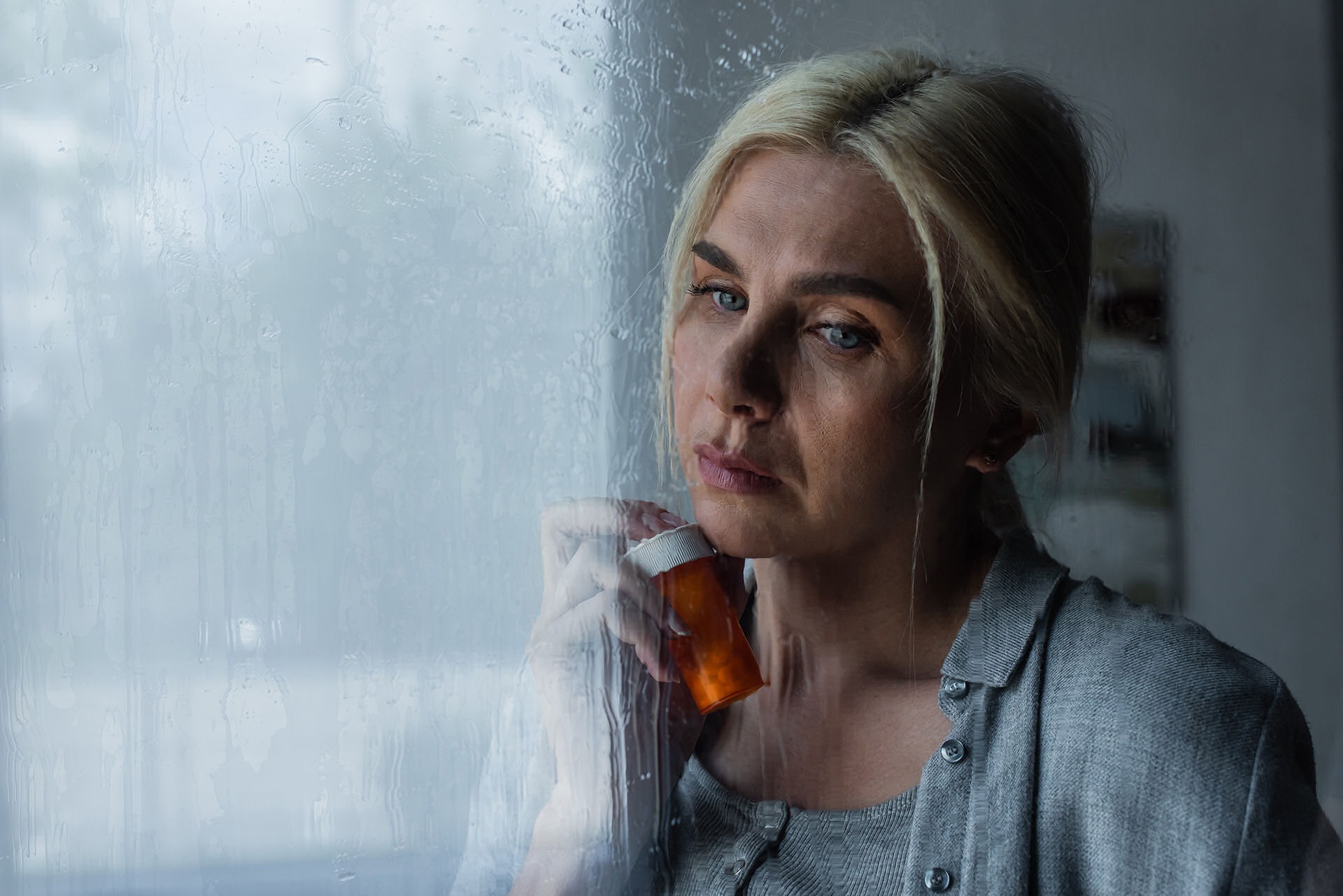
When you stop taking gabapentin, you'll need to reduce your dose gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms. Do not stop taking gabapentin without talking to your doctor. Talk to your doctor if you're concerned about becoming physically dependent on gabapentin. Other side effects. These are not all the side effects of gabapentin. Adding alcohol to the mix is strongly cautioned in the use of gabapentin. Alcohol use disorder PLUS the prescription depressant can be a recipe for disaster. Let’s consider each separately and then when used as a whole. How Does Alcohol Affect the Body? Nearly 90% of adults age 18 and older report having consumed some alcohol in their lives. While the evidence suggests that gabapentin alone does not cause memory loss, it can lead to brain fog or minor confusion. However, combining gabapentin with other drugs like baclofen can result in significant memory loss and impairment. 4. Can the combination impact my memory? Yes, both gabapentin and alcohol can individually impair memory. When combined, the risk for memory gaps and difficulties concentrating can increase. 5. I'm on gabapentin. What should I watch out for if I drink alcohol? For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Neurontin (gabapentin) is associated with memory loss in a dose dependent fashion, meaning the higher doses you take, the more chance there is of having some sort of Combining gabapentin with alcohol poses significant risks. Understanding these dangers is crucial for anyone considering using gabapentin alongside alcohol. The interplay between gabapentin and alcohol can amplify each other's effects, leading to heightened side effects. Gabapentin carries a significant risk when mixed with alcohol. Both substances act as depressants, and their combined effects can lead to serious health complications. It's crucial to understand the dangers and potential consequences of combining these substances to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Doctors often prescribe gabapentin off-label to treat conditions such as: alcohol addiction. In people with partial seizures, gabapentin works by decreasing abnormal activity in the brain. Experts believe gabapentin may cause brain cells to produce more of a chemical called GABA, which reduces abnormal electrical activity of brain cells. Gabapentin and alcohol both suppress brain activity, resulting in many cognitive issues, such as: Difficulty focusing or staying concentrated on tasks. Short-term memory loss making it difficult to remember recent events or conversations. Increased confusion, specifically in unfamiliar situations. Memory loss. Weight gain. Movement problems: coordination problems, being unsteady, tremors, jerky movements. Drinking alcohol with gabapentin could increase Gabapentin and alcohol can enhance each other’s depressant effects on the central nervous system, leading to intense intoxication and impaired function. If you suspect that you or someone you know is overdosing on alcohol and gabapentin, call 911 immediately. An overdose is potentially life-threatening. Gabapentin and Alcohol Memory Loss. Gabapentin and alcohol can impair memory formation. It is not well-known why these substances can impact memory. Such drugs are on the list because they share troubling side effects—confusion, clouded thinking, and memory lapses—that can lead to falls, fractures, and auto accidents. What the studies found It's important to note that neither of these studies was a randomized controlled clinical trial, so neither proved that either type of drug causes Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. Memory loss related to gabapentin use may range from mild forgetfulness to noticeable difficulties with recall or focus. For some, these changes may resolve as the body adjusts to the medication, while for others, they might persist, requiring medical attention. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin works in the brain to prevent seizures and relieve pain for certain conditions in the nervous system. It is not used for routine pain caused by minor injuries or arthritis. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. The risk of memory loss is heightened when the drugs are taken for more than a short time or used with other anticholinergic drugs. Older adults are particularly vulnerable to the other adverse effects of anticholinergic drugs, including constipation (which, in turn, can cause urinary incontinence), blurred vision, dizziness, anxiety Prolonged combined use of gabapentin and alcohol creates lasting health complications that extend beyond immediate risks. Regular consumption of both substances leads to severe cognitive decline, affecting memory formation and information-processing abilities.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/alcohol-dementia-62980_final-9155b590ac9749fbadc70810f3c9414c.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |