Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/common-causes-of-foot-and-ankle-swelling-1337777-5c04ad02c9e77c0001b0f9e0.png) |
 |  |
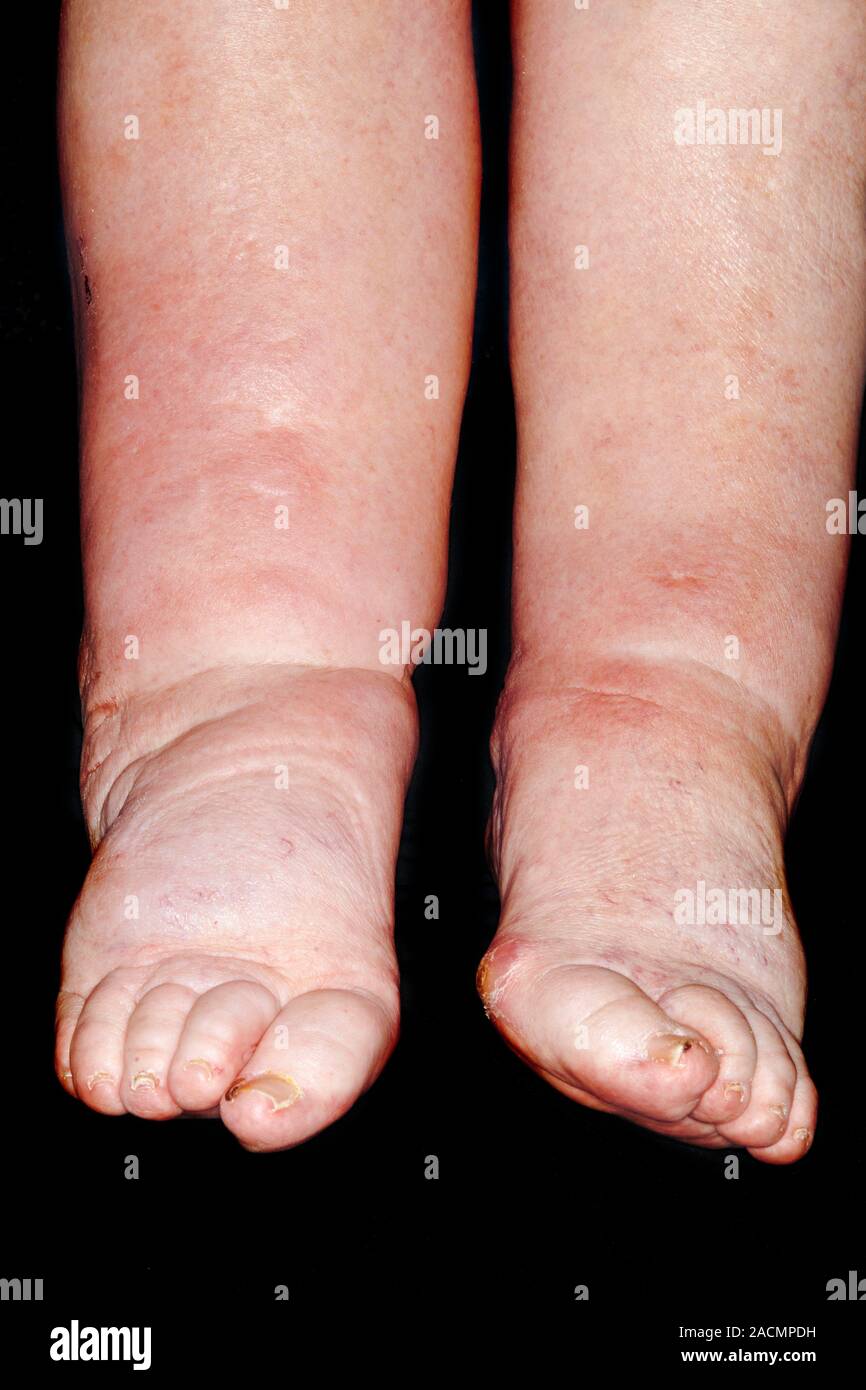
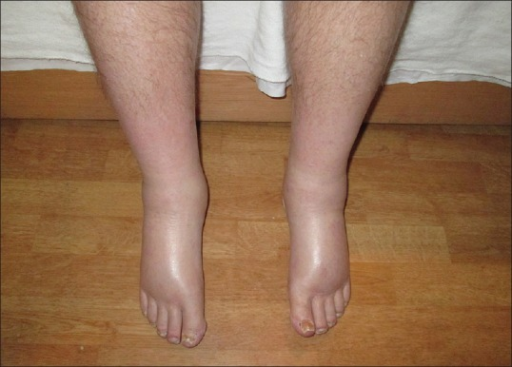
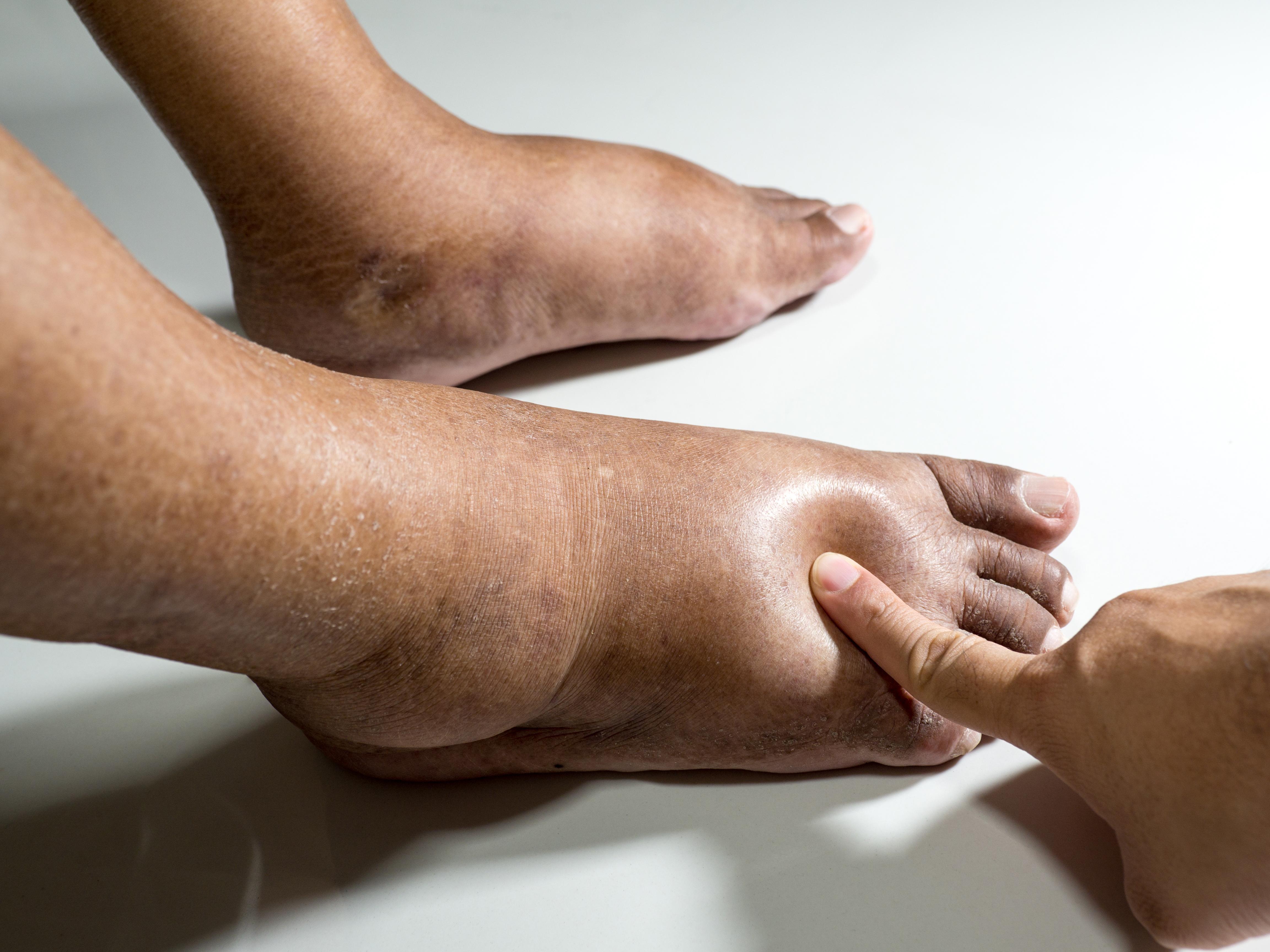
I take 600 mg of gabapentin, 300 mg twice daily. No swelling in my feet. I still get some cramping and stabbing. I hope everything is going well with others. He noticed significant leg swelling almost immediately upon starting treatment; this persisted for nearly three weeks before gradually improving after his doctor reduced his dosage. These cases highlight how individual responses vary widely based on dosage levels and personal health backgrounds while using gabapentin. Swelling in the feet and ankles. Patients taking Neurontin may experience swelling in the feet and ankles. The presence of lower leg swelling may cause discomfort and impair walking. My mother-in-law was unable to wear regular shoes because of swelling of her feet and ankles, so we found her socks and soft slippers that fit her feet comfortably. Gabapentin was discontinued and his lower extremity swelling improved over subsequent days. Incidence of pedal edema with gabapentin use is approximately 7 to 7.5% with all studies being in elderly patients receiving doses above 1200 mg/day. Peripheral edema from gabapentin is not always dose related, however. There are 3 published case reports 6,7,11 of patients who developed peripheral edema at doses lower than 1800 mg/d. One case published by Kanbay et al 6 described peripheral edema related to gabapentin in a 76-year-old male. The authors reported bilateral pretibial edema Seven days after the administration of the gabapentin, the patient complained from pain and edema and scaling and hyperesthesia in his lower extremities and pitting edema, pain and tenderness. The range of motion of the extremities was been increased. Presence of gabapentin induced leg swelling can thus confound the clinical picture. Keywords. Edema, gabapentin, lower extremity. Introduction. Gabapentin was originally developed as a muscle relaxant/anti‑spastic agent. It was later approved by the Food and Drug Administration for epilepsy and postherpetic neuralgia. Will swelling go away while taking gabapentin 200 mcg at bedtime. I was on this medication for quite awhile and it did cause a lot of swelling. Then I started gaining weight and I was tired all the time. I had many other bad side effects so I’m tapering off it now. I wish that I had never started taking it. A classical pharmacodynamic effect of CCBs is to induce diffuse and bilateral swelling of the feet, ankles and sometimes lower legs that worsens throughout the day and improves overnight. 3 The peripheral oedema observed with CCBs can differ in appearance from more traditional oedema states in that lower extremity redness, warmth and a Acute heart failure, which may be associated by peripheral edema (i.e., cardiogenic peripheral edema), seems to be a risk specific to pregabalin exposure that is not found with gabapentin [10]. This apparent polymorphism of gabapentinoid-associated edematous states (i.e., of non-cardiogenic or cardiogenic origin) could be due to several One case published by Kanbay et al6 described peripheral edema related to gabapentin in a 76-year-old male. The authors reported bilateral pretibial edema after 3 weeks of gabapentin 300 mg/d for neuropathic pain. Within 3 days of discontinuation of gabapentin, the edema resolved. being unremarkable. Gabapentin was discontinued and his lower extremity swelling improved over subsequent days. Incidence of pedal edema with gabapentin use is approximately 7 to 7.5% with all studies being in elderly patients receiving doses above 1200 mg/day. This case illustrates that lower doses of gabapentin can also cause this adverse effect. Edema is a well-described side effect of gabapentinoid drugs (i.e., gabapentin and pregabalin). In this study from Ontario, Canada, researchers used provincial databases to examine whether gabapentinoid use was followed by diuretic prescriptions — a so-called “prescribing cascade” in which a drug is prescribed to treat an adverse effect of another drug. Amlodipine (Norvasc), gabapentin (Neurontin, Horizant, Gralise), and pregabalin (Lyrica) can cause puffy legs and ankles. Birth control pills, certain over-the-counter pain medications, and steroids are a few other culprits. Although gabapentin is generally well tolerated, 1 potential reported adverse effect is peripheral edema. However, due to the extensive number of etiologies of peripheral edema, medication causes may be overlooked on an inpatient psychiatric unit. Managing gabapentin-induced edema requires a multi-faceted approach, considering both lifestyle modifications and potential medication adjustments. Our article will provide practical tips and strategies that can help alleviate and manage the swelling effectively. Similarly, the incidence of peripheral edema caused by CCB is dose related and common in the elderly, comparable to reports of gabapentin induced edema. This case illustrates that gabapentin induced leg swelling can confound the clinical picture and it is thus important to recognize this side effect of gabapentin. I have swelling in my legs caused by lymphedema and have to wear compression socks but mine was not caused by a medication. I also would be concerned if it's been over 5 months since stopping gabapentin and the swelling and pain is still in the hands and feet. Gabapentin is a common medication-related cause of peripheral edema. This is when you experience swollen tissues in the body, often in the arms and legs. Up to 8% of people report edema with gabapentin clinical studies. But it’s more likely to occur in older adults.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/common-causes-of-foot-and-ankle-swelling-1337777-5c04ad02c9e77c0001b0f9e0.png) |
 |  |