Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
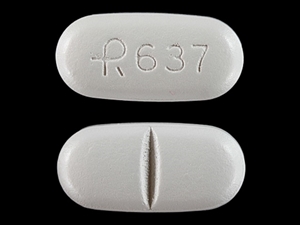
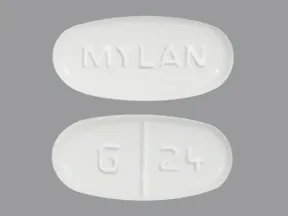
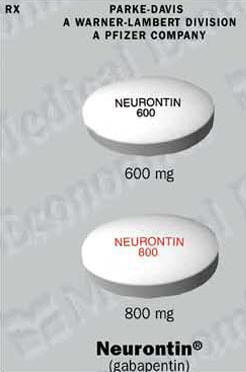
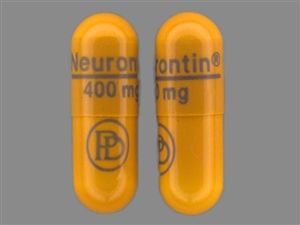
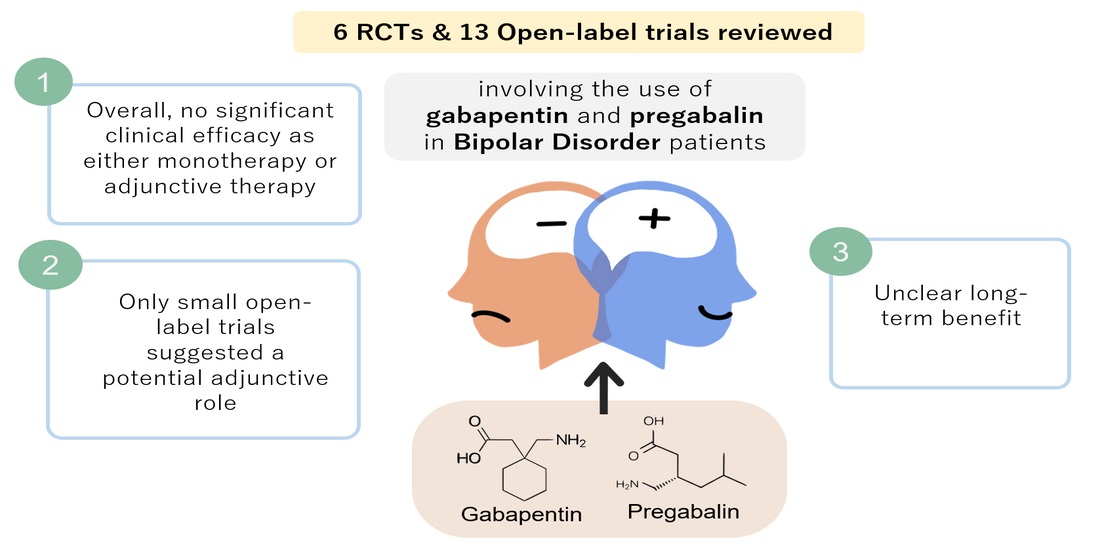
Your child needs to take the medicine called gabapentin (say: GA-ba-pen-tin). This information sheet explains what gabapentin does, how to give it and what side effects or problems your child may have when they take this medicine. Gabapentin, with its low incidence of adverse effects, may be ideal as first-line pharmacological therapy in pediatric neuropathic pain. Multicenter pediatric studies are needed to validate and empower the existing prescribing practices of gabapentin for neuropathic pain in children. Child 12–17 years Initially 300 mg once daily on day 1, then 300 mg twice daily on day 2, then 300 mg 3 times a day on day 3, alternatively initially 300 mg 3 times a day on day 1, then increased in steps of 300 mg every 2–3 days in 3 divided doses, adjusted according to response; usual dose 0.9–3.6 g daily in 3 divided doses (max. per dose 1.6 g 3 times a day), some children may not Gabapentin ([1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneaceticacid], Neurontin® 11), a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog, 12 is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat partial epilepsy in children as young as 3 years and post-herpetic neuralgia in adults. 13,14 Gabapentin has and continues to be used in cases of seizures, pain, and It is generally well tolerated and offers several advantages over older anticonvulsants, with a milder adverse effect profile and few drug interactions.1-3 This article will review the use of gabapentin in children, both as an anticonvulsant and as an analgesic. Insomnia is prevalent in pediatrics, particularly in those with neurodevelopmental disorders. Gabapentin has shown promise in treating insomnia in adults. The purpose of our study was to review our experience with using gabapentin to treat insomnia in children. We identified 23 children, seen by the Gabapentin is used in combination with other antiseizure (anticonvulsant) drugs to manage partial seizures with or without generalization in individuals over the age of 12. Gabapentin can also be used to treat partial seizures in children between the ages of three and 12. Gabapentin and pregabalin (gabapentinoids) are increasingly prescribed to children and adolescents off label for various conditions despite limited data and concerns for adverse outcomes including misuse and overdose. Gabapentin is FDA-approved for treating partial seizures in children ages 3 and older. It can be used as an add-on therapy in children who may need additional control for their seizures. Child 12–17 years Initially 300 mg once daily on day 1, then 300 mg twice daily on day 2, then 300 mg 3 times a day on day 3, alternatively initially 300 mg 3 times a day on day 1, then increased in steps of 300 mg every 2–3 days in 3 divided doses, adjusted according to response; usual dose 0.9–3.6 g daily in 3 divided doses (max. per dose 1.6 g 3 times a day), some children may not 4. Nayak, S. and M. Cunliffe, Lidocaine 5% patch for localized chronic neuropathic pain in adolescents: report of five cases. Paediatr Anaesth, 2008. 18(6): p. 554-8. 5. Orellana Silva, M., et al., 5% lidocaine medicated plaster use in children with neuropathic pain fr Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. The safety and efficacy of gabapentin in children undergoing surgery has been evaluated in several clinical trials. In 2010, Rusy and colleagues conducted a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of gabapentin in 59 children 9 to 18 years of age undergoing spinal fusion.7 Patients were randomized to receive gabapentin G We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Gabapentin may cause drowsiness, which is increased when used with other medicines that cause drowsiness. Any dose change must be guided by your doctor. Gabapentin should be decreased slowly over at least a week. Stopping gabapentin suddenly can cause withdrawal symptoms (anxiety, difficulty sleeping, nausea, pain, sweating or seizures). The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Gabapentin may be used to treat seizures in children as young as 3 years old. The dosages will be different from what you’d give an adult, and the doctor may specify a particular brand name A retrospective single-center study was performed in infants younger than 1 year who received gabapentin at Boston Children’s Hospital between 2015 and 2021. The primary outcome was indication, initiation and maximum gabapentin dose. Ultimately, gabapentin was used safely to treat neuropathic pain in children and adolescents with limb amputation and limb-sparing procedures alike, but with the majority of the patients receiving gabapentin, efficacy was not able to be defined. Gabapentin . Brand name: Neurontin. This leaflet is about the use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). Why is it important for my child to take Gabapentin? Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. What is Gabapentin available as? Tablets: 600 mg, 800 mg
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |