Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
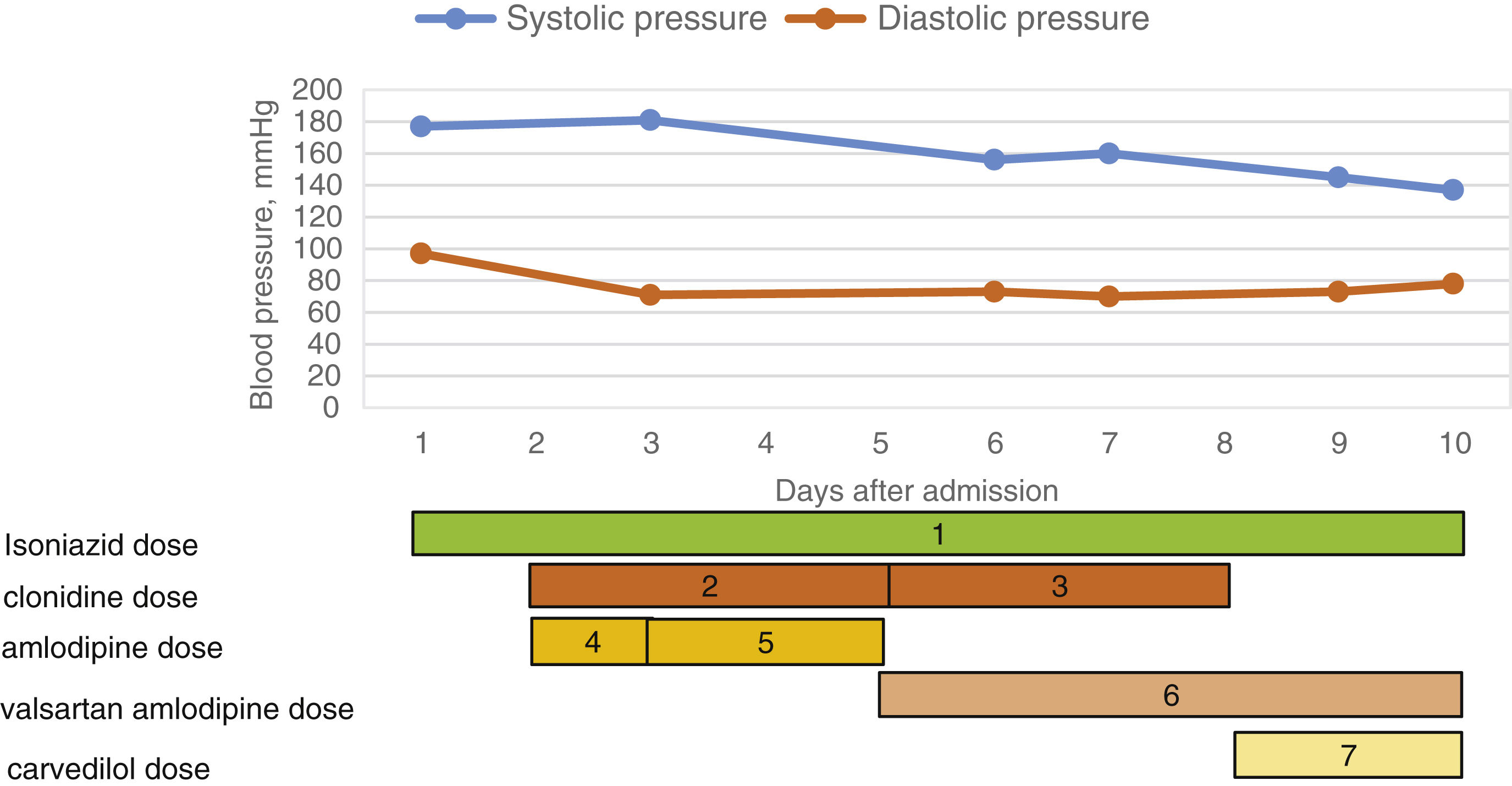
Clonidine ER Interactions. There are 375 drugs known to interact with Clonidine ER (clonidine), along with 5 disease interactions, and 1 alcohol/food interaction. Of the total drug interactions, 42 are major, 325 are moderate, and 8 are minor. Benefits and Risks of Using Clonidine and Gabapentin for Sleep. The potential benefits of using clonidine and gabapentin for sleep are numerous and can vary depending on the specific sleep disorder being treated. For individuals with insomnia, the combination may help reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and increase total sleep time. How can I avoid or manage potential interactions with clonidine? Talking to your healthcare provider or pharmacist is the best way to manage clonidine interactions. They can review your current medication list for any issues. They can also suggest medication changes as needed. Both Clonidine and Gabapentin have effects on the CNS and can cause sedation, which might affect the ability to perform skilled tasks (see 'Drugs and Driving' in Guidance on Prescribing). In some cases, use of two or more drugs that have effects on the CNS might also increase the risk of CNS depressant effects (which could range from sedation Intrathecal gabapentin is effective for phase 2 of the formalin response but not for acute pain. Unlike gabapentin, intrathecal clonidine and neostigmine attenuate both acute pain and phase 2 of the formalin response. We evaluated gabapentin's interactions with either clonidine or neostigmine in the formalin test. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were Taking gabapentin with clonidine can increase the risk of sedation. Sometimes the foods we eat and the beverages we drink can also interact with our medications. Food and drink that may interact with this drug include: Gabapentin and AWS. After reviewing the previous case report published regarding the dangerous side effects of gabapentin,[] we noticed a few similarities between the cases such as: the patient was stable before initiating gabapentin, young adults in 30–40 s, symptoms started within 2 weeks of initiating the medication, and the same dose was administered – 300 mg TID, their partners His discharge medication list with instructions was as follows: two patches of clonidine 0.1 mg/24h, of which one was to be removed in 3 days and the other on the fourth day, oral gabapentin (strength: 300mg) one capsule three times a day, then one capsule twice a day followed by two capsules daily at bedtime and then discontinue and oral To answer your first question, I did find that there are (moderately unsafe) interactions between Clonidine and Gabapentin (so it wouldn't be wise to take a full dose of each one together). Information that I've gathered on this states the following: Applies to: Clonidine ER (clonidine) and gabapentin Using cloNIDine together with gabapentin may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination. Both oral clonidine and gabapentin are effective in obtunding pressor response to direct laryngoscopy, clonidine being better in terms of controlling HR. Gabapentin produces more postoperative sedation than clonidine. Compare Clonidine vs Gabapentin head-to-head with other drugs for uses, ratings, cost, side effects and interactions. Use WebMD’s Drug Interaction Checker tool to find and identify potentially harmful and unsafe combinations of prescription medications by entering two or more drugs in question. Drug interactions are reported among people who take Clonidine (clonidine) and Gabapentin (gabapentin). Common drug interactions include vomiting among females and drug ineffective among males. The phase IV clinical study analyzes what interactions people have when they take Clonidine and Gabapentin, and groups them by gender, age and more. In our study, we found that both clonidine and gabapentin are effective premedicants by oral route 2 h before induction of anesthesia to blunt the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and intubation as compared to placebo. The percent maximum possible effect data at the time of peak effect after intrathecal gabapentin, clonidine or the gabapentin plus clonidine combination were employed to fit the dose–response curves followed by the calculation of the respective ED 50 values using a 4 parameter Hill equation. Therefore, the peak effect for dose–response Both Gabapentin and Clonidine have effects on the CNS and can cause sedation, which might affect the ability to perform skilled tasks (see 'Drugs and Driving' in Guidance on Prescribing). In some cases, use of two or more drugs that have effects on the CNS might also increase the risk of CNS depressant effects (which could range from sedation As can be seen in Table 1, the groups do not difference significantly in terms of gender, and medication (P > 0.05).The mean and standard deviation of the age of the participants in the clonidine + gabapentin group was equal to 50.20 ± 7.44, and in the gabapentin group was equal to 50.47 ± 7.57, and based on the independent t-test results, it was shown that there was no significant Using cloNIDine together with gabapentin may increase side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. Some people, especially the elderly, may also experience impairment in thinking, judgment, and motor coordination.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |