Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
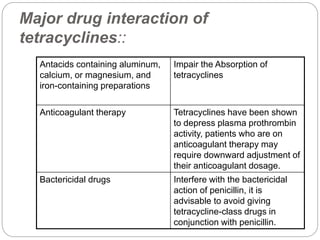
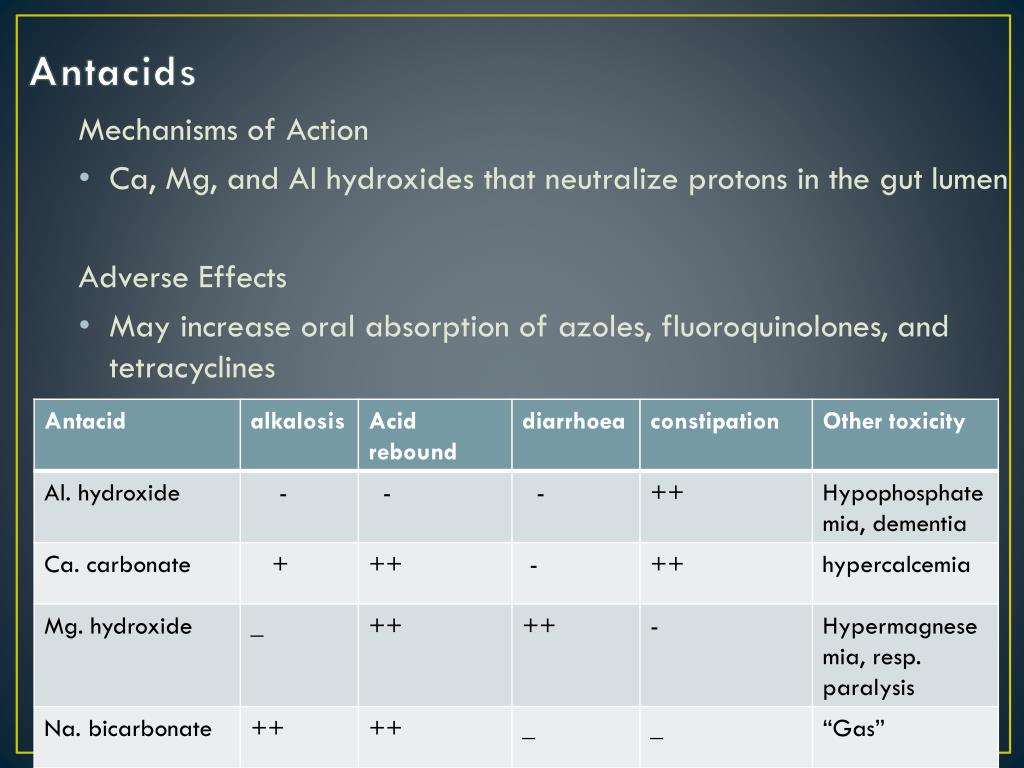
The interaction between gabapentin and antacids, particularly magnesium oxide, significantly reduces gabapentin's bioavailability, which can compromise its therapeutic efficacy. In the context of perioperative pain management, gabapentin offers some benefits in reducing opioid consumption and postoperative pain, but these benefits are A dose of aluminum or magnesium hydroxide should precede a dose of gabapentin by at least two hours. Other antacids that contain aluminum or magnesium may interact with gabapentin in a similar fashion. For instance, antacids can hinder gabapentin absorption and reduce its therapeutic benefits, while other medications may increase gabapentin levels to dangerous levels. Special Considerations It is vital to note that certain health conditions and life circumstances also impact the safe use of gabapentin: Antacids. Antacids (Maalox aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide) can reduce the oral bioavailability of gabapentin by 20%. To avoid problems, administration of gabapentin and antacids should be separated by at least 2 h . Cetirizine. Cetirizine can decrease mean plasma gabapentin levels, probably via interaction with renal drug transporters Note: Do not take antacids and gabapentin at the same time. Antacids may alter the absorption and metabolism of gabapentin. Make sure you ask your doctor before using antacids with gabapentin. All of these over-the-counter medicines can relieve the symptoms of heartburn. A Minor Drug Interaction exists between gabapentin and Heartburn Antacid Extra Strength. View detailed information regarding this drug interaction. Coadministration of gabapentin and an antacid containing aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide reduced the bioavailability of gabapentin by about 20%. Administer gabapentin at least 2 hours after an antacid containing aluminum and magnesium. Gabapentin, a medication primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain, is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, like many medications, it can interact negatively with other substances, leading to unwanted side effects or reduced efficacy. Generally speaking, you need to avoid combining Gabapentin with substances that increase drowsiness, such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and alcohol. Also avoid some antacids, because they reduce the absorption of gabapentin into the bloodstream. Key Takeaways: Drugs Interacting with Gabapentin Understand Drug Interactions: Gabapentin interacts with opioids, antacids, and more. Opioid Risks: Combining gabapentin with opioids can lead to increased sedation. Antacid Timing Matters: Take antacids at least two hours apart from gabapentin. The aim of this open-label, randomized, and 3-period crossover study was to evaluate the influences of concomitant antacid administration on the plasma disposition, intestinal absorption, and urinary excretion of gabapentin in humans. If you have any questions about the interaction between gabapentin and an antacid, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. Gabapentin and Benzodiazepines. Like gabapentin,benzodiazepinesare classified as CNS depressants and can intensify the drowsiness and dizziness side effects of gabapentin. While it is generally recommended that this combination Antacids can reduce the amount of gabapentin that the body takes in so it does not work as well. To stop this happening, if you need to take an antacid, take it at least 2 hours before or after your dose of gabapentin. Antacids with Al or Mg may cause a drug interaction that reduces the availability of gabapentin by about 20%, and may lower the effectiveness of the medicine. Common antacids that contain Al or Mg include: Amphojel, Gaviscon, Gelusil, Maalox and Mylanta. Some medicines may affect how gabapentin works or increase the chance of you having side effects. Antacids can reduce the amount of gabapentin that the body takes in so it does not work as well. To stop this happening, if you need to take an antacid, take it at least 2 hours before or after your dose of gabapentin. Gabapentin’s official labeling recommends waiting at least 2 hours after taking an antacid that contains magnesium or aluminum before taking a dose of gabapentin. This should help minimize the interaction between the two. What are the more common side effects of gabapentin? Common side effects of gabapentin include: Feeling tired. Dizziness. Headache. Nausea and vomiting. Fever. Difficulty speaking. Recurring infections. Memory loss. Weight gain. Movement problems: coordination problems, being unsteady, tremors, jerky movements. Some studies suggest that gabapentin's effectiveness can be reduced by antacids like magnesium oxide due to decreased absorption, while other studies indicate that gabapentin can improve pain management and reduce opioid use but may increase sedation and dizziness. The aim of this open-label, randomized, and 3-period crossover study was to evaluate the influences of concomitant antacid administration on the plasma disposition, intestinal absorption, and urinary excretion of gabapentin in humans. Gabapentin (200 mg) was orally administered alone, with 1 g magne What happens if you take antacids with gabapentin? Do not take antacids and gabapentin at the same time. Antacids may alter the absorption and metabolism of gabapentin. Make sure you ask your doctor before using antacids with gabapentin. What kind of antacid can I take with gabapentin? You should avoid taking antacids with gabapentin. However
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |