Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
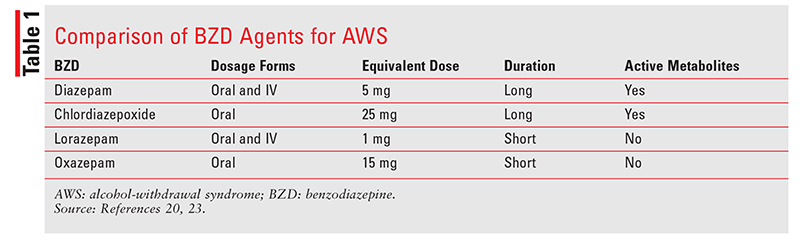
(2020) tested gabapentin (up to 1200/mg/day), versus placebo, combined with medical management and found that the clinical benefits of gabapentin were apparent in the high-alcohol withdrawal group only (Anton et al. 2020). Gabapentin prevented heavy drinking and promoted alcohol abstinence among patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms in a trial in JAMA Internal Medicine. “For patients at low risk of severe complications of alcohol withdrawal (e.g., PAWSS < 4), clinicians should consider offering nonbenzodiazepine medications, such as gabapentin, carbamazepine or clonidine for withdrawal management in an outpatient setting (e.g., primary care, virtual). (p. E1368).” 18. CONTENTS Rapid Reference Preamble & disclaimer Diagnosis Alcohol withdrawal vs. hepatic encephalopathy Therapeutic target (CIWA vs RASS) Treatment: Phenobarbital monotherapy Phenobarbital pharmacology Advantages of phenobarbital over benzodiazepines Contraindications to phenobarbital ️ Phenobarbital guideline Checking phenobarbital levels? ️ Pitfalls of phenobarbital Alternative agents alcohol withdrawal delirium (DTs), yet some signs of early withdrawal may be present Alcohol Withdrawal Delirium (DTs) Usually appear 1–3 d after cessation; peak intensity on 4–5th day w5% In most cases (80%) the symptoms of DTs resolve within 72 h, in those that do not, the mortality rate in cases of DTs has been reported between 1% and 15% This is different from our study that included patients with a history of complicated alcohol withdrawal, including those with alcohol withdrawal seizures or alcohol withdrawal delirium. One important factor was that in our evaluation of the gabapentin protocol, a significant number of patients were found to have received valproate (36.4%). We hypothesized that patients treated with fixed-dose gabapentin taper would experience shorter clinically significant alcohol withdrawal with equivalent safety compared with those treated with CIWA-triggered benzodiazepines. valproic acid, gabapentin, and clonidine, all have comparable effectiveness in managing alcohol withdrawal when compared with benzodiazepines as monotherapies (1). Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Conclusion: Implementation of a benzodiazepine-sparing pathway that uses primarily clonidine and gabapentin to prevent and treat alcohol withdrawal syndrome in trauma patients is safe, reduces the daily maximum CIWA-Ar, and significantly decreases the need for benzodiazepines. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. • Maldonado JR, Sher Y, Ashouri JF, Hills-Evans K, Swendsen H, Lolak S, Miller AC. The "Prediction of Alcohol Withdrawal Severity Scale" (PAWSS): systematic literature review and pilot study of a new scale for the prediction of complicated alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Alcohol. 2014 Jun;48(4):375 -90. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.01.004. Combining clonidine and gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal treatment offers several advantages. When taken together, these medications work synergistically to help manage withdrawal symptoms effectively and safely. 1. Enhanced Efficacy The ambulatory management of mild alcohol withdrawal, the initial diagnosis and treatment of alcohol use disorder, and specific conditions due to alcohol-related organ damage (eg, cirrhosis, pancreatitis) are discussed separately. Alcohol detox manages withdrawal symptoms, a necessary step in treating alcohol dependence since heavy alcohol consumption affects brain function.According to a study by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) titled “Assessing Alcohol Consumption Trends,” 2021, approximately 14.1 million adults in the United States meet the criteria for Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD). Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. treatment of alcohol withdrawal. A detailed summary of guideline recommendations can be found in Table 2. Table 1: Selection Criteria Criteria Description Population People with alcohol dependence commencing treatment for alcohol withdrawal in an outpatient setting Intervention Any treatment for alcohol withdrawal Comparator Not applicable Benzodiazepines are considered the drugs of choice for treating alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has been studied as a potential treatment for acute alcohol withdrawal, based on its modulatory action on brain excitatory (i.e., glutamergic) and inhibitory (i.e., GABAergic) pathways.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |